Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 73 years old man
- Presented with chronic cough
- Associated with loss of weight
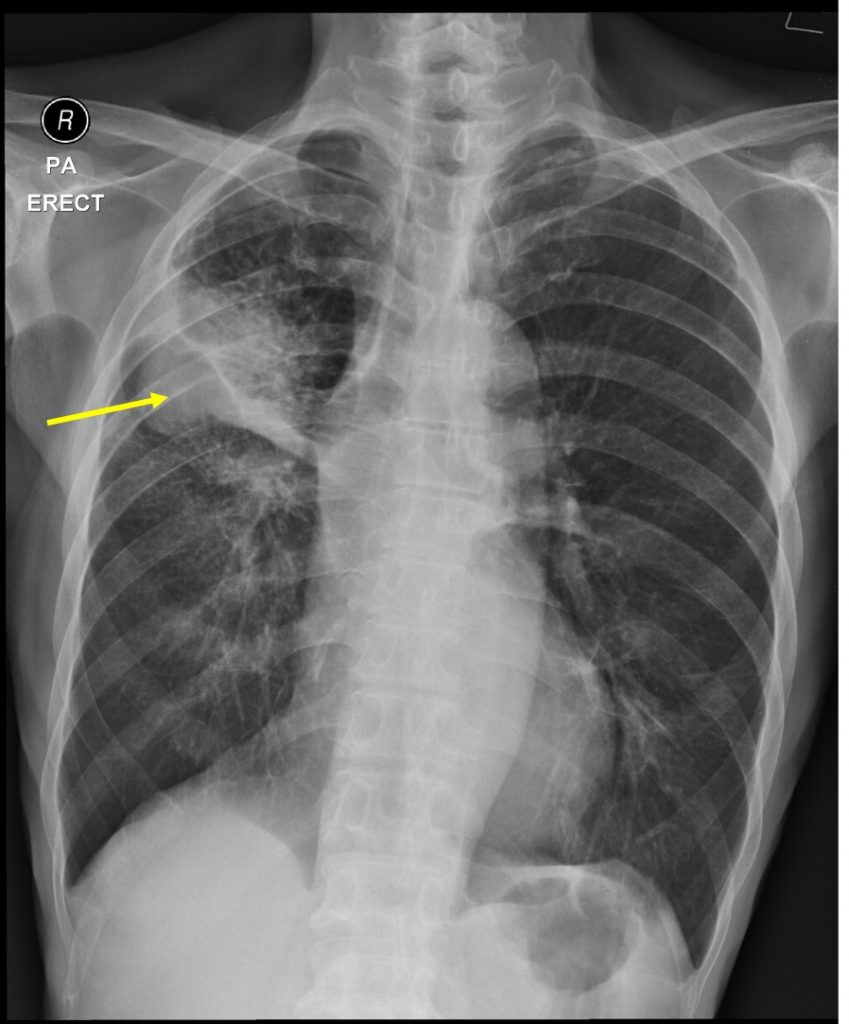
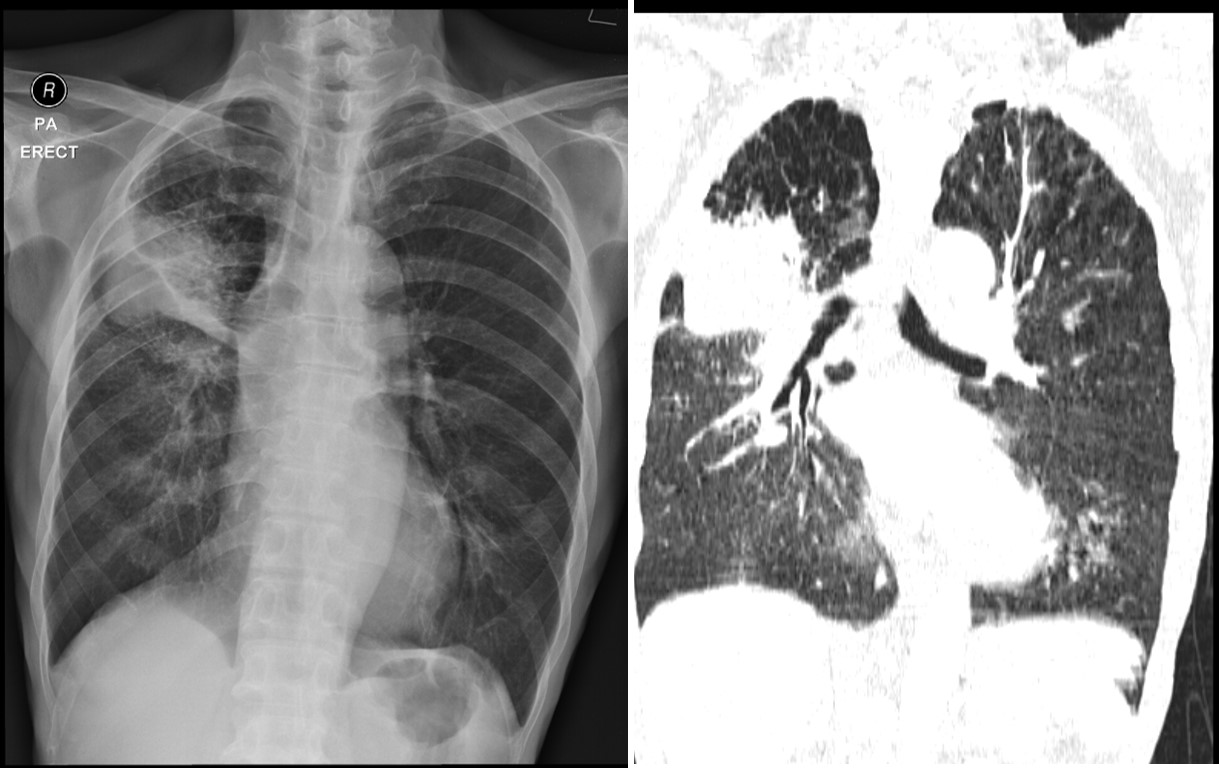
Radiographic findings:
- There is a lobulated lesion at left midzone (yellow arrow).
- It shows well defined inferior border and ill-defined superior border.
- No calcification or obvious cavitation within the lesion.
- There is extensive ground glass opacities surrounding the lesion both in upper and lower zones of lung.
- Thickening of the adjacent fissure is also seen.
- The lungs are hyperinflated. No mediastinal widening.
- No cardiomegaly. No pleural effusion or pneumothorax.
- No obvious bone lesion.
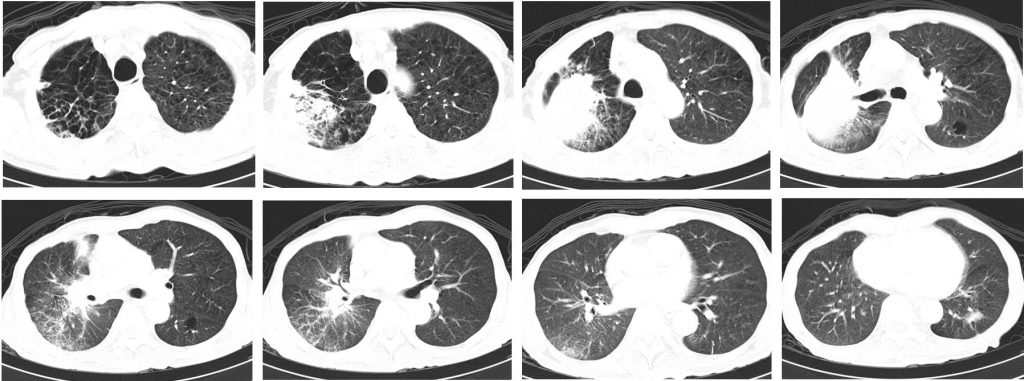
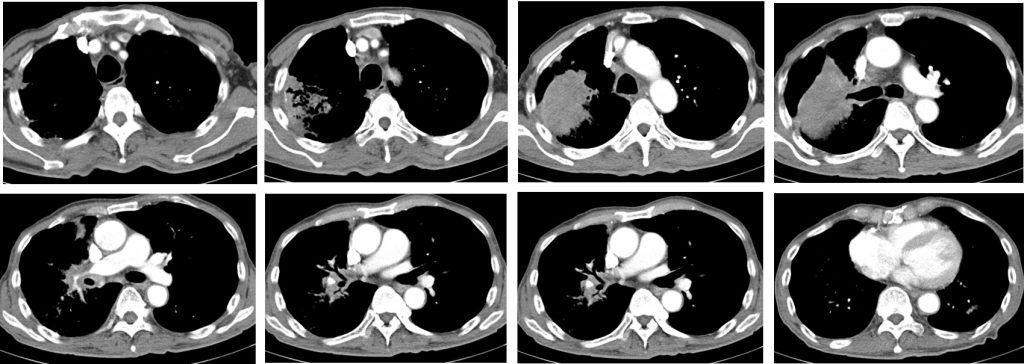
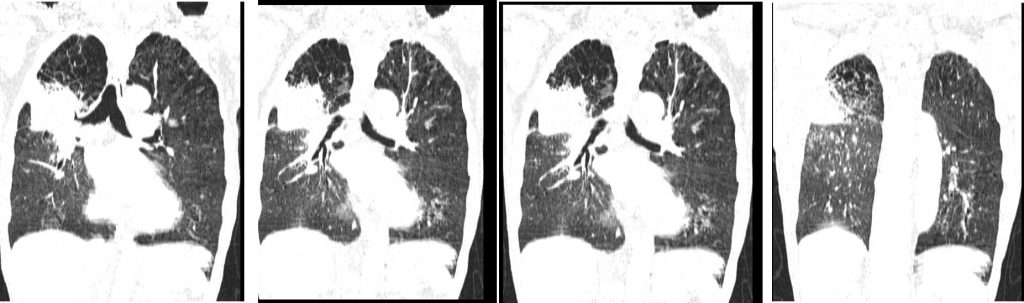
CT scan findings:
- There is collapsed consolidation of the posterior segment of right upper lobe.
- Presence of mass lesion is seen within this collapsed lung measuring about 58 mm.
- Surrounding ground glass opacities are seen. Patchy ground glass opacities are also seen involving the right lower lobe and to a lesser degree of the left lower lobe.
- There is extensive emphysematous change involving both upper lobes.
- Associated irregular septal thickenings are also seen at similar region.
- There are multiple enlarged mediastinal nodes.
- There is narrowing of distal right main pulmonary artery due to external compression by enlarged mediastinal nodes. However opacification of distal branches are still seen. Other major arteries are normal.
- There is no pleural effusion or pleural thickening. No pneumothorax.
- Heart is not enlarged. No pericardial effusion.
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: specimen labelled as mucosa of anterior segment lobe consist of multiple pieces of brownish tissue.
- Microscopy: section shows fragments of tumour tissue composed of malignant cells arranged in vague glandular pattern and clusters having moderate nuclear pleomorphism, hyperchromatic to vesicular nuclei, occasional nucleoli and moderate amount of cytoplasm. Intracytoplasmic vacuolation is also present. Desmoplastic stromal reaction is evident.
- Immunohistochemistry: The malignant cells are positive to CK7 and TTF1. Negative for CK20 and CDX2.
- Interpretation: non-small cell carcinoma favours adenocarcinoma
Diagnosis: Non-small cell lung carcinoma; adenocarcinoma
Discussion:
- Most lung cancers are non-small cell lung cancers, and most non-small lung cancers are adenocarcinomas.
- This form of lung cancer accounts for more than 30 percent of all lung cancers and about half of all non-small cell lung cancers.
- Lung adenocarcinoma usually occurs in the lung periphery, and in many cases, may be found in scars or areas of chronic inflammation
- The main risk factor is smoking tobacco.
- Other risk factors include a family history of lung cancer, or occupational exposure to other agents such as silica, asbestos, radon, heavy metals, and diesel fumes, though these are less prevalent.
- It is often impossible to distinguish between other histological lung cancer types based on imaging findings.
Recent Comments