Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 45 years old man
- Underlying hypertension
- Presented with painful swelling of left mandible for 4 years
- History of tooth extraction due to tooth motility at the same region
- Start to have swelling and yellowish discharge on and off after the procedure
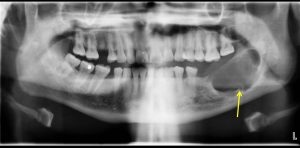
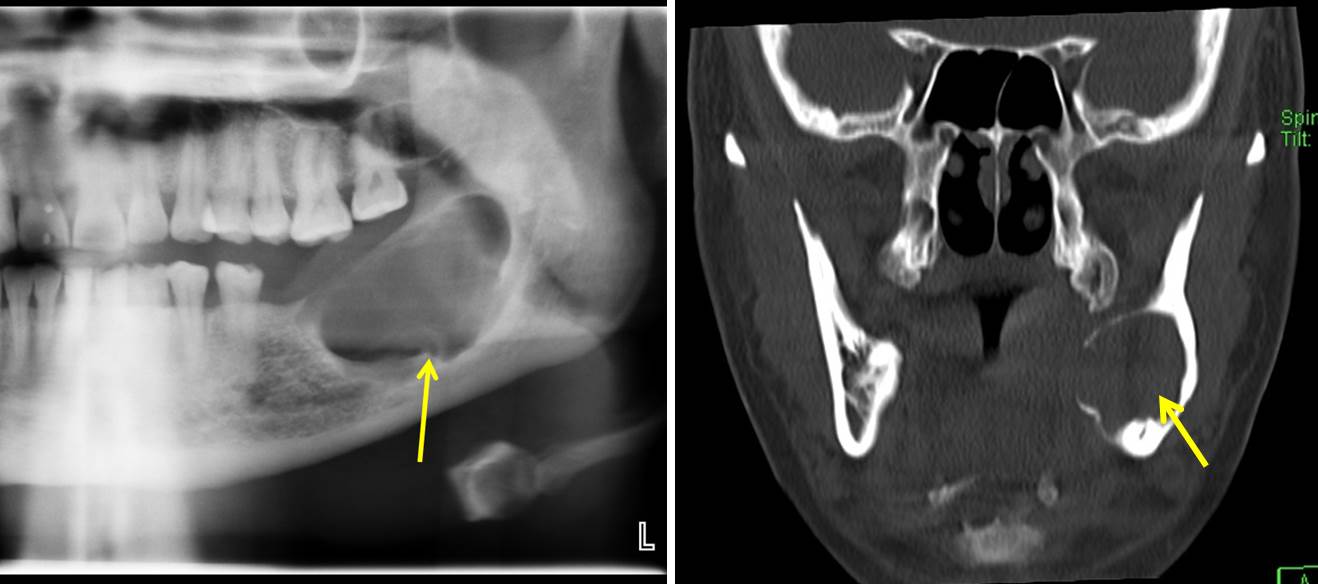
Radiographic findings:
- A well defined expansile lytic lesion
- It shows scalloped sclerotic margin
- Presence of internal septation
- No tooth in keeping with previous extraction
- No obvious soft tissue swelling
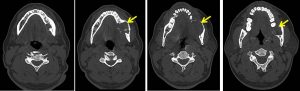
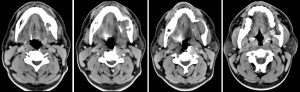
CT scan findings:
- There is a large well defined non enhancing expansile lesion arising from the body of left mandible measuring 2.8 x 3.4 x 2.9 cm (AP x W x CC).
- It is seen extending to the angle and ramus of the left mandible.
- The lesion shows scalloping margin and causing thinning of the cortex, with cortical defects seen overlying the anterior and inner aspect of the left mandible.
- The lytic region is filled with soft tissue mass.
- The left lower molar tooth is not seen.
- No calcification or air pocket seen within. No air fluid levels.
- No significant surrounding fat streakiness.
- No other lesion seen in the rest of the visualised bones.
- The left masseter muscle and tongue are normal.
- No significant cervical lymphadenopathy.
HPE findings:
- macroscopy: specimen labelled as lining of cyst at left posterior mandible, consist of multiple pieces of brownish tissue
- Microscopy: the sections show odontogenic tumour comprises of odontogenic epithelium with peripheral palisading basal cells resembling ameloblast. Stellate reticulum-like cells are observed within the neoplastic islands. Plexiform and follicular pattern are observed throughout the lesion with some areas showing acanthomatous pattern. In some region, degenerated epithelium is observed with mixed acute and chronic inflammatory cells infiltrate. Elsewhere the fibrous connective tissue of variable maturity.
- Interpretation: Ameloblastoma
Discussion:
- Ameloblastoma is also known as adantinoma of jaw
- It is a benign locally aggressive epithelial neoplasm
- It affect male and female equally, presentation at 3rd to 5th decade of life
- It is found in ramus or posterior of mandible in 75% and maxilla in 25%
- Radiographically seen as well defined, well corticated unilocular lucent lesion or multilocular lesion with internal septations (soap bubble appearance).
- It is typically expansile with scalloped margin
- It may perforate the lingual cortex and infiltrate adjacent soft tissue
- It is also often associated with the crown of an impacted unerupted tooth with resorption of the root of tooth