Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 23 years old man
- History of right testicular carcinoma
- Orchidectomy and completed chemotherapy about one year ago
- Presented with occasional chest discomfort and cough
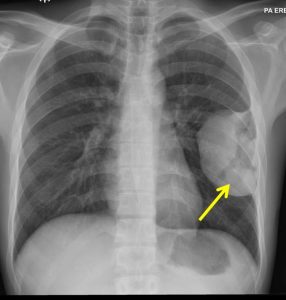
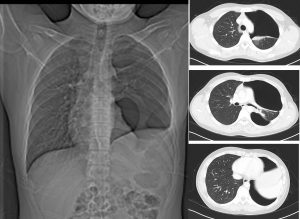
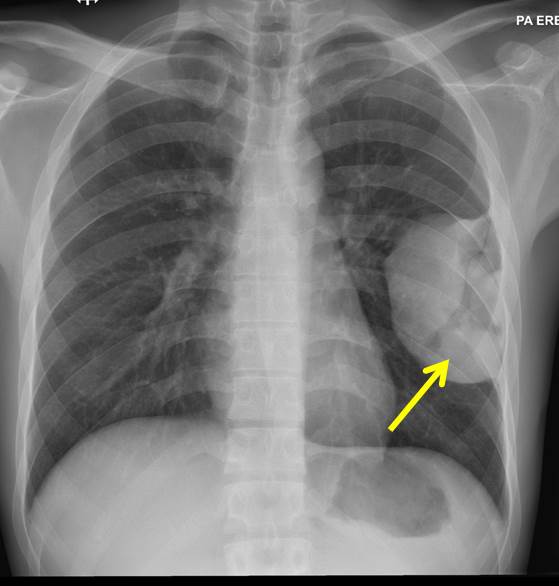
Radiograph findings:
- A huge mass seen in the left thoracic region (yellow arrows)
- Peripherally located with obtuse margin
- No fluid levels or calcification within it
- No obvious adjacent ribs destruction
- No pleural effusion or pneumothorax.
- No hilar mass. No cardiomegaly. No mediastinal widening
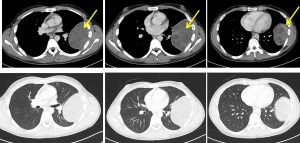
CT scan findings:
- A large pleural based mass is observed at the left hemithorax measuring about 9.9 x 6.5 x 9.2cm (AP x W x CC).
- It appears heterogeneously hypodense, with multiple enhancing solid component observed. Internal septations are also seen within the mass.
- No erosion of the adjacent ribs noted.
- Another round hypodense nodule is also seen in the left lung base (image not shown)
- No pleural effusion is detected bilaterally.
- No enlarged mediastinal node. Shotty nodes are observed in both axillary regions.
Diagnosis: Metastatic pleural based mass.
Discussion:
- Differential diagnosis of pleural based mass include pleural tumours, metastatic pleural disease, loculated fluid, mass related to chest wall or ribs, mass related to intercostal nerve and infection.
- Metastatic pleural disease are particularly from adenocarcinoma from bronchogenic carcinoma, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, GI adenocarcinoma and renal cell carcinoma.
- Pleural metastases are more common than malignant mesothelioma.
- Pleural metastasis usually affect the visceral and parietal pleura.
- Pleural effusion almost always occurs due to impaired lymphatic drainage or capillary permeability increased by inflammation or rupture or endothelium
Progress of patient:
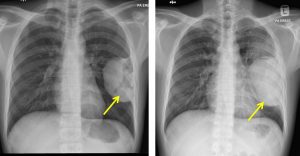
- Worsening of lung metastasis and the pleural based lesion grew bigger
- Left thoracotomy with excision of tumour, lower lobectomy and non-anatomical resection of lingula and posterior subsegmentectomy of apipoposterior segment with phrenectomy done
- Repeat CT scan shows an air-filled left hemithorax with small residual aerated left lung (possibly posterior segment of the left upper lobe) are in keeping with post-operative changes. No evidence of recurrence