Clinical:
- A 34 years old man
- Young stroke under investigation.
- Risk factor: smoking, type II DM, hypercholesterolaemia and obesity.
- CT scan shows lacunar infarctions
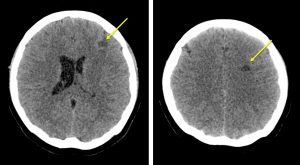
CT findings:
- Hypodensity at the left corona radiata and left frontal suggestive an infarcts
- No intracranial bleed. No hydrocephalus.
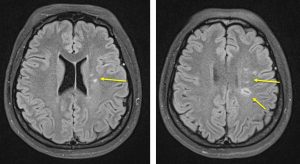
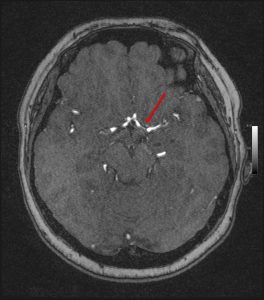
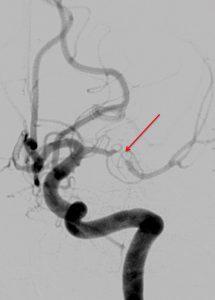
MRI and angiogram:
- There are multiple lesions seen at the left corona radiata and centrum semiovale (yellow arrows). These lesions are hypointense in T1 and hyperintense in T2 and FLAIR. There is no restricted diffusion in all of the lesions.
- No enhancing brain lesion seen post contrast.
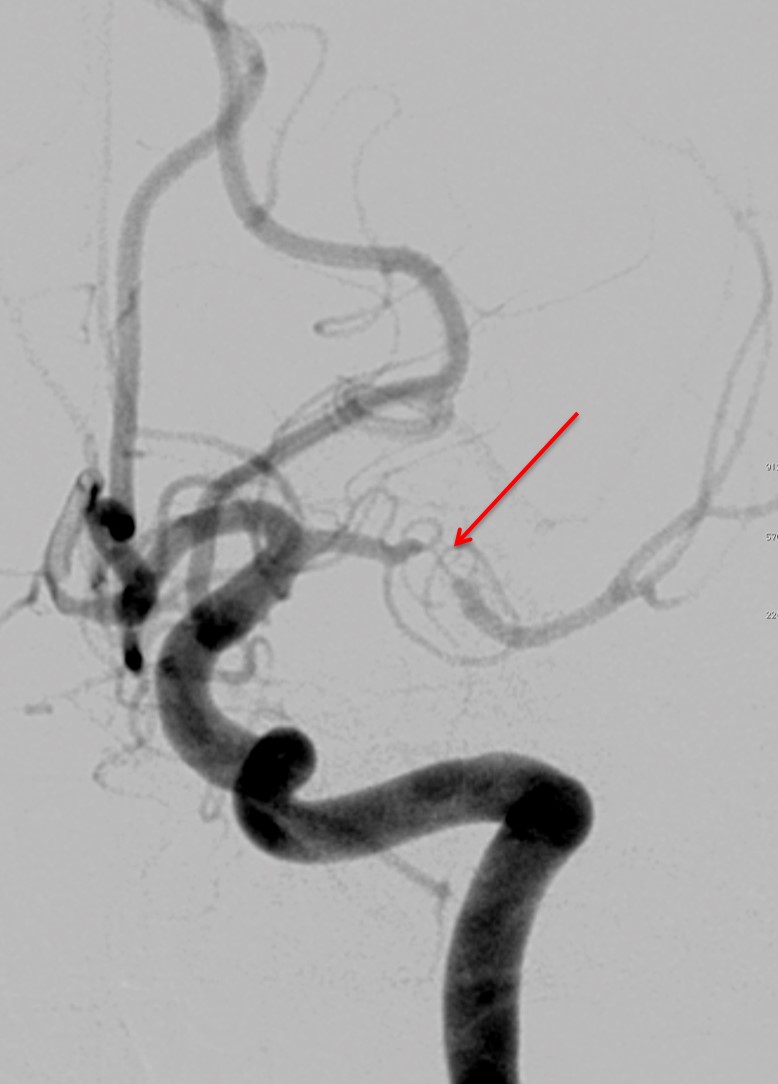
- On MRA image, there is short segment stenosis of the left M1. Subsequent DSA cerebral confirmed the stenosis (red arrows).
Diagnosis: Left MCA stenosis causing cerebral infarction
Discussion:
- Intracranial artery stenosis is highly prevalent in stroke patients of Asian, African, and Hispanic ancestry
- In older patient, atherosclerosis is the widely accepted underlying etiology
- In patients at a young age, however, intracranial stenosis has varied causes, such as dissection, moyamoya disease, fibromuscular dystrophy, and vasculitis
- The conventional MRI underestimates the degree of stenosis in this case
- MRA sequence is helpful in workout of stroke patient to identify possible underlying cause of the disease
Acknowledgement:
- Prof Ahmad Sobri Muda
- Assoc. Prof. Datin Dr. Shahizon Azura Mohamed Mukari
Recent Comments