Clinical:
- A 59 years old male
- Presented with headache for 2 months
- Gradual worsening affecting his daily activity
- No vomiting, no blurring of vision
- No fever, no loss of appetite or loss of weight
- Clinically no neurological deficit
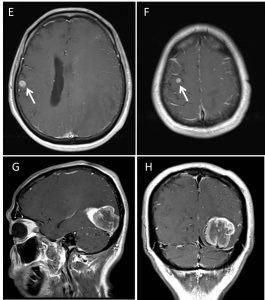
MRI findings:
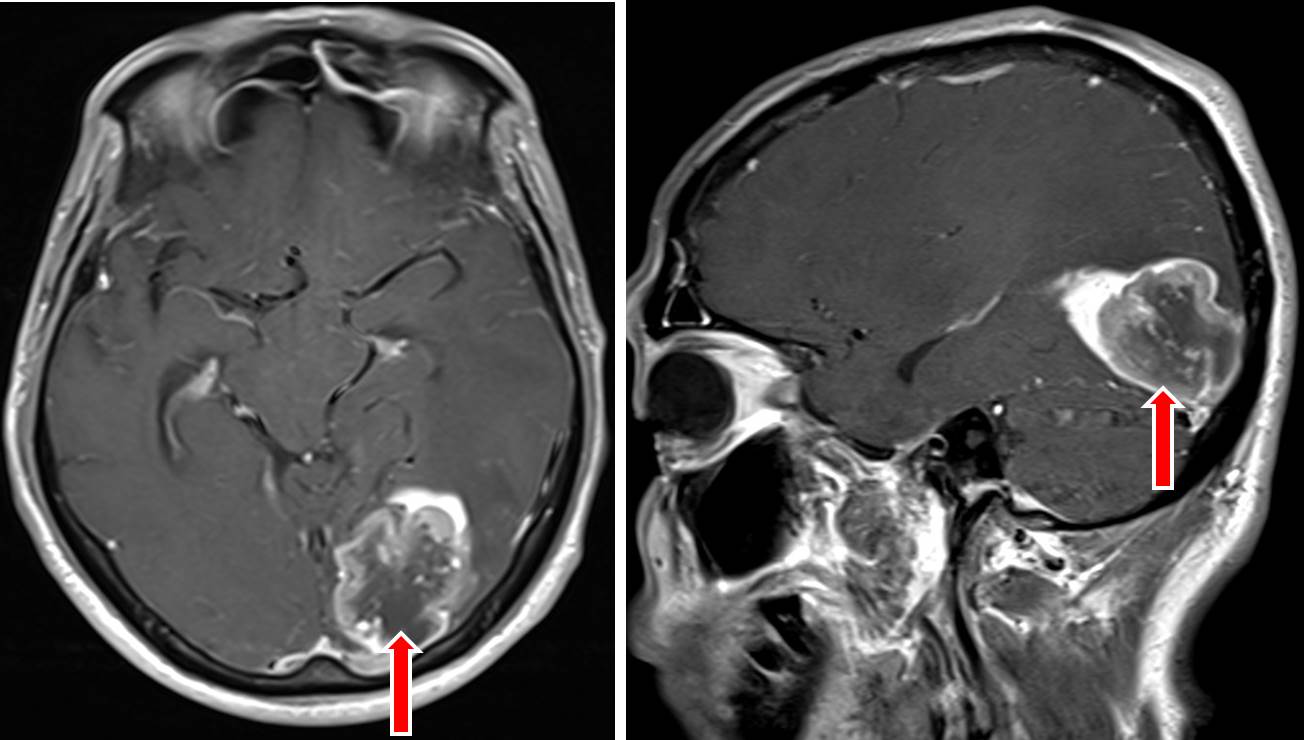
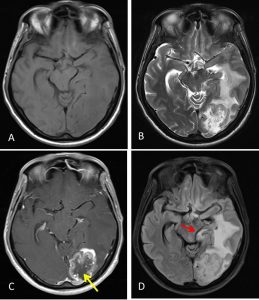
- There is a lobulated mass lesion in the left occipital lobe measuring about 3.9 x 4.7 cm. This lesion showed marked enhancement post contrast with central non-enhancing region suggestive of tumour necrosis (yellow arrow).
- There is significant vasogenic oedema in the left temporo-parietal region.
- There is compression of the midbrain, causing distortion of its shape on the left side.
- The left PCA is also compressed (red arrow), however this vessel is still patent.
- There is no hydrocephalus.
- Small enhancing lesions are seen at the right vertex and right temporal lobe (white arrows).
- There is no abnormal leptomeningeal enhancement.
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: specimen labelled as brain tumour and dura.
- Microscopy: section of tumour shows an epithelial tumour arranged as complex glandular pattern and some papillary configuration. These glands and papillae are lined by pleomorphic tumour cells, having vesicular nuclei with prominent nucleolus. The cystoplasm is abundant. Mitosis and tumour necrosis is evident. No normal brain tissue seen. Dura is also positive for malignancy.
Diagnosis: metastatic adenocarcinoma
Discussion:
- Cerebral metastasis is a cancer that has spread to the brain from another location in the body and is therefore considered as secondary brain tumour.
- The metastasis typically shares cancer cell type similar with the original site of the primary cancer.
- Metastasis is the most common cause of brain cancer, far more common than primary brain cancer.
- The most common sites of primary cancer which metastasize to the brain are lung, breast, colon, kidney, and skin cancer.
Progress of patient:
- Left craniotomy and tumour excision done
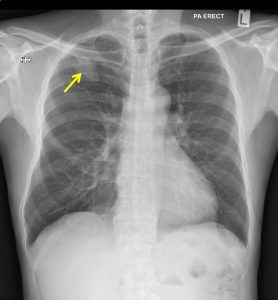
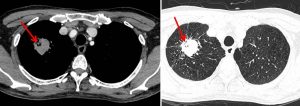
- Further workout after HPE findings shows a lesion in the lung
- Patient referred to oncologist
- Chemotherapy started however treatment discontinued as patient requested for conservative treatment