Clinical:
- A 28 years old lady
- Presented with dysmenorrhoea
- Associated with menorrhagia
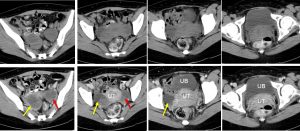
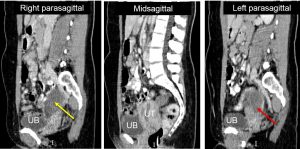
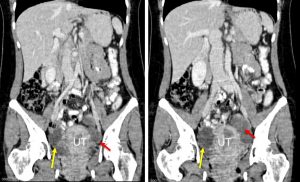
CT scan findings:
- There are two well-defined cystic lesions in the pelvic region. These lesion lying to the right (yellow arrows) and left (red arrows) of the uterus measuring 4x6x7 cm and 4x5x6 cm respectively.
- There are septations within the lesions.
- No calcification or fat component within.
- Post contrast images show contrast enhancement of wall and septa.
- The uterus appears bulky with fluid within the uterine cavity.
Intraoperative findings:
- Right endometriotic cyst measuring 5×5 cm, adhered to right fallopian tube and POD. Ruptured during manipulation, chocolate material drained.
- Left endometriotic cyst multiloculated 4×6 cm, adhere to left fallopian tube and POD. Adhered to rectum. Left tube blocked.
- Omentum, small bowel are normal.
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: Right and left cyst walls consist of multiple fragments of cyst wall.
- Microscopy: Section shows dense fibrocollagenous cyst wall devoid of epithelial lining. There is foci of hemorrhage with numerous hemosiderin laden macrophages seen within the inner surface. No evidence of malignancy.
- Interpretation: Endometriotic cysts
Diagnosis: Bilateral endometriotic cysts
Discussion:
- Endometriotic cysts are also known as endometriomas are a localised form of endometriosis.
- It is usually seen within the ovary. Other locations include cul-de-sac, posterior broad ligament, uterosacral ligament, uterus and colon.
- Endometriomas contains dark degenerated blood products following repeated cyclical haemorrhage. The cysts may be up to 20 cm in size although they are usually smaller (2-5 cm).
Recent Comments