Clinical:
- A 23 years old lady
- Involved in MVA
- On arrival in ED, GCS 15/15, vital sign stable
- Pain and tenderness at right lumbar region
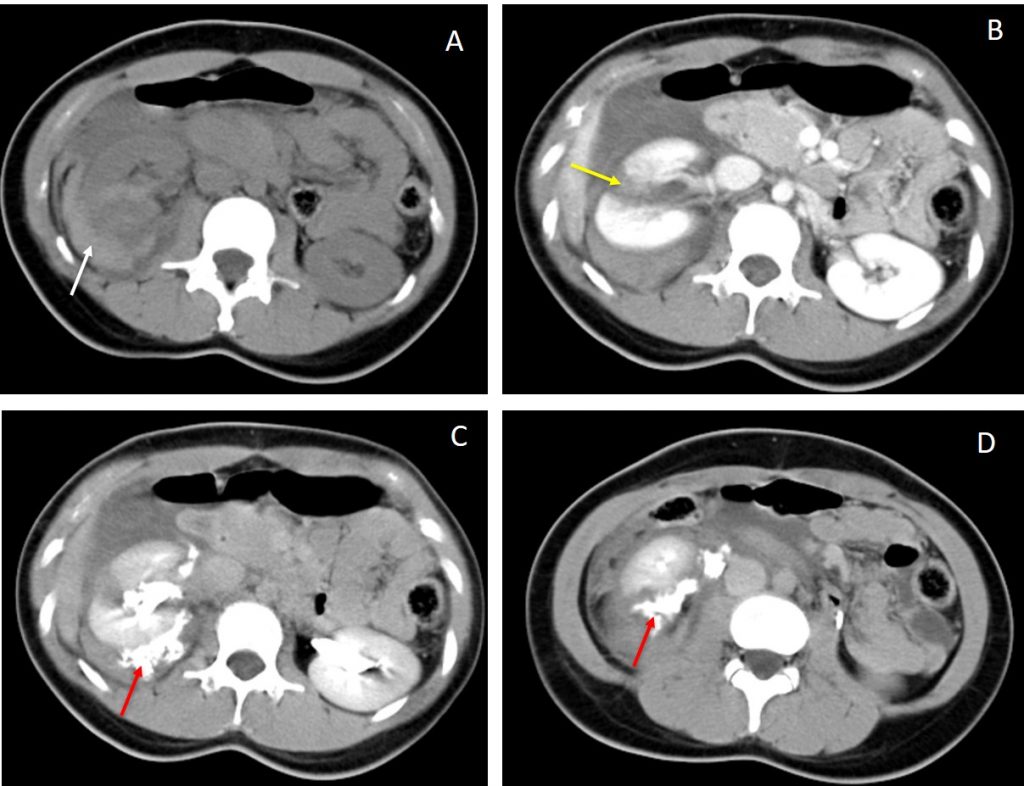
CT scan findings:
- A: Non-contrast CT scan shows hyperdense collection surrounding right kidney suggestive of perinephric hematoma.
- B: Post contrast CT scan shows multiple right renal lacerations. One of the laceration is seen deep through the renal cortex and communicates with the collecting system.
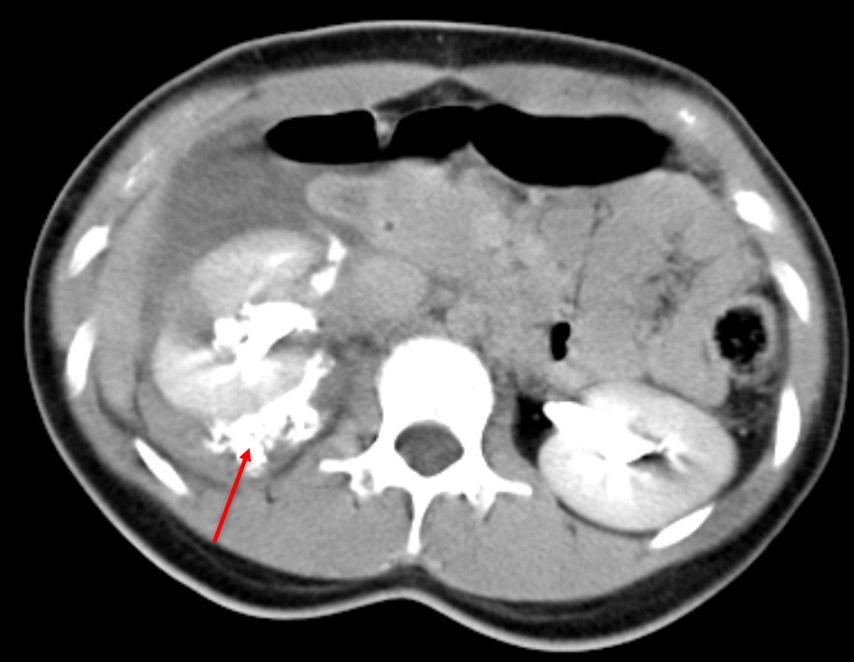
- C &D: Delayed phase CT scan demonstrate contrast extravasation from the renal collecting systems into the perinephric region confirming the injury to the collecting systems.
- Otherwise both kidneys are well opacified by contrast.
Diagnosis: Grade IV right renal injury.
Discussion:
- To determine the appropriate management for a renal injury, the renal injury needs to be accurately staged.
- The American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) Grade IV Renal injury is defined as cortical laceration extending into the collecting system (as noted by contrast extravasation), or a segmental renal artery or vein injury (noted by a segmental parenchymal infarct), or main renal artery or vein injury with a contained hematoma.
- The AAST guidelines recommend dual arterial/portal venous phase imaging for evaluation of these injuries.
- If there are imaging or clinical findings suggesting collecting system injury (e.g. hematuria or blood at the meatus), additional delayed excretory phase images should be obtained after 5-15 minutes delay to evaluate for urine extravasation.
- Urinary contrast is usually hyperdense and readily distinguished from hemorrhagic vascular contrast.