Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 41 years old man
- Active smoker, underlying DM and HPT
- Presented with left cheek swelling for 3 years
- Gradually increase in size, no hypersalivation, no pain, no fever, no facial discomfort or asymmetry
- No ear pain or hearing loss
- Clinical examination shows left parotid swelling about 4x3x3 cm, non tender, no redness, soft to firm in consistency.
- Intra-oral examination shows no pus discharge, stensen and wharton duct examinations are normal.
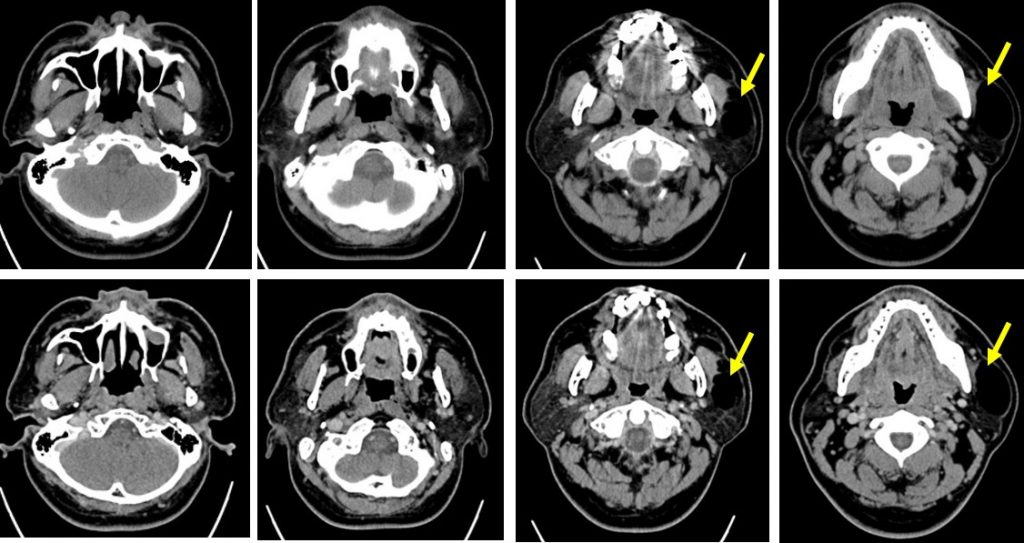
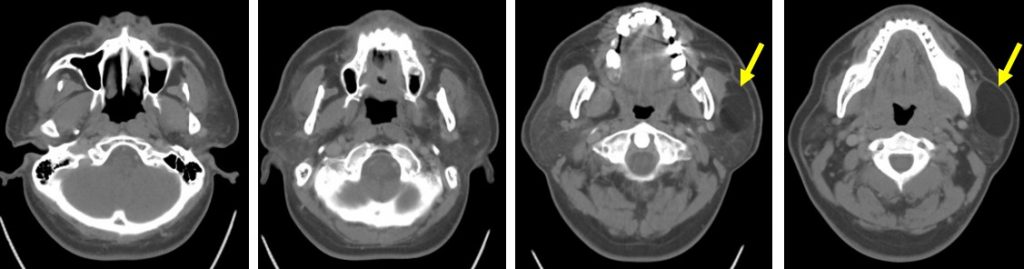
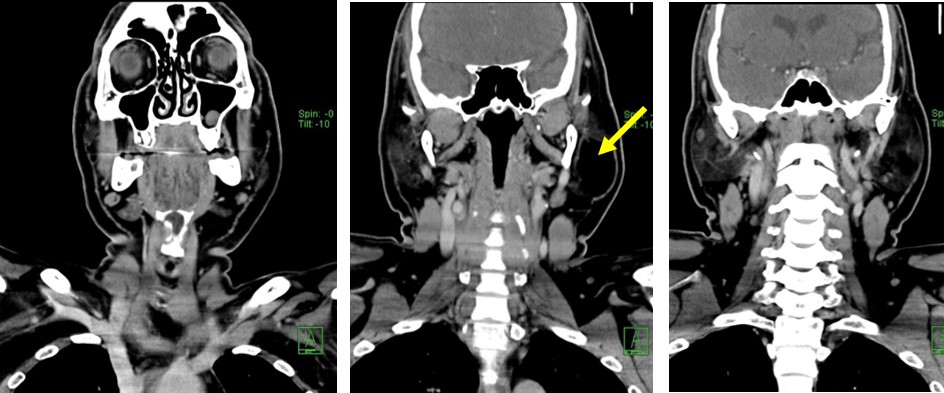
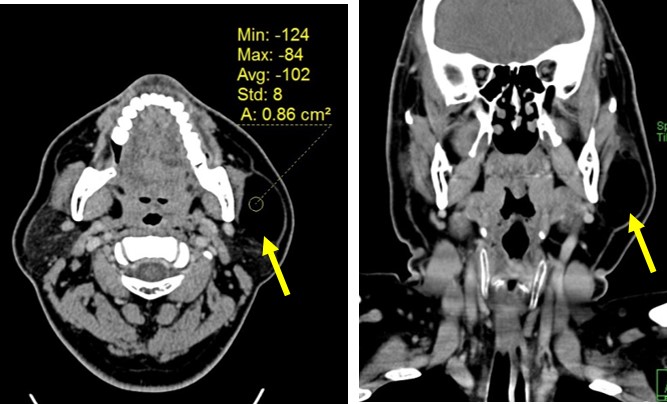
CT scan findings:
- A well-defined hypodense lesion is seen within the left parotid gland (yellow arrows)
- The density is similar to fat density
- It do not enhance on post contrast images.
- No calcification or septae within the lesion.
- The fat surrounding the left parotid is not streaky.
- No cervical lymphadenopathy. No bone changes.
FNAC report:
- Smears show small tissue fragments composed on univacuolated adipocystes displaying fairly uniform elongated nuclei, regular chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli, and smooth nuclear membrane. Delicate capillaries are seen traversing the tissue fragments. Occasional foamy histiocytes are noted. No atypical cells seen.
- Interpretation: consistent with lipomatous lesion.
Diagnosis: Parotid lipoma.
Discussion:
- Benign lipomatous lesions involving soft tissues are classified into lipoma, lipomatosis, lipomatosis of nerve, lipoblastoma or lipoblastomatosis, angiolipoma, myolipoma of soft tissue, chondroid lipoma, spindle cell lipoma and pleomorphic lipoma.
- Soft tissue lipoma accounts for about 50% of all soft tissue tumours.
- Parotid lipoma are rare benign non-epithelial salivary gland neoplasm. It accounts about 0.6 -4.4% of benign parotid tumour
- Imaging characteristics are similar of fat-containing lesion elsewhere
- Mean age at presentation: more than 50 years
- Predominant predisposition for male
- It may be related with chronic alcoholism, malnutrition and medication
- On ultrasound parotid lipomas are seen as well-defined lesion with parallel linear ehogenic lines, usually hyperechoic to adjacent muscle but sometimes can also be isoechoic or hypoechoic.
- CT scan shows homogenous lesion with occasional septation with density from -50 to -150HU. There is no contrast enhancement.
- MRI shows the lesion to be hyperintense on T1 and hypointense on T2 with complete suppression on fat suppressed T1WI.
Recent Comments