Clinical:
- A 27 years old lady
- No known medical illness
- Presented with abdominal pain
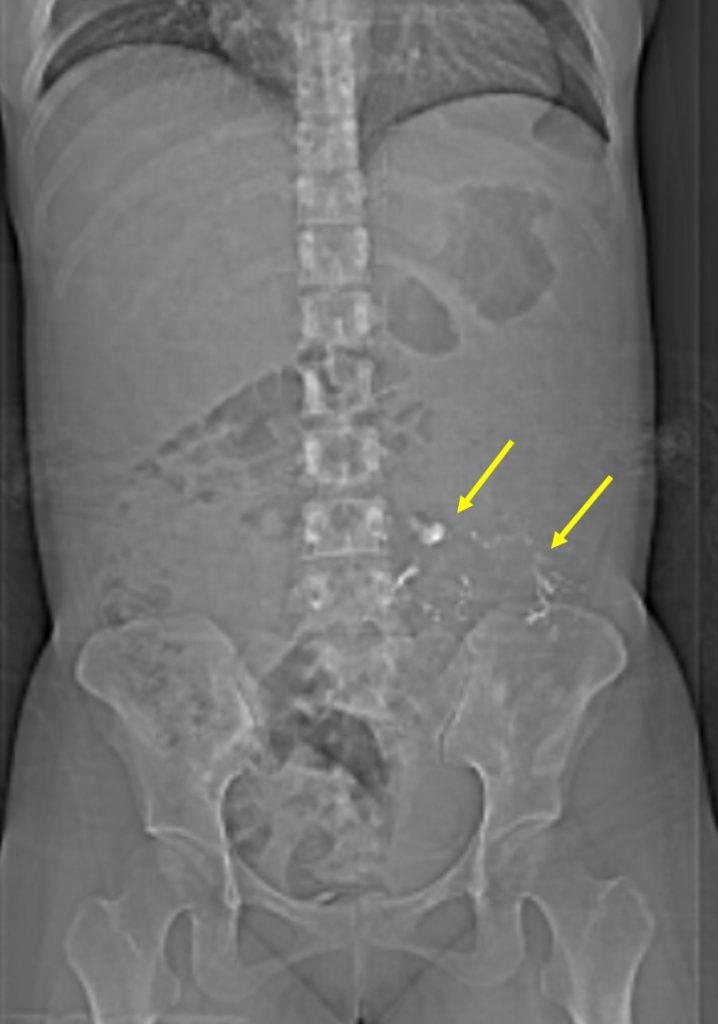
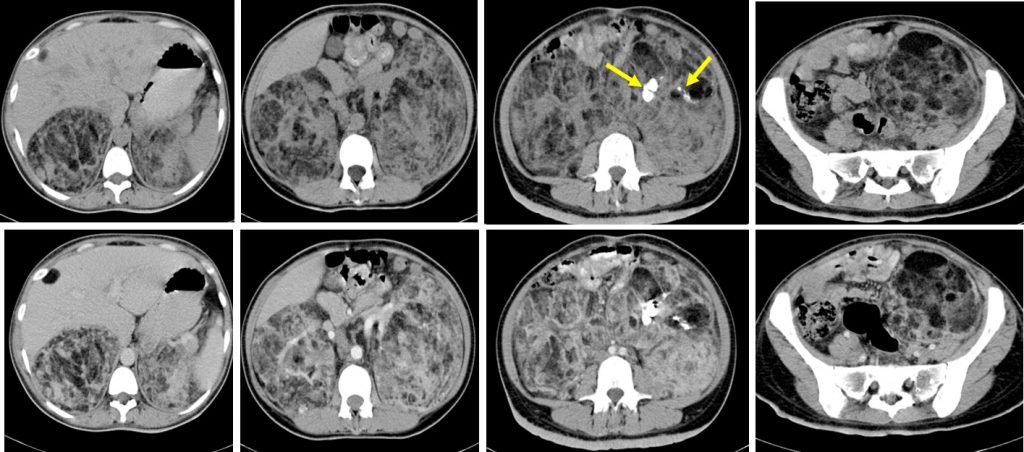
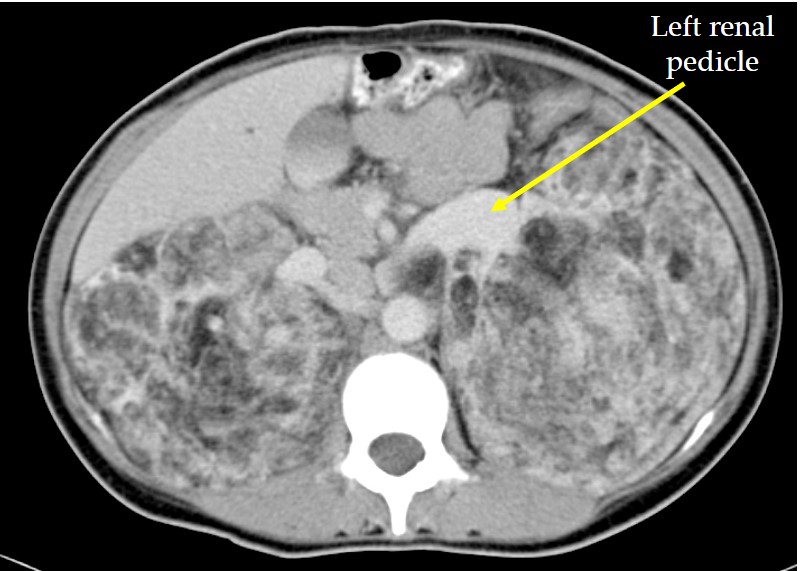
CT scan findings:
- Huge mass lesion at both renal region
- Conforming to shape and configuration of kidneys
- Presence of fat components within
- Dystrophic calcifications (yellow arrows) are also seen within the mass lesion
- There is no contrast extravasation to suggest active haemorrhage
- No hydronephrosis bilaterally
- Displacement and compression effect to surrounding structures however clear plane of demarcation is seen
Diagnosis: Bilateral renal angiomyolipomas.
Discussion:
- Angiomyolipoma (AML) is the most common benign solid renal tumor
- Most AMLs contain fat that is clearly visible on CT and MR images, so these tumors can be easily diagnosed without biopsy or surgery
- The majority of angiomyolipomas are sporadic (80%) and are typically identified in adults
- It is more common in females
- The tumour have the risk of rupture with bleeding or secondary damage/destruction of surrounding structures as they grow.