Image 1
Questions:
- Name the examination.
- Name the labelled structures:
- What is pulmonary hilum and hilar point?
- What are possible disease process with an abnormal hilum?
Answers:
- Chest radiograph, PA erect view.
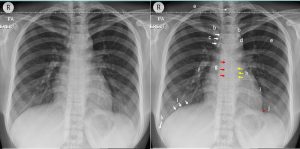
- The labelled structures:
- a. Spinous process of T2,
- b.Medial end of claviclec.Right paratracheal striped.Aortic knucklee.6th posterior left rib
f.Right descending pulmonary artery
g.Azygoesophageal recess
h.Left paraspinal stripe
i.Left ventricular border
j.Left cardiophrenic angle
k.Right costophrenic angle
l.Right hemidiaphragm
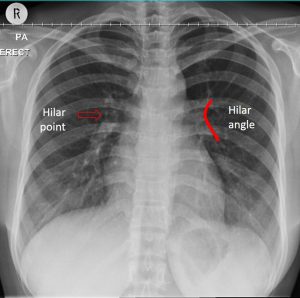
- In the chest radiograph, the hila represent the pulmonary vascular pedicles composed by pulmonary arteries and veins, main bronchi, bronchial vessels, nodes and lymphatic channels. Right and left pulmonary hilum may be seen at the same level but commonly the left hilum is higher than the right side. Hilar point is an angle formed by the descending upper lobe veins as they cross the lower lobe arteries (refer to Image 2). Hilar angle should be concave in normal chest radiograph.
- Pathologies associated with abnormal appearance of hilum on chest radiograph include:
- Abnormal position: displaced hilum can be caused bu atelectasis or lung collapsed.
- Abnormal morphology: abnormal and lobulated hilar contours can be caused by enlarged nodes which may be unilateral or bilateral.
- Abnormal size: normal hila should gradually taper peripherally. Enlargement of pulmonary arteries can cause increased hilar size and density. Pulmonary hypertension is the most frequent cause of enlarged hilar vessels.
Image 2:
Recent Comments