Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 43 years old
- Presented with irregular menstrual bleeding
- Ultrasound shows ovarian cyst
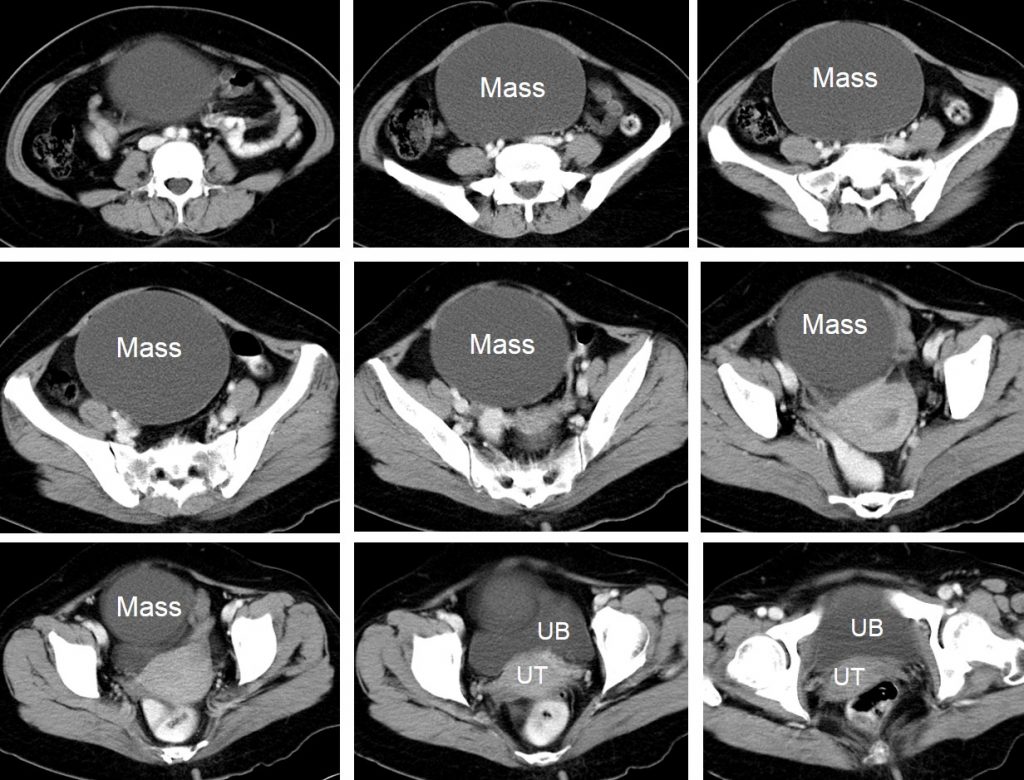
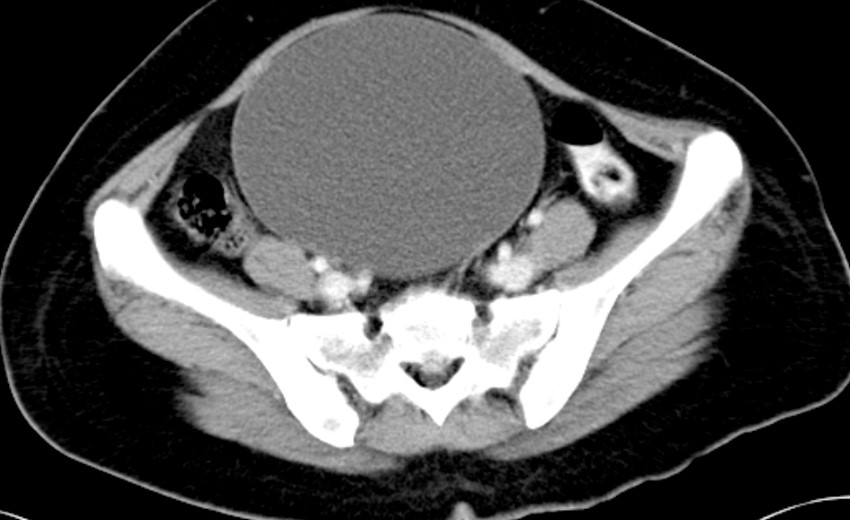
CT scan findings:
- There is a large well-encapsulated cystic mass in the pelvis measuring 16x13x11 cm.
- No solid component or septation seen.
- No calcification or fat component.
- The uterus is normal. No ascites.
Intra-operative findings:
- Large left ovarian cyst measuring 20×15 cm. Removed intact. Opened up after surgery, benign-looking, clear cyst.
- Uterus is normal in size.
- Right ovary and both fallopian tubes are normal.
- No ascites. No endometriotic spot.
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: specimen labelled as TAHBSO and left ovarian cyst consist of a uterus, cervix, both ovaries and fallopian tubes with attached ovarian cyst. The left ruptured unilocular cystic lesion located between the left ovary and left fallopian tube. This lesion measures 100×75 mm with the cyst wall 2-4 mm in thickness. No solid area seen.
- Microscopy: Sections of the left ovarian cyst is lined by cuboidal epithelium to tubal type epithelium. The ecto and endocervix are unremarkable. The endometrium is non-secretory. The right ovary shows cystic follicles and corpora albicans. No malignancy.
- Interpretation: left ovarian cyst: serous cystadenoma.
Diagnosis: Ovarian serous cystadenoma.
Discussion:
- Ovarian serous cystadenomas are benign epithelial tumours and comprise about 20% of all benign ovarian tumours.
- It is usually seen in women between 20 – 60 years
- Present clinically as cystic adnexal masses
- 15% are bilateral
- Imaging findings: average size of 5-10 cm but frequently grow larger, cysts that may have thin septations and occasionally papillary projections, tend to be unilocular, but may also be multilocular.
- Histologically lined by a single layer of non-ciliated cuboidal to tall columnar epithelium.