Clinical:
- A 32 years old man
- No known medical illness
- Presented with fever, cough and shortness of breath
- CXR shows military pattern, sputum +ve for AFB
- Had seizure while on anti-TB treatment (2 months after treatment)
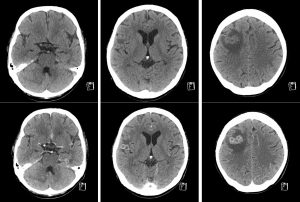
CT scan findings:
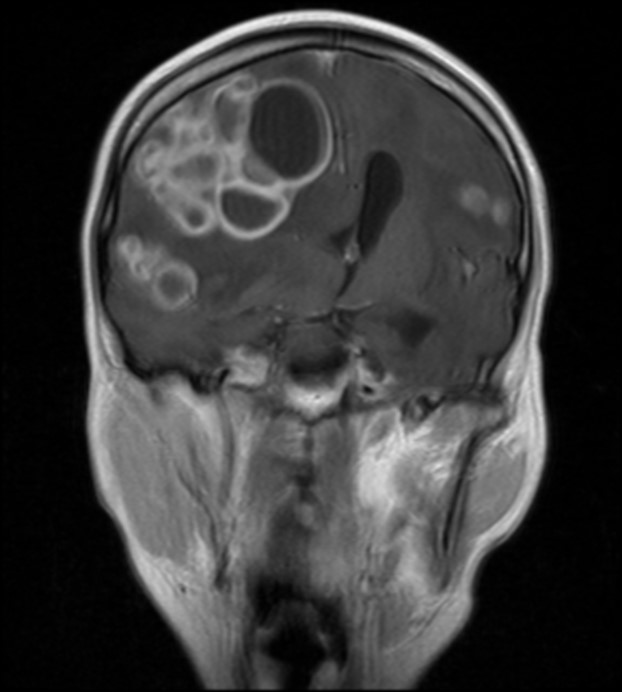
- There are multiple ring enhancing lesions of various sizes in bilateral cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum and pons
- The lesions demonstrate smooth thin wall and some of the lesions show clustering
- There are various severity of surrounding perilesional oedema are seen
- No abnormal leptomeningeal or basal enhancement
- No hdyrocephalus
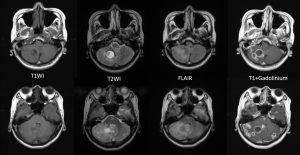
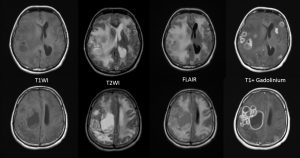
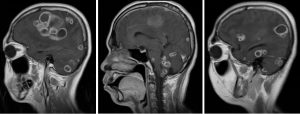
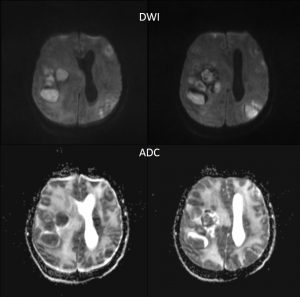
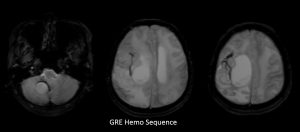
MRI findings:
- There are numerous ring enhancing lesions seen in the cerebrum and cerebellum
- The lesions are of various sizes and some lesions are clustered
- Different signal intensities are observed of these lesions
- Some lesions are hypointense on T1 and hyperintense on T2 weighted images, whereas others are iso on T1 and T2-weighted images
- Some of the lesions show restricted diffusion
- Hemo sequence shows minimal blooming artifact surrounding some of the lesions
- Wedge-shaped area of restricted diffusion is also seen in the left parietal region that could represent infarction
- Compression of ipsilateral lateral ventricles with mild hydrocephalus are seen
- No leptomeningeal enhancement
Diagnosis: CNS tuberculosis with tuberculomas (proven via biopsy)
Discussion:
- Tuberculoma is the most common parenchymal lesion in CNS tuberculosis which could be found in any portion of the intracranial space.
- The lesion may be solitary or multiple and may be seen with or without meningitis.
- MR Imaging findings of tuberculomas are varied depending on its three stages of maturation: noncaseating, caseating with a solid center and caseating with a liquefied center
- Noncaseating tuberculomas generally exhibit hypointense signal on T1-weighted images and are hyperintense on T2-weighted and FLAIR images. They generally demonstrate homogeneous nodular enhancement on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images.
- Caseating lesions with a solid center appear relatively iso- to hypointense on both T1-weighted and T2-weighted images with an isointense to hyperintense rim on T2-weighted images, and with ring-like enhancement. The rim may be inseparable on T2-weighted images with the presence of peripheral oedema.
- Caseating lesions with liquefied centers are hypointense on T1-weighted images and hyperintense with a hypointense rim on T2-weighted images, and show ring-like enhancement as well.
- Complications of TB CNS include hydrocephalus, ischaemia and arteritis
Recent Comments