Clinical:
- A 60 years old man
- Presented with chronic cough
- Associated with loss of appetite and loss of weight
Radiographic findings:
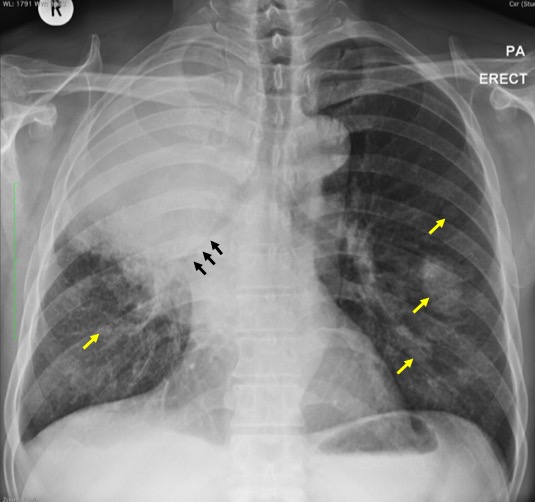
- There is homogenous opacity at right upper and mid zone.
- No airbronchogram seen within the opacity. No calcification.
- There is compression with narrowing of the right lower lobe bronchus (black arrows).
- There is slight deviation of the trachea to the left side. However the trachea is still centrally located and grossly normal in appearance
- There are a few rounded opacities of various sizes (yellow arrows); the largest is seen at left middle zone measuring about 32 mm.
CT scan findings:
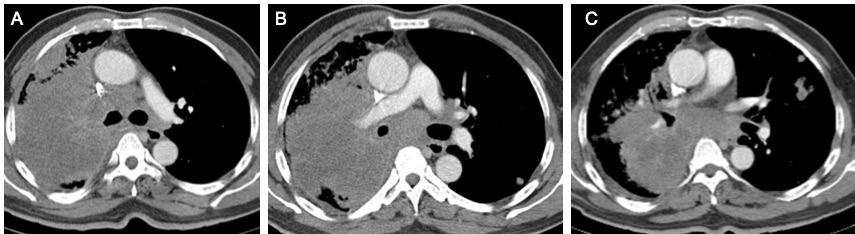
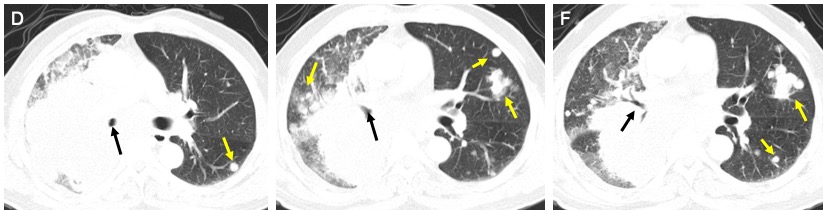
- There is narrowing of right upper lobe bronchus causing collapsed consolidation of the lung distally. There are multifocal relatively non-enhancing region within the collapsed lung which may represent lesions.
- The superior bronchi of right lower lobe is also narrowed by external compression from enlarged matted nodes. There is segmental collapsed of the superior segment of right lower lobe.
- There are multiple lung nodules in both right and left lungs. These nodules are of various sizes asymmetrically distributed in all lobes. The largest in the left upper lobe measures 17 mm near the fissure. The left lower lobe nodule measures 12 mm.
- There is compression effect and narrowing of the superior vena.
- There is no cardiomegaly and no pericardial effusion. No pneumothorax.
HPE findings:
- Microscopy: biopsy of lung mass consist of multiple whitish tissues
- Microscopy: Fragments of tumour tissues composed of tumour cells arranged in clusters and vague glandular architexture. These cells have moderate nuclear pleomorphism, hyperchromatic nuclei, occasional nucleoli and moderate amount of cytoplasm. Mitoses are seen. Tumour necrosis is present. Desmoplastic stromal reaction is evident.
- Immunohistochemistry: the tumour cells are positive for TTF-1
- Interpretation: Lung mass; Non small cell carcinoma, favours adenocarcinoma.
Diagnosis: Lung cancer, adenocarcinoma.
Discussion:
- Adenocarcinoma is the most common histologic type of lung cancer.
- It represents 31% of all lung cancers, including bronchoalveolar carcinoma.
- No definite radiological features to differentiate between different type of lung cancers.
- Adenocarcinomas are typically peripherally located and measure <4 cm in diameter, which is not seen in clearly demonstrated in this case.
- Only 4% show cavitation. Hila or hila and mediastinal involvement is seen in 51% of cases on chest radiography
- A recent study describes two characteristic appearances on CT: either a localized ground glass opacity which grows slowly (doubling time >1 yr) or a solid mass which grows more rapidly (doubling time <1 yr)
