Clinical:
- A 43 years old lady
- Presented with abdominal distension for many months
- Associated with occasional discomfort
- No constitutional symptoms
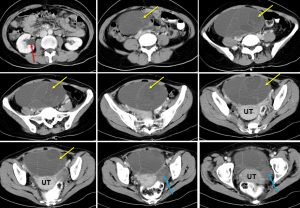
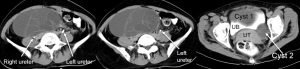
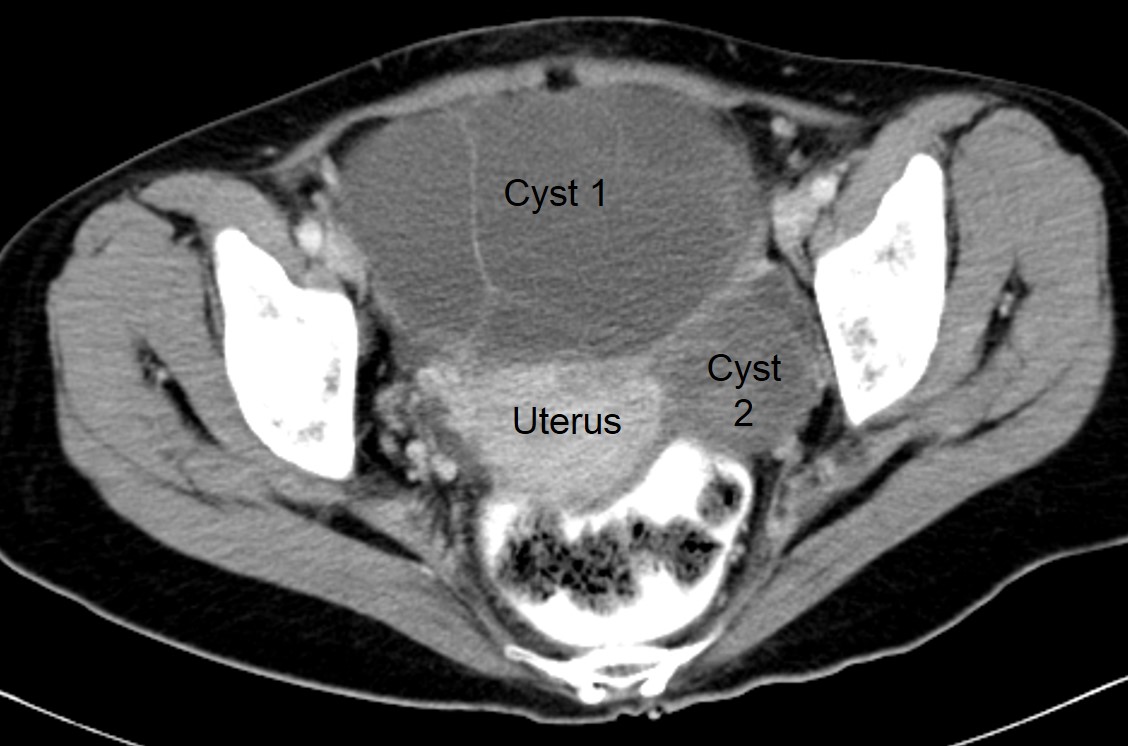
CT scan findings:
- A cystic mass measuring about 16x14x9 cm in pelvis (yellow arrows)
- The mass has thin wall with multiple thin septae within
- No calcification, no local infiltration and no fat component
- Another smaller cystic lesion is seen on the left side (blue arrows)
- There is right hydronephrosis (red arrow), compression of right distal ureter by the larger mass on the right side
- No distant metastasis, No ascites
Intra-operative findings:
- Right ovary-multiloculated mass 18×16 cm
- Left ovary- multiloculated cyst, leak during manipulation, sebum content
- Uterus and both fallopian tubes are normal
- Lymph node not enlarged
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: specimen labelled as uterus, bilateral ovaries, both fallopian tubes, cervix and omentum weighing 2000gms. The right ovarian mass measures 195x160x110 mm. The left ovarian mass measures 65x45x32 mm. Cut section of right ovarian mass shows a multiloculated cystis filled with yellowish jelly like material. The locules varies in sizes ranging from 2 mm to 80 mm in diamter. No solid area. The cyst wall thickness is about 1 mm. Cut section of left ovarian mass shows solid and cystic cut surfaces. The solid area measures 42x30x30 mm. The cystic area ranging from 13 to 25 mm in diameter. The cyst wall thickness is less than 1 mm. Both ovarian mass have intact capsule.
- Microscopy: Section from the solid area of left ovarian mass show a malignant tumour infiltrating the stroma. The tumour is composed of malignant cells arranged in glandular structures with back to back pattern and solid papillary with very scanty intervening stroma. The cells have moderately pleomorphic vesicular nuclei with prominent nucleolus. Many mitotic feature figures are seen. No obvious lymphatic or vascular permeation and tumour necrosis seen. The cystic area shows cyst wall lined by uniform cuboidal epithelium. The capsule is intact. Section from right ovarian mass show a benign cystic tumour and the cyst wall lined by a single layer of mucinous epithelium. The cells have basally located and benign looking nucleoli with abundant intracytoplasmic mucin. No borderline features are seen. No evidence of malignancy.
- Interpretation: left ovary: endometrioid adenocarcinoma and right ovary: mucinous cystadenoma
Diagnosis: Endometriod adenocarcinoma (left ovary), mucinous cystadenoma (right ovary)
Discussion:
- Endometrioid carcinomas account for 8-15% of all ovarian carcinomas.
- It is considered the second commonest malignant ovarian neoplasm.
- It is frequently associated with endometriosis
- The typical gross appearance of these tumours is similar to that of other epithelial lesions, with variable cystic and solid components. Occasionally, it may be completely solid.
- Bilateral involvement can be seen in 25-40% of cases
- Imaging findings are often non-specific and include a large, complex cystic mass with solid components. There may be associated endometrial thickening, evidence of endometriosis or a contralateral mass.
Recent Comments