Clinical:
- A 52 years old man
- Presented with acute hemoptysis
- Associated with dyspnoea and mild fever
- History of major operation (total knee replacement) about 2 weeks ago
- Clinically patient is tachypnoeic
- Lungs crepitation at both lower zones
- Chest radiograph showed no significant findings
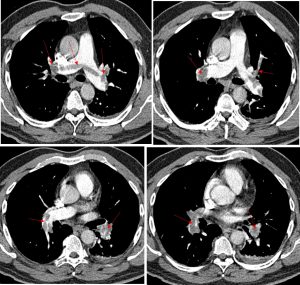
CT pulmonary angiogram findings:
- There is large thrombus seen that straddles the bifurcation of pulmonary trunk extending into the right and left pulmonary arteries (red arrows).
- The thrombus is seen extending into superior and inferior segmental pulmonary arteries in both sides (red arrows).
- Minimal contrast is seen within the peripheral of the arteries.
- There is associated expansion of the arteries suggestive of its acute nature.
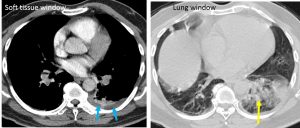
- Consolidation involving the left lower lobe (yellow arrow).
- Minimal left pleural effusion is seen (blue arrows).
Diagnosis: Acute saddle pulmonary embolism
Discussion:
- A pulmonary embolism is an obstruction of the pulmonary artery or 1 of its branches by a thrombus, tumor, air, or fat matter.
- A saddle pulmonary embolism is a thromboembolus that occurs at the bifurcation of the main pulmonary artery.
- It represents a potentially large, unstable clot associated with sudden hemodynamic collapse.
- Untreated pulmonary embolisms have a high mortality rate
Recent Comments