Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 27 years old man
- Presented with recurrent painless hematuria for the last 10 years.
- US KUB showed no evidence of renal / ureteric calculus.
- CT KUB showed persistent small focal hypodense lesion at posterior prostate.
- MRI for further characterization of the lesion.
MRI findings:
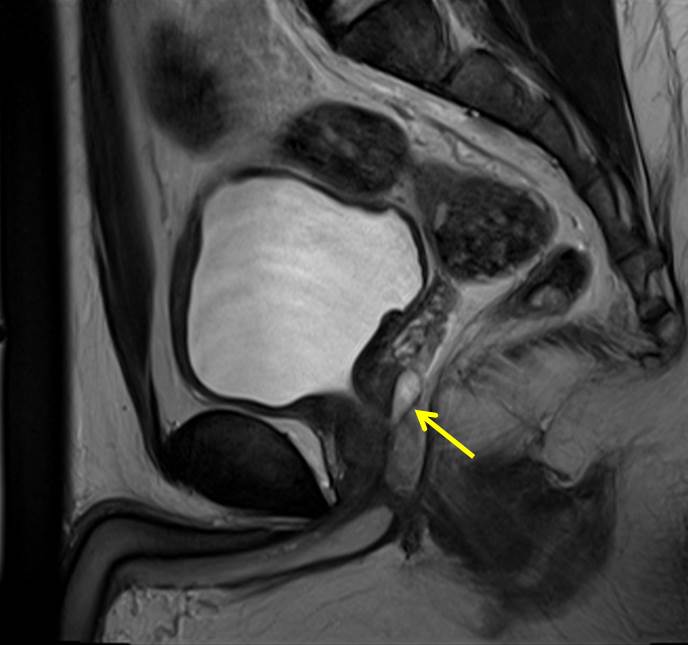
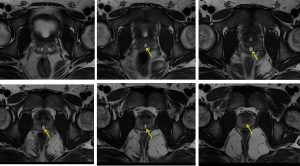
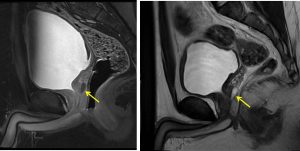
- A small focal midline cystic prostatic lesion is noted (yellow arrows), located within the mid-posterior transition zone.
- It measures at 0.9 cm x 0.6 cm x 1.8 cm (AP x W x CC).
- The lesion returns hypointense signal on T1 and hyperintense on T2. Minimal rim enhancement observed following IV gadolinium. No restricted diffusion is observed.
- It shows continuation with the prostatic urethra.
- Seminal vesicles are normal.
- The prostate gland itself is normal in size.
- The urinary bladder is normal.
Diagnosis: Prostatic utricle cyst
Discussion:
- Prostatic utricle is a remnant of Mullerian duct in males.
- Prostatic utricle cyst results from focal dilatation of the prostatic utricle ranging from few millimeters to 2 cm.
- The incidence of prostatic utricle cyst is 11% to 14% in association with hypospadias or intersex anomalies and up to 50% in the presence of perineal hypospadias.
- It is usually seen during the first to second decades of life, with a mean age range of 26 years.
- Most prostatic utricular cysts are asymptomatic.
- When symptomatic it typically consist of urinary incontinence, recurrent infections, or stone formation.
- Malignant degeneration has been reported in 3% of prostatic utricles.
- On ultrasonography, a well-defined midline cystic lesion is seen posterior to the urinary bladder.
- MRI shows as a cystic lesion in the substance of the prostate gland posterior to the urinary bladder with a typical midline location. Communication of the cyst with the prostatic urethra is typically noted.
- The differential diagnosis to be considered on imaging appearance include bladder diverticulum, urachal cyst, Mullerian duct cyst, or a seminal vesicle cyst.
- Prostatic utricle cyst communicates with the prostatic urethra and are located in the midline, posterior to the bladder, and anterior to the rectum, as described in this case.
- Mullerian duct cysts, on the other hand, do not typically communicate with the prostatic urethra, although they are also midline.
- Urachal cysts are clearly distinguished from a prostatic utricle cyst due to their anterior relationship to the urinary bladder while seminal vesicle cysts are located lateral to midline and are usually unilateral.