Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 72 years old lady with background history of hyperlipidaemia and DM
- Semidependant and ambulating mostly using wheelchair
- Also had recurrent CVA
- She become forgetful since lass 2 years,
- Unable to control bowel motion
- Clinically she is intermittently delirious with paucity of speech, appears thin and undernourished, contracture at left upper and lower limbs with hyperreflexia.
- Lumbar puncture shows opening pressure of 12 cmH2O
- CSF analysis Glucose 4.8, Protein 0.5, Albumin 264, no organism stain, AFB negative and cyctology acellular smear with CSF RPR negative
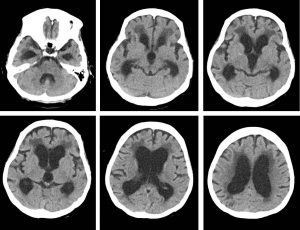

CT scan findings:
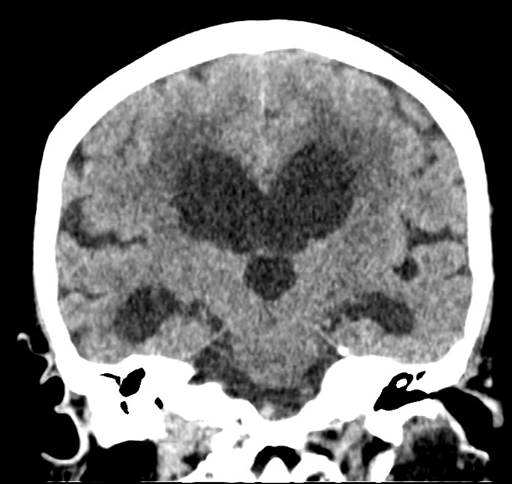
- There is generalised cerebral atrophy
- Dilatation of the lateral, third and fourth ventricles
- Dilatation of the temporal horn of lateral ventricles bilaterally
- Bilateral and symmetrical hypodensity at periventricular region
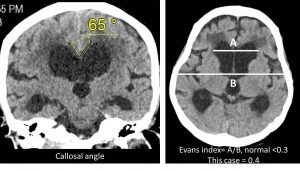
- Narrowing of the callosal angle
- Evans index measured 0.4
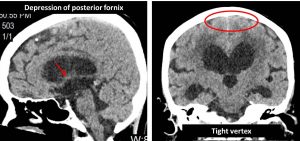
- Depression of the posterior fornix and shortening of mamillopontine distance
- Narrowing of CSF space at vertex (tight sign)
Diagnosis: Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Discussion:
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus is also called as malresorptive hydrocephalus
- It is a form of communicating hydrocephalus with normal or slightly elevated cerebrospinal fluid pressure
- Normal CSF pressure in adult is 7-16 mmH2O
- Majority are idiopathic
- The incidence is higher in elderly population
- The classical findings are urinary incontinence, deterioration in cognition (dementia), gait disturbances
- Features that favor hydrocephalus include
- Dilatation of temporal horns
- Lack of dilatation of parahippocampal fissure
- Increased frontal horn radius
- Acute ventricular angle
- Periventricular odema from transependymal flow
- Intraventricular flow void from CSF movement on MRI
- Widening of the third ventricular recesses; midsagittal plane
- Depression of posterior fornix; midsagittal plane
- Decreased mamillopontine distance;midsagittal plane, normal 7-9 mm
- Narrow callosal angle: normal 100-120 degrees, in NPH 50-80 degrees
- Cingulate sulcus sign- MRI feature
Recent Comments