Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 43 years old lady
- With underlying connective tissue disease
- On prolong steroid treatment
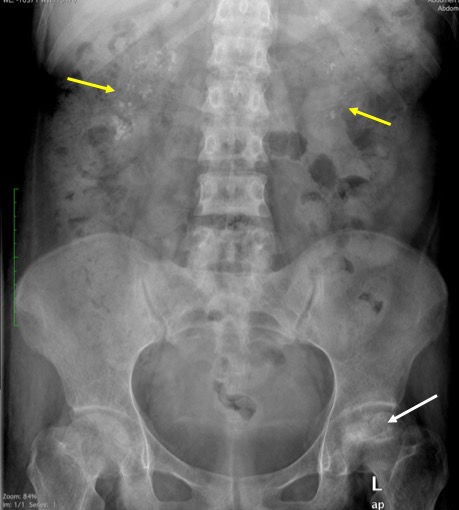
Radiographic findings:
- There is flattening of left femoral head (white arrow)
- The flattening involving less than one third of the head region
- Associated with mixed lytic and sclerotic changes
- There is presence of crescent sign
- The joint space is not narrowed
- Medullary nephrocalcinosis also noted at both renal region (yellow arrows), more on the right side
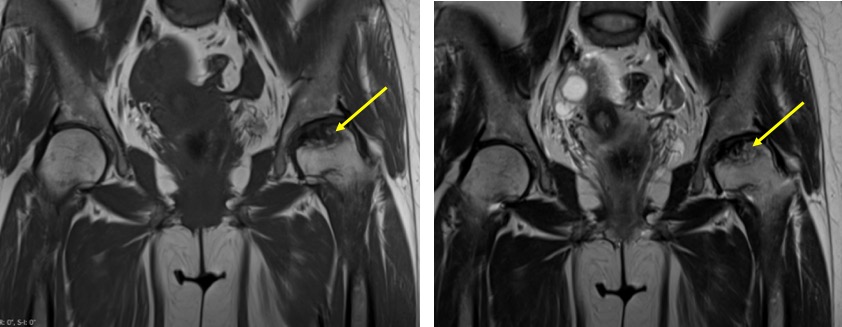
MRI findings:
- There is abnormal flattening of left femoral head, about 2-3 mm depression
- Abnormal signal intensity which is hypointense on both T1 and T2-weighted images
- Area of abnormal signal involving less than 30% of femoral head region
- No joint effusion, no joint space narrowing
- No obvious acetabular involvement is seen.
Diagnosis: Avascular necrosis of left hip.
Discussion:
- Avascular necrosis also known as osteonecrosis
- It can be traumatic or non-traumatic, bilateral in 40-80% of non traumatic cases
- Risk factors: chronic corticosteroid therapy, alcoholism, smoking, SLE, hyperlipidaemias, HIV, hemoglobinopathies, chronic renal failure, DM and pregnancy-related.
- A few classification and staging based on clinical, x-rays, mri and bone scan
Stage Ficat and Arlet classification Steinberg staging Stage 0 Plain radiograph normal, MRI normal, clinical symptoms nil normal or non-diagnostic radiograph, MRI or bone scan Stage 1 Plain radiograph normal or minor osteopenia, MRI oedema, Bone scan increased uptake, clinical symptoms: pain at groin Normal radiograph, abnormal bone scan and/or MRI; A-mild head involvement <15%, B-moderate: 15-30% and C severe >30%.
Stage II Plain radiograph mixed osteopenia and/or sclerosis and/or subchondral cyst without any subchondral lucency, MRI geographic defect, bone scan increased uptake, clinical symptoms pain and stiffness Cystic and sclerotic radiographic change A-mild head involvement <15%, B-moderate: 15-30% and C severe >30%.
Stage III Plain radiograph crescent sign and eventual cortical collapsed, MRI same as plain radiograph, clinical symptoms pain and stiffness +/- radiation to knee and limp Subchondral lucency or crescent sign; A-mild <15% head involvement, B-moderate, 15-30% and C-severe >30% Stage IV Plain radiograph end stage with evidence of secondary degenerative change, MRI same as plain radiograph, Clinical sypmtoms oain and limp Flattening of femoral head, with depression graded into A mild (<2mm), B-moderate (2-4 mm) and C-severe (>4 mm) Stage V – Joint space narrowing with or without acetabular involvement (A, B, C-depends on femoral head involvement as in Stage IV) Stage VI – Advanced degenerative changes
| Mitchell classification | T1WI | T2WI | Signal analogous |
| Stage A | Hyperintense | intermediate | To that of fat |
| Stage B | Hyperintense | Hyperintense | To that of subacute blood |
| Stage C | Hypointense | Hyperintense | To that of fluid or odema |
| Stage D | Hypointense | Hypointense | To that of fibrosis |
Recent Comments