Clinical:
- A 37 years old lady
- Presented with abdominal discomfort
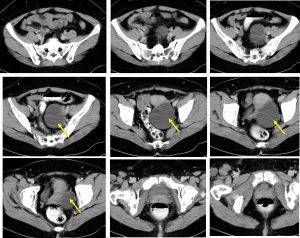
CT scan findings:
- There is a well-defined cystic lesion with thin wall at left adnexal region measuring 7×8 cm. There are thin septa within the lesion.
- No soft tissue component, no calcification
- No fat component within the lesion.
- The uterus appears normal. No abnormal lymph node is seen.
Intraoperative findings:
- Laparoscopic cystectomy done
- Uterus is normal in size.
- Left ovary embedded at POD, mobilised easily, appears benign, smooth surface with no abnormal vessels seen.
- Left fallopian tube is normal looking.
- Right ovary is normal.
- Bowel, liver surfaces are normal.
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: specimen labelled as left cyst wall consists of a piece of tissue measuring 50x1x6 mm. The cyst wall thickness is less than 1 mm.
- Microscopy: Section shows multiple pieces of fibrous cyst wall mainly devoid of epithelial lining and a few areas lined by single layer of mucinous type epithelium with basally located nuclei. No stratification of nuclei or cytological atypia is identified. No evidence of malignancy.
- Interpretation: Mucinous cystadenoma
Diagnosis: Left mucinous cystadenoma
Discussion:
- Mucinous tumors represent a spectrum of benign, border to malignant histologic variants.
- Among benign ovarian neoplasms, mucinous cystadenomas account for approximately 10–15 % of all cases.
- Mucinous cystadenomas usually occur as a large, multiloculated cystic mass with mucus-containing fluid.
- These tumors occur most commonly in women in their twenties to forties.
- The mean size at presentation is 18 cm, and mucinous tumors can become extremely large and fill the entire abdominopelvic cavity, occasionally presenting with ureteral obstruction or abdominal compartment syndrome.
- Most mucinous tumors are unilateral, especially when primarily ovarian in origin.
- A mucinous tumor grossly limited to the ovary will not have occult lymph node metastasis.
Recent Comments