Clinical:
- A 69 years old female
- Background history of hypertension, right CVA with left hemiparesis.
- Newly diagnosed AF
- Complaining of headache with dizziness and diplopia for 1 day
- Noted clinically worsening of nystagmus with left sided cerebellar sign
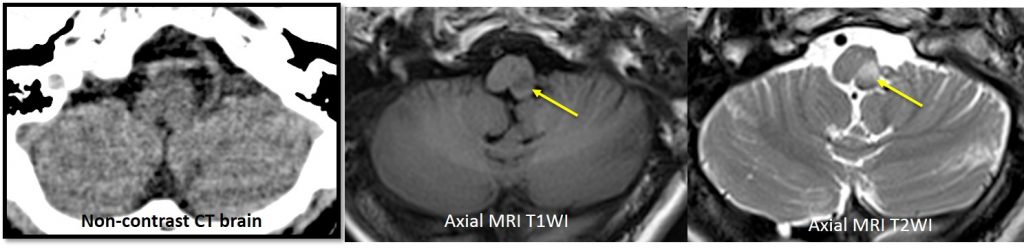
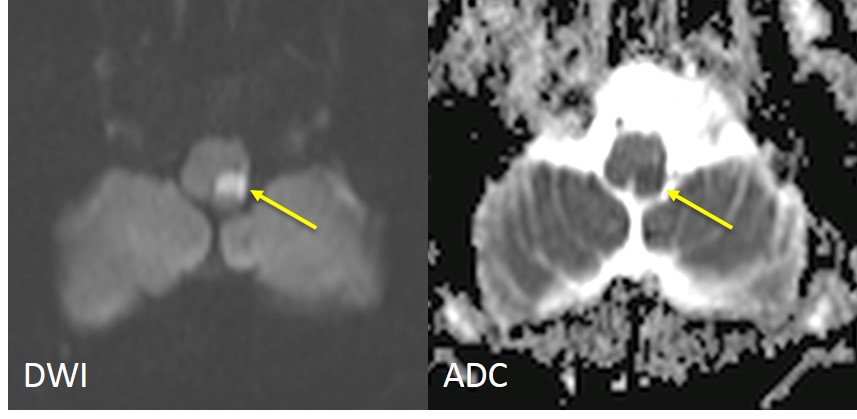
Imaging finding:
- Plain CT brain do not demonstrate any abnormality except of old infarction at right corona radiata
- MRI show abnormal signal at left side of medulla (yellow arrows) which is hypointense on T1, hyperintense on T2 and restricted diffusion on DWI/ADC images
Diagnosis: Acute infarction at left lateral medulla
Discussion:
- Lateral medullary syndrome also known as Wallenberg syndrome
- A clinical syndrome caused by acute ischaemic infarction of the lateral medulla oblongata
- Hypertension is the commonest risk factor followed by smoking and diabetes mellitus
- Constellation of neurologic symptoms due to injury to the lateral part of the medulla in the brain
- Clinical symptoms include difficulty swallowing, slurred speech, facial pain, vertigo, Horner syndrome, and possibly palatal myoclonus
- Sensory deficits affecting the trunk (torso) and extremities on the opposite side of the infarction
- Sensory deficits affecting the face and cranial nerves on the same side with the infarct.
