Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 3 years old girl, no known medical illness
- Had a fall from staircase and brought to hospital with complaint of blood in urine after the fall
- Clinically no tenderness or bruise
- BP=92/54mmHg, PR=125 bpm and GCS=15/15
- UFEME: gross hematuria, presence of leukocytes and protein
- Renal function test normal, INR normal
- CT scan to rule out urinary sytem injury
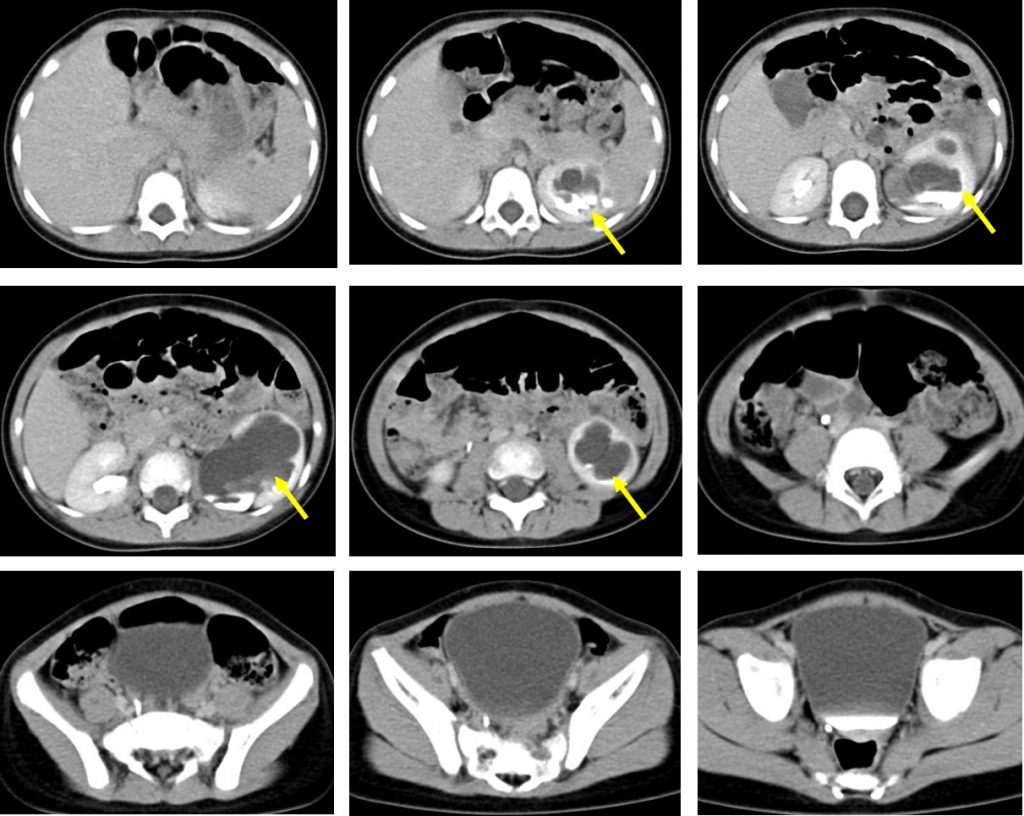
CT scan findings:
- Left kidney is enlarged with gross hydronephrosis (yellow arrows).
- There left renal pelvis is also dilated. However ureter is not dilated.
- Right renal is normal in size and no hydronephrosis seen.
- No evidence of injury. No perinephric collection.
- Urinary bladder is grossly normal.
Diagnosis: Congenital PUJ obstruction.
Progress of patient:
- She was admitted and treated for urinary tract infection.
- Referred to other hospital for further management.
- Operation done (Anderson Hynes pyeloroplasty). Intra-operative findings of left kidney slightly rotated with pelvis facing anteriorly. Renal pelvis was dilated and thick-walled. PUJ non-dependant and narrowed. Proximal ureter is also narrowed. Distal ureter was normal. Renal parenchymal was good.
- DTPA was done 5 months after operation that shows good function of both kidneys. No urinary flow obstruction seen. Differential function of left kidney was 52% and right kidney was 48%.
Discussion:
- Congenital PUJ is by far the most common cause of paediatric hydronephrosis.
- It is demonstrated as dilatation of pelvicalyceal system with abrupt end at pelviureteric junction. The ureter is usually not dilated and this differentiates it from vesicoureteric reflux.
- Many cases are asymptomatic and identified incidentally when the renal tract is imaged for other reasons. If symptomatic, symptoms include recurrent urinary tract infections, stone formation or a palpable flank mass.
- They are also at high risk of renal injury even by minor trauma.
- It is commonly unilateral and more common in males.
- There is a recognised predilection towards the left side.
- Associated renal anomalies include renal duplication, multicystic dysplastic kidneys, horse-shoe kidney and cross fused ectopia.
Recent Comments