Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 16 years old lady
- Underlying SLE with AHA
- History right IJV and sigmoid sinus thrombosis 2 years ago
- Presented with headache and left sided weakness, difficult to ambulate
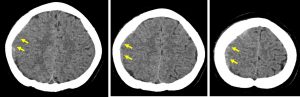
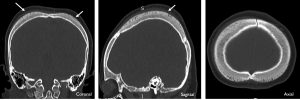
CT scan findings:
- A crescent-shaped iso to slightly hyperdensity seen at right cerebral hemisphere (yellow arrows) in keeping with subacute subdural hemorrhage
- Effacement of the ipsilateral cerebral sulci
- No mass effect, no midline shift
- Thickening of the parietal bones (white arrows)
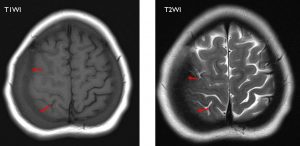
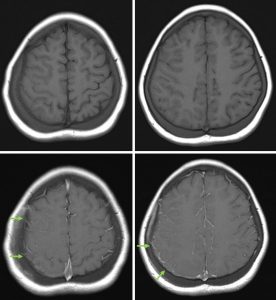
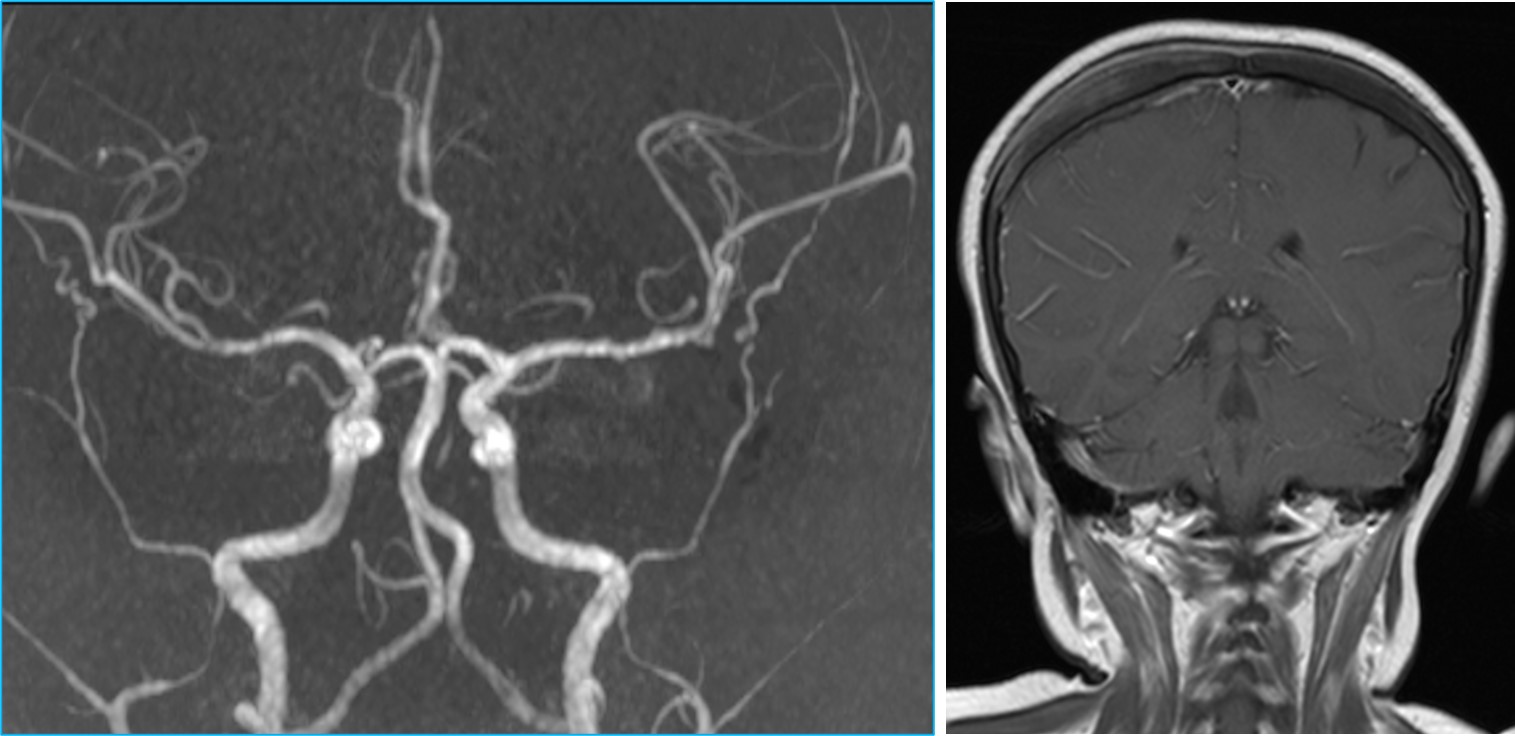
MRI brain in axial plane T1WI pre and post contrast that shows leptomeningeal enhancement on the right side.
MRI findings:
- Right subacute subdural hemorrhage seen (red arrows)
- No intraparenchymal lesion
- Leptomeningeal enhancement on the right side
- Parietal bone thickening as seen on CT scan
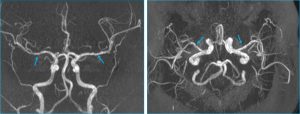
- Irregularity of wall of both MCA suggestive of vasculitic change
- MRV shows no thrombosis (images not shown)
Diagnosis: CNS manifestation of SLE
Discussion:
- CVA: small vessel disease and cerebral atrophy, ischaemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, dural venous sinus thrombosis, cerebral vasculitis. In this case vasculitis and previous dural venous thrombosis. Subdural hemorrhage is most likely complication of dural venous thrombosis.
- Myelopathy: transverse myelitis, optic neuritis (not seen in this case)
- Other manifestations: aseptic meningitis, brain abscess, PRES and anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis. Aseptic meningitis is probably the cause of leptomeningeal enhancement in this case.
- Calvarial thickening may be related to extramedullary haematopoesis due to chronic anemia.
Recent Comments