Clinical:
- An 18 years old girl
- Recently diagnosed smear positive PTB
- Complicated by recurrent pneumothorax
- Presented after one month of diagnosis and on TB medication with tonic clonic seizures
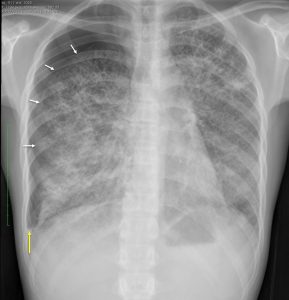
Chest radiograph findings:
- Extensive lesions in both lungs, mainly small cavities
- Some confluent areas are see
- Right pneumothorax with visualization of pleural lining (white arrow) and no lung markings peripheral to it
- No mediastinal shift is seen
- There is right pleural effusion seen as blunted right costophrenic angle (yellow arrow)
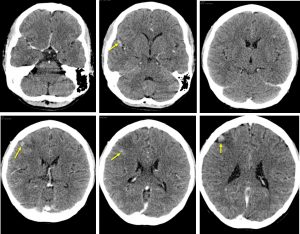
CT scan findings:
- There are multiple small rounded enhancing lesions in the brain parenchyma
- Most of the lesions are peripherally located at cortical regions.
- The largest in right frontal lobe is associated with perilesional oedema.
- There is slight meningeal enhancement seen at right temporal lobe.
- No hydrocephalus.
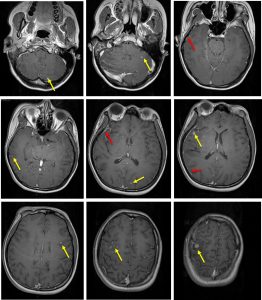
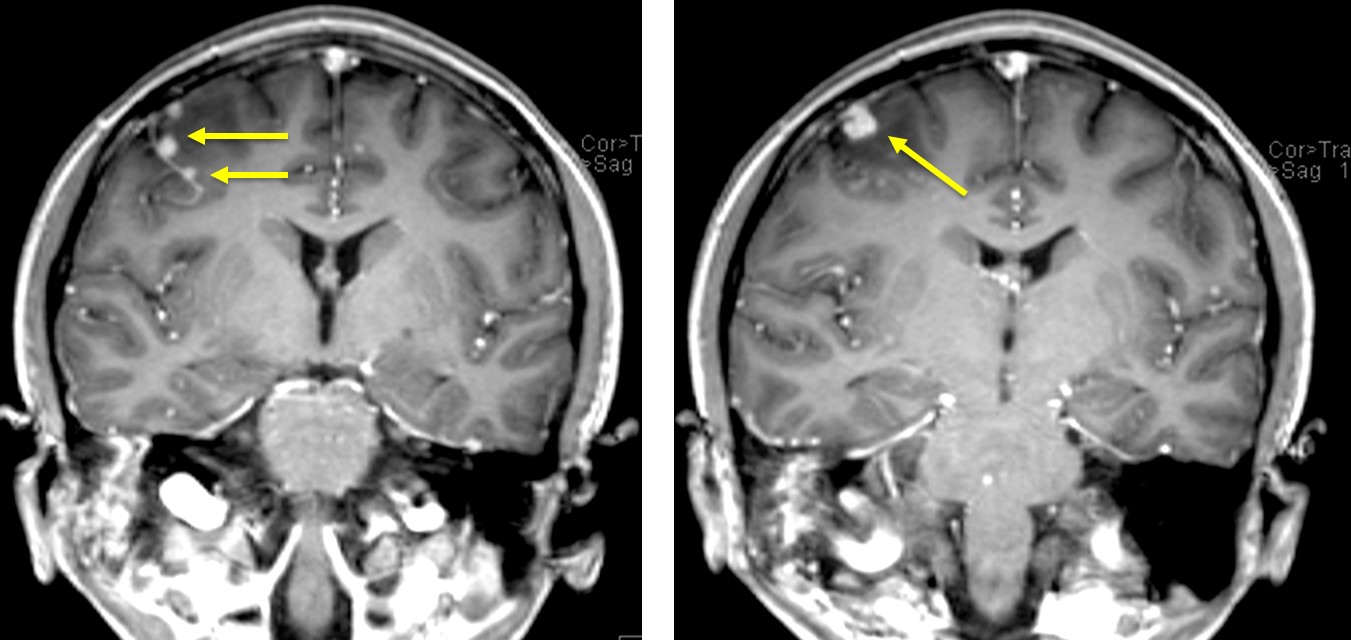
MRI findings:
- There are multiple small homogeneously nodular enhancing lesions in the cerebellum and cerebrum (yellow arrows)
- The lesions are seen peripherally located adjacent to the sulci may be arising from the leptomeninges of the cerebellum, bifrontal and in the right sylvian fissure.
- The subjacent gyri show white matter oedema, especially at the right middle frontal gyrus where the largest leptomeningeal lesion is seen.
- Leptomeningeal enhancements are seen (red arrows)
- No abnormal enhancement at leptomeningeal region.
Diagnosis: CNS tuberculosis (meningitis and tuberculomas) with pulmonary TB.
Discussion:
- Involvement of the CNS is seen in about 5% of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis
- CNS tuberculosis usually results from hematogenous spread.
- CNS tuberculosis can manifest in many forms, including tuberculous meningitis, tuberculomas, tuberculous abscesses, tuberculous cerebritis, and miliary tuberculosis.
- Tuberculous meningitis is the most common manifestation of CNS tuberculosis
- The most common CNS parenchymal lesion of tuberculosis is tuberculoma, also known as tuberculous granuloma.
- Tuberculomas can exist in conjunction with tuberculous meningitis