Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 58 years old man
- No known medical illness
- Presented with left sided abdominal pain for 2 days
- Associated with PR bleed and fever
- FBC showed elevated white blood cells
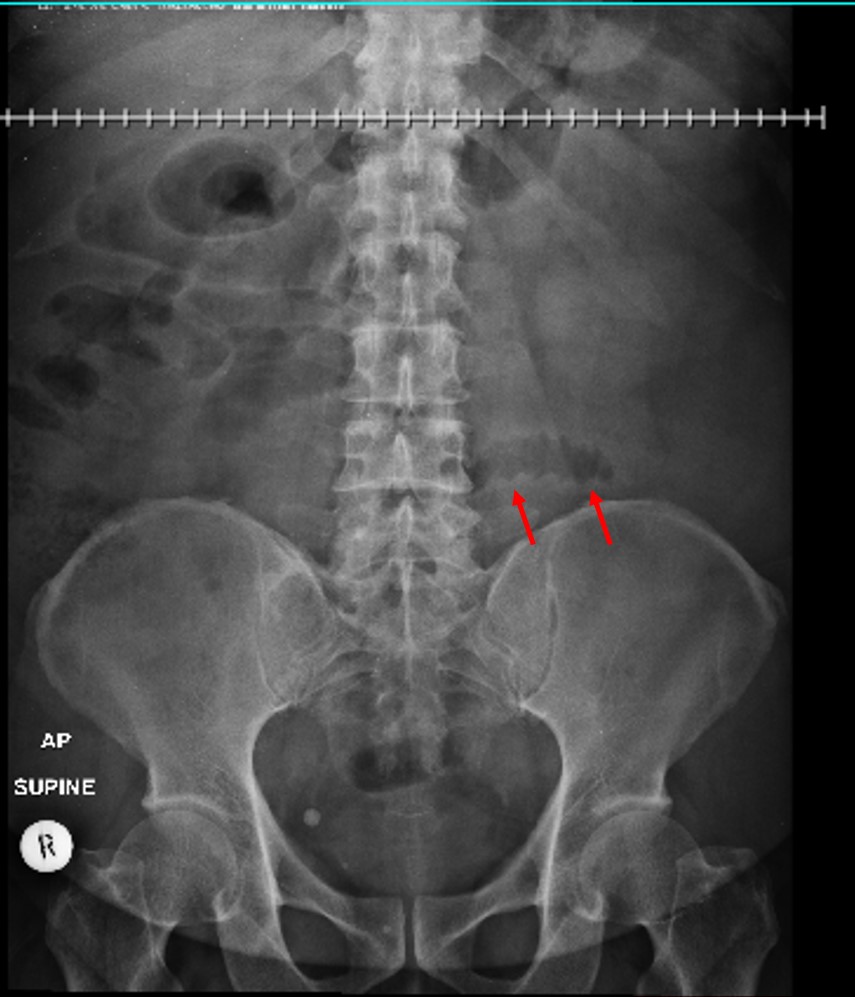
Radiographic findings:
- Abdominal radiograph shows a focal bowel loops at left lumbar region (red arrows) with thickened mucosa.
- No abnormal dilatation of bowel loops seen.
- No free air.
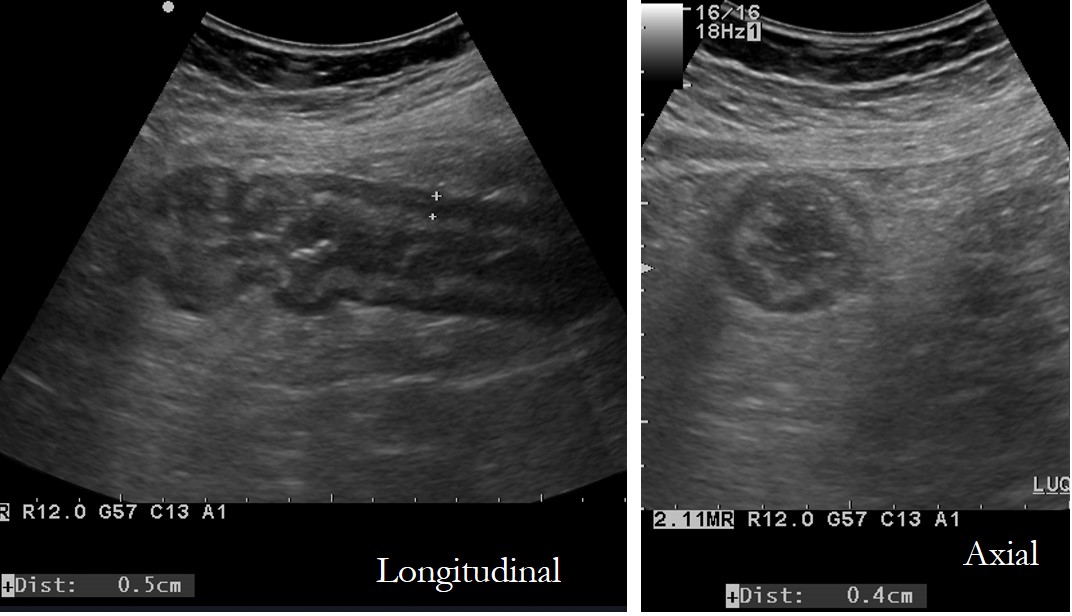
Ultrasound findings:
- A focal bowel loop with thickened and oedematous wall is seen at left lower abdomen region. Absence of peristalsis of this bowel loop.
- No bowel dilatation seen. No free fluid.
- No other abnormality seen.
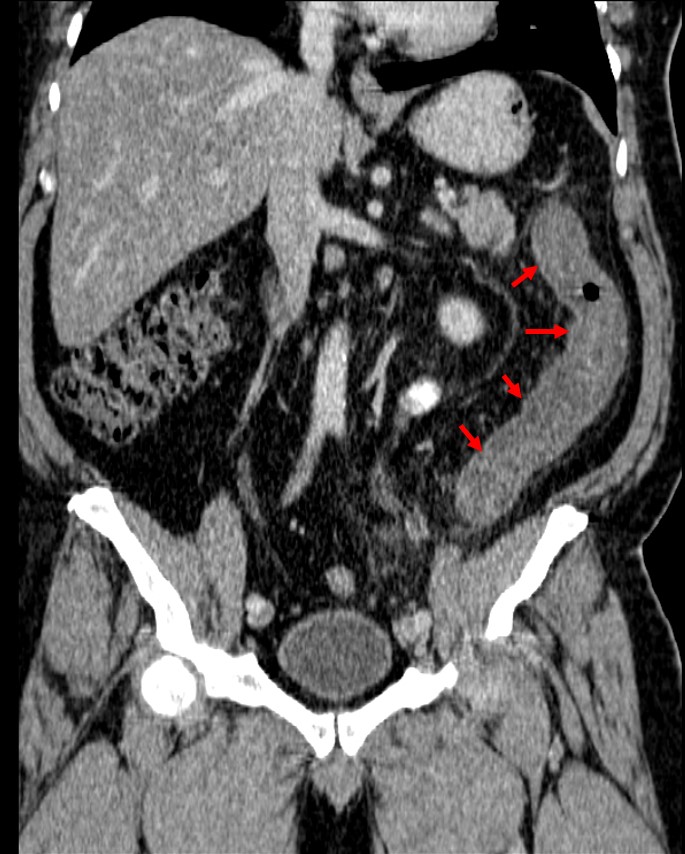
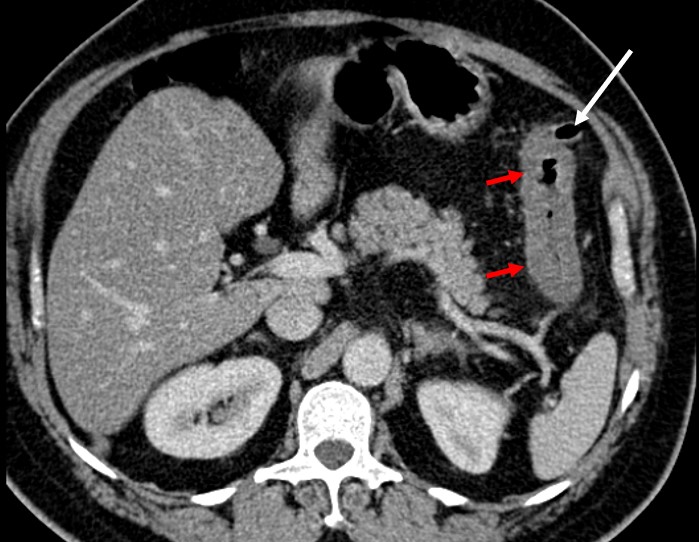
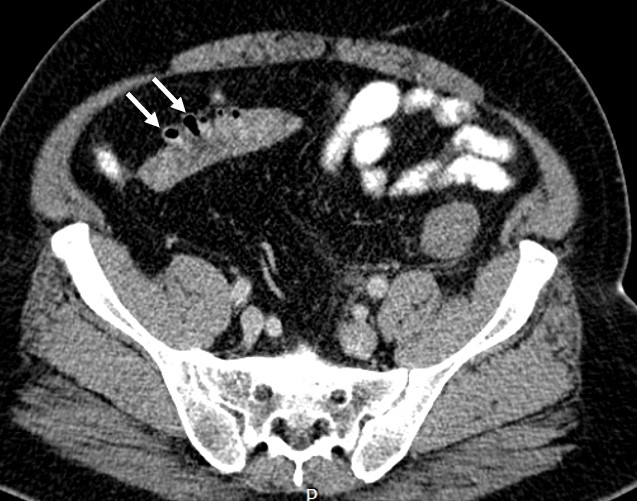
CT Scan findings:
- There is a long-segment wall thickening involving the distal transverse colon to sigmoid colon (red arrows).
- This thickened wall showed abnormal mucosal enhancement.
- The thickening causes significant narrowing of the lumen, however no dilatation of bowel loops proximal to this.
- Multiple diverticulosis (white arrows) are seen at sigmoid and distal descending colon.
- There is no obvious contrast extravasation or extraluminal air to suggest perforation.
- There is no focal collection to suggest abscess formation.
- There is mesenteric streakiness adjacent to the thickened bowel loops.
- A few shotty mesenteric and paraortic nodes are seen.
Diagnosis: Acute colonic diverticulitis.
Discussion:
- Colonic diverticulitis is an inflammation and a complication of the colonic diverticulosis (outpouchings of the bowel wall).
- Imaging findings of uncomplicated diverticulitis include edematous thickening of the bowel wall, pericolic mesenteric fat stranding and enhancement of colonic wall.
- Complications include perforation, phlegmon, abscess, ascending septic thrombophlebitis (phylephlebitis), bleeding, intestinal obstruction, and fistula.
- Uncomplicated diverticulitis can be treated conservatively; however, complicated diverticulitis may not be responsive to medical treatment and life-threatening conditions may occur.
- Differential diagnosis include colorectal carcinoma, ischaemic colitis and inflammatory bowel disease
Progress of patient:
- Patient was discharged well after conservative treatment
Recent Comments