Clinical:
- A 28 years old lady
- Complaint of suprapubic fullness
- Ultrasound showed cystic pelvic mass
CT scan findings:
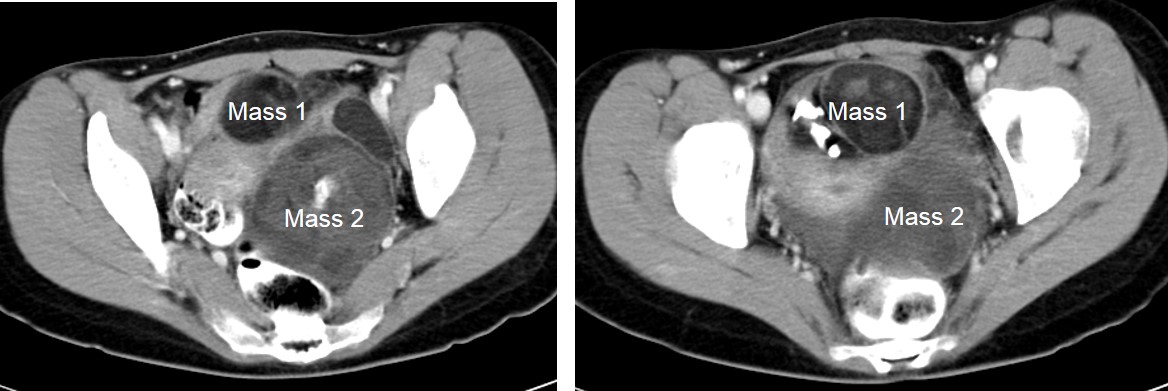
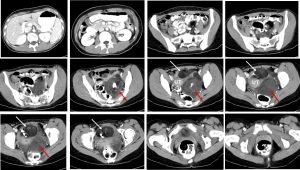
- There are 2 masses seen within the pelvis lying towards the left side
- One lesion is anterior (white arrows) and the other is posterior (red arrows) to the uterus
- Both lesions are heterogenous in density, mainly cystic with presence of fat component and intralesional calcifications, no septae and no enhancement
- No infiltration to surrounding structures and no ascites
- Uterus is grossly normal in size
- No hydronephrosis bilaterally
Intra-operative findings:
- Right teratoma measuring 6×7 cm, mobile, situated anterior to uterus. Right cystectomy done, cyst ruptured during manipulation. Right fallopian tube is normal.
- Left teratoma measuring 8×8 cm with irregular surface, no healthy ovarian tissue seen. Multiloculated, situated at POD, adhesion to sigmoid colon, lateral pelvic wall and post wall of uterus, embedded to the retroperitoneal space. Adhesiolysis done. Left fallopian tube adhered to the cyst.
- Uterus: multiple endometriotic spots on anterior uterine wall
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: specimen labelled as right ovarian teratoma is a ruptured cystic mass with abundant cheesy material and clumps of hair noted on the ruptured surface. The mass measuring 50x40x30 mm. Areas of bone formation are noted. Another specimen labelles as left ovarian teratoma is a ruptured cystic mass showing cheesy material and clumps of hair on the ruptured surface. The mass measuring 80x60x50 mm in size with focal solid protuberance measuring 40 mm in diameter. The central part of the protuberance shows bony tissue.
- Microscopy: sections taken from both right and left ovarian cysts show similar histological features. The cysts show benign epidermal lining and contains keratinous material with areas of mature skin admixture structures in the cyst wall. Focal areas of adipose tissue and occasional glial tissues are noted. No evidence of malignancy or immature element seen.
- Interpretation: Right and left ovarian cyst: bilateral mature cystic teratoma
Diagnosis: Bilateral ovarian mature cystic teratoma
Discussion:
- Ovarian mature cystic teratomas is also known as “dermoid cyst”.
- They affect a younger age group (mean patient age, 30 years) than epithelial ovarian neoplasms
- Most mature cystic teratomas are asymptomatic. Abdominal pain or other nonspecific symptoms occur in the minority of patients.
- The tumors are bilateral in about 10% of cases.
- The diagnosis of mature cystic teratoma at CT and MR imaging is fairly straightforward because these modalities are more sensitive for fat detection compared to ultrasound.
- At CT, fat attenuation within a cyst, with or without calcification in the wall, is diagnostic for mature cystic teratoma.
- Fat is reported in 93% of cases and teeth or other calcifications in 56%.
- Complications of mature cystic teratoma include rupture, malignant degeneration, or (most commonly) torsion.