Clinical:
- A 49 years old lady
- Presented with recent onset of fitting episodes
- No neurological deficit
MRI findings:
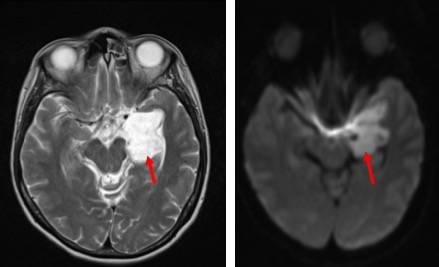
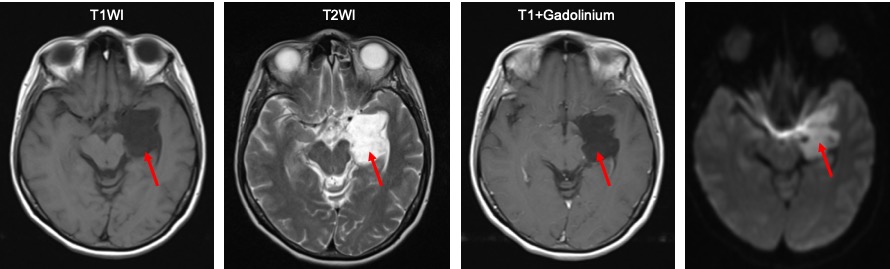
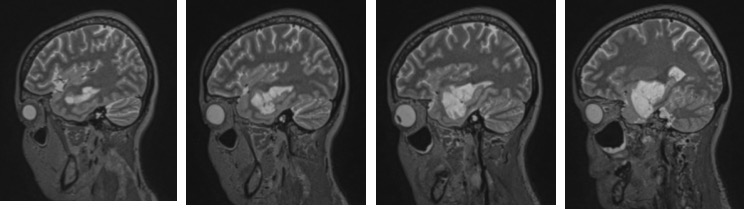
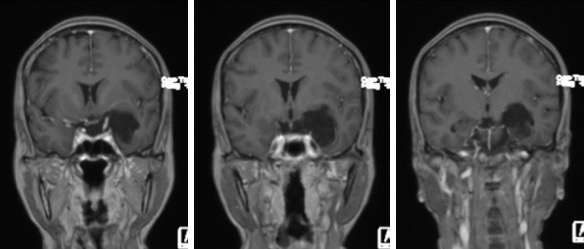
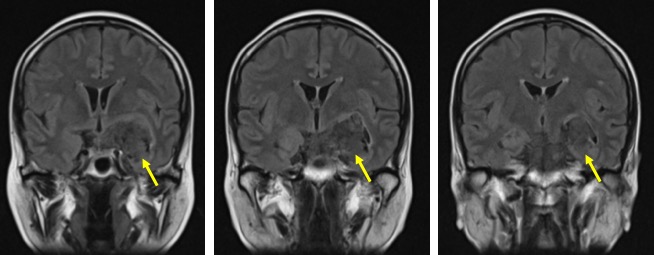
- An extra axial mass at left temporal lobe measuring 4x3x4 cm (red arrows)
- It shows intermediate signal on T1, hyperintense on T2
- Not suppressed on FLAIR (yellow arrows).
- No enhancement post contrast.
- Restricted diffusion on DWI/ADC sequences
- No extension into the cavernous sinus
- No enhancing nodule or abnormal leptomeningeal enhancement
Diagnosis: Epidermoid cyst (HPE proven)
Discussion:
- Intracranial epidermoid cyst is also known as ectodermal inclusion cyst or congenital inclusion cyst.
- It represent 0.2-1.8 % of all primary intracranial tumours
- It is the most common congenital intracranial tumours
- Symptoms depends on the site of tumour
- Location: CP angle (40-50%), 4th ventricle (17%), middle cranial fossa (10-15%)
- CT scan shows round or lobulated mass, >95% hypodense resembling CSF, 10-25% contain calcifications, no enhancement post contrast. It may cause bone erosion.
- MRI shows slightly hyperintense to CSF on T1WI, isointense (65%) to slightly hyperintense (35%) to CSF on T2WI, does not fully suppressed on FLAIR and restricted diffusion on DWI. No contrast enhancement post contrast. MRS shows no NAA, choline or lipid, resonance from lactate.