Clinical:
- A 19 years old boy
- No known medical problem
- Presented with generalized tonic clonic seizure
- No neurological deficit
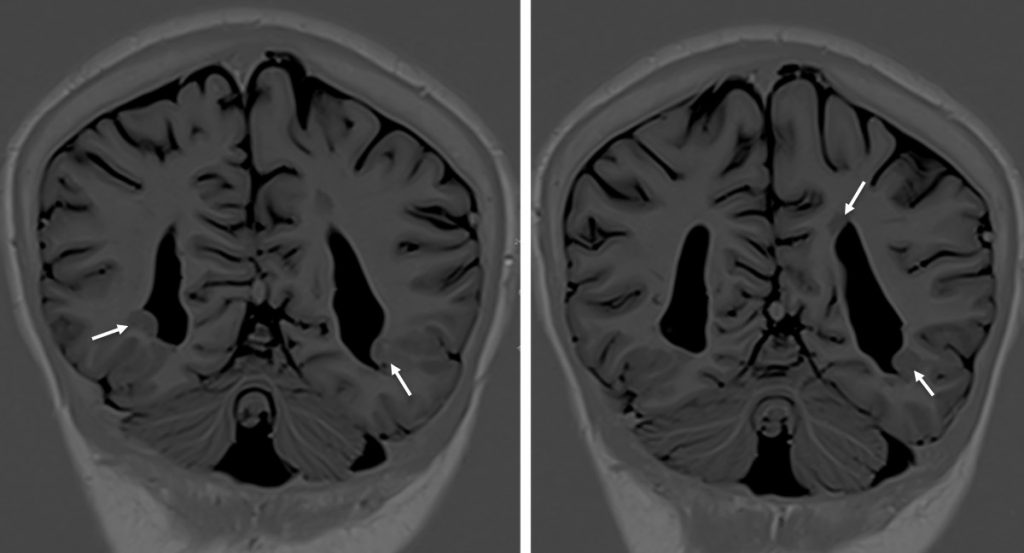
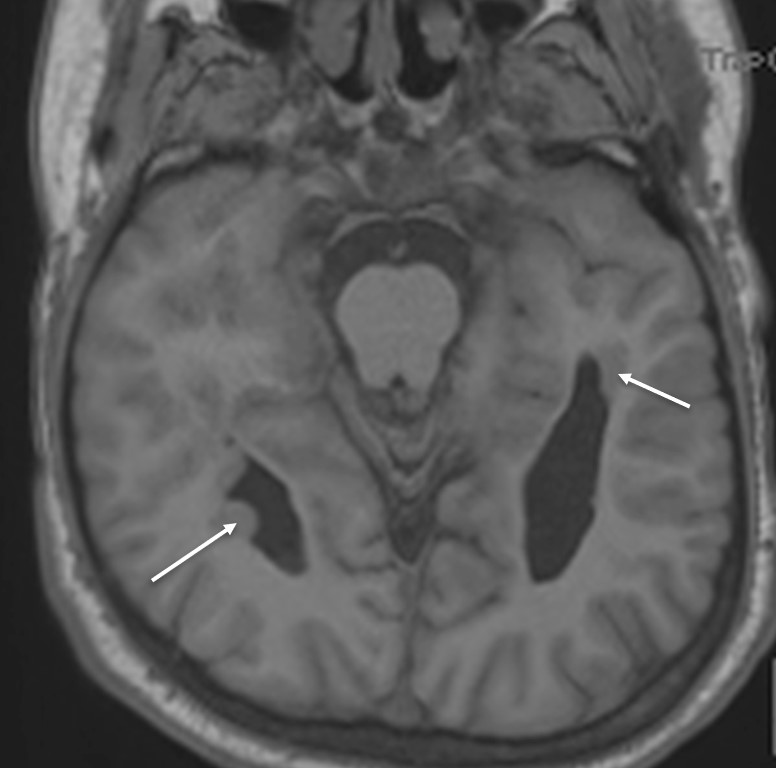
MRI findings:
- Bilateral hippocampus are symmetrical with normal signal intensity (images not shown).
- The amygdalar grey matter shows normal signal intensity. No evidence of significant alteration in size or focal asymmetry.
- There are multiple subependymal grey heterotopia seen along occipital horns of bilateral lateral ventricle (white arrows). They follow grey matter signal on T1 and T2 sequences. They do not show enhancement in post contrast sequences.
Diagnosis: Subependymal grey matter heterotopia
Discussion:
- Heterotopias represents rest of neurons along migration pathways (anywhere from ventricular walls to subcortical regions)
- Most common presentation: intractable seizures
- Most heterotopias are of the nodular types which is seen as foci of gray matter along ependymal surface of ventricles (differential diagnosis: tuberous sclerosis)
- Multiple heterotopias may be considered diffuse disease and surgery is not indicated
- Heterotopias may also be subcortical and mass-like, may involve the entire thickness of white matter and be transmantle
- Hetrotopias do not enhance
Recent Comments