Clinical:
- A 79 years old lady
- Presented with left-sided blurring of vision for one month
- Associated with headache and dizziness.
- Clinical examination shows both optic discs are pale.
- No neurological deficit
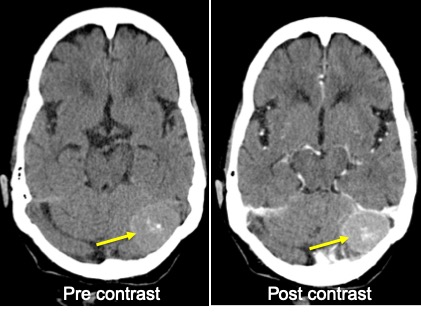
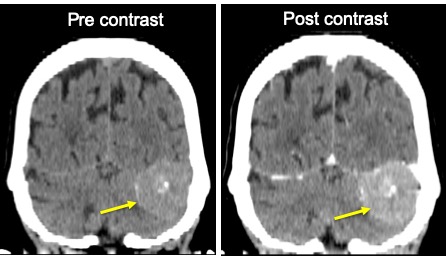
CT scan findings:
- There is extra-axial enhancing mass seen at the left posterior cerebellum
- The mass measures about 3.1 x 2.3 cm
- There is associated minimal perilesional oedema.
- Presence of calcification within the mass lesion is seen.
- There is adjacent cortical buckling with mass effect to left cerebellum.
- No adjacent bony hyperostosis.
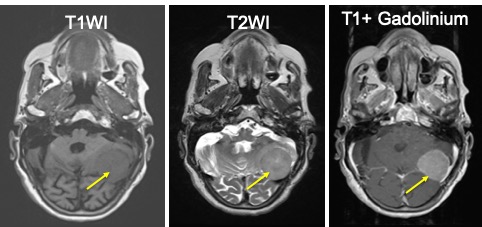
MRI of brain in axial plane 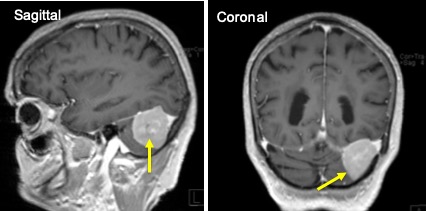
MRI of brain T1 post gadolinium MRI findings:
- There is well defined avidly enhancing extraaxial mass with dural tail seen at left posterior fossae.
- It measures 3.3×3.1×3.5cm (WxAPxCC).
- This mass causing elevation of the left tentorium cerebellar and in close contact with the left tentorial cerebelli.
- No filling defect of the left tranverse sinus to suggest thrombosis.
Diagnosis: Tentorium cerebelli meningioma (HPE proven)
Discussion:
- Meningioma is the most common extra-axial tumour in adults
- It is one of the most common intracranial tumours (15-20%) in adults.
- Mainly occurs in middle-aged women.
- Common site include: parasagittal-falcine (50%), sphenoid wing (20%), floor of the anterion cranial fossa (10%), parasellar region (10%), tentorium and cerebello-pontine angle region.
- Histologic types: typical (90% to 95%), atypical (3-5%), and frankly malignant (1%).
- A dural tail suggests an extra-axial mass but is probably related to reactive changes rather than tumour extension.
- On CT scan it is sharply circumscribed smooth mass abutting dura, 70-75% are hyperdense and 25% are isodense. Calcification seen in 20-25% of cases, necrosis and hemorrhage in 8-23%. Peritumoral hypodense vasogenic oedema in 60% of cases. More than 90& shows intense homogenous enhancement.
- On MRI,
- typically iso to slightly hypointense with cortex on T1
- necrosis, cyst and hemorrhage in 8-23%
- gray matter buckling sign
- variable ‘sunburst’ appearance on T2WI
- hyperintense T2/FLAIr dural tail and oedema
- GRE sequence to look for calcification (common) and hemorrhage (rare)
- variable appearance on DWI and ADC for typical meningioma
- Enhances homogenously and intensely on post contrast
- dural tail sign in 35-80% of cases, non specific feature
