Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 3 months old baby girl
- Uneventful antenatal history
- Delivered normal SVD
- Presented with seizures
- No history of fever, no trauma
MRI findings:
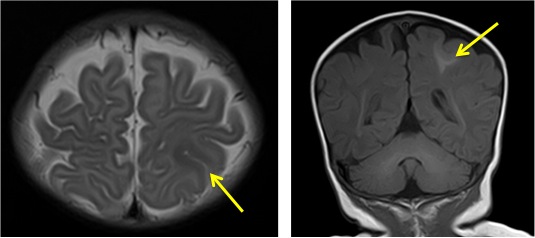
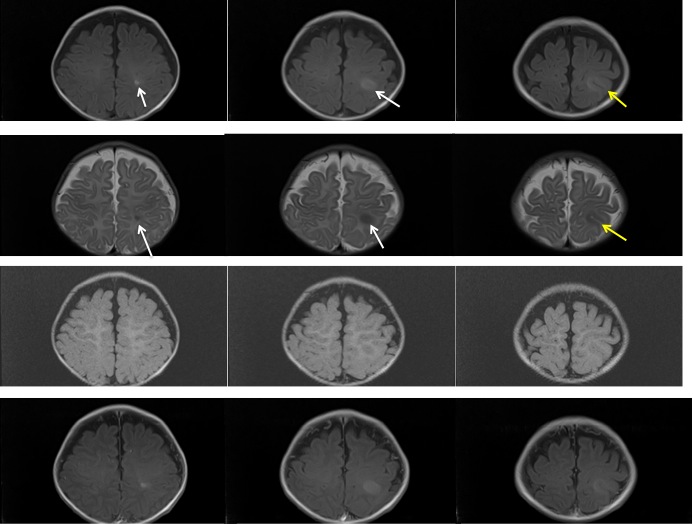
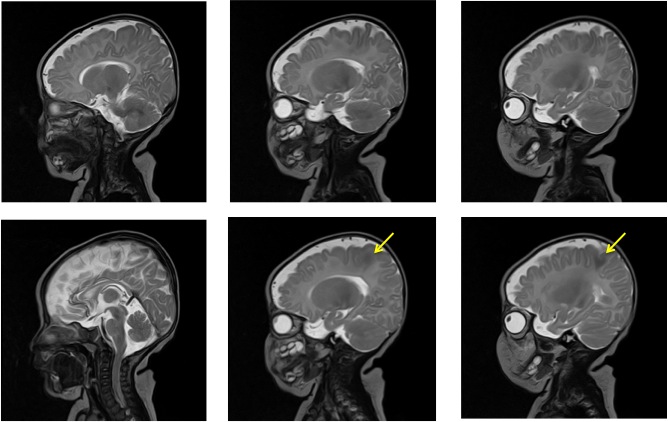
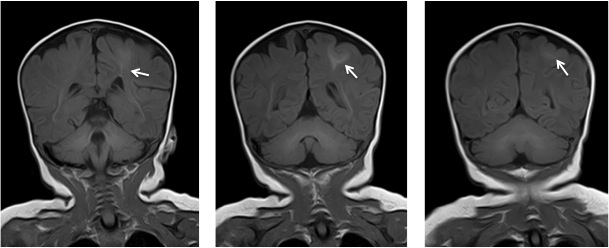
- A focal cortical thickening seen at the left posterior parietal lobe (yellow arrows)
- It is slightly hyperintense on T1WI, hypointense on T2WI, not well seen on FLAIR and do not demonstrate any enhancement post contrast
- Adjacent focal white matter signal changes also seen which is hyperintense on T1WI and hypointense on T2, which is extending from the ventricle to the cortex in keeping with transmantle sign
- Grey white matter junction is blurred on T2WI
- No significant mass effect
- No structural abnormality is seen
Diagnosis: Focal cortical dysplasia
Discussion:
- Focal cortical dysplasia is a heterogenous group of disorders of cortical formation
- It is one of the most common cause of epilepsy
- Can be associated with hippocampal sclerosis and cortical glioneuronal neoplasms
- MRI features include
- cortical thickening,
- blurring of grey white matter junction with abnormal subcortical layer,
- T2/FLAIR hyperintense signal of white matter with or without the transmantle sign,
- T2/FLAIR signal hyperintensity of grey matter,
- abnormal sulcal or gyral pattern and segmental and/or lobar hypoplasia/atrophy
- In this case, different signal intensity is due to incomplete myelination.