Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 60 years old lady
- Presented with right hearing loss
- Also noted to have imbalance on and off
- Examination showed right sensorineural hearing loss
- Positive cerebellar signs
MRI brain and IAM done:
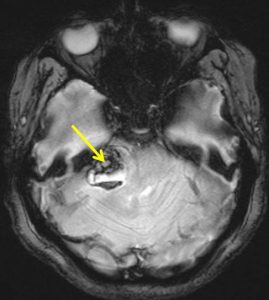
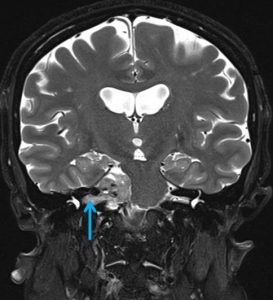
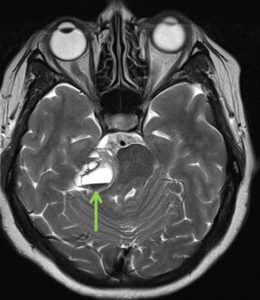
MRI findings:
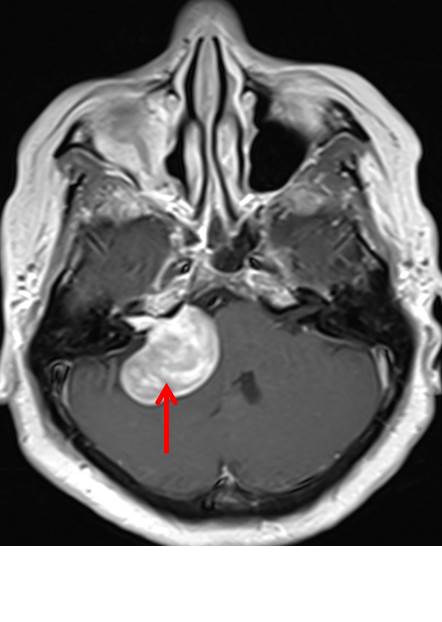
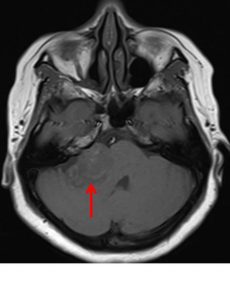
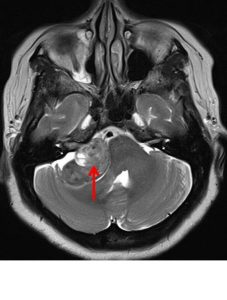
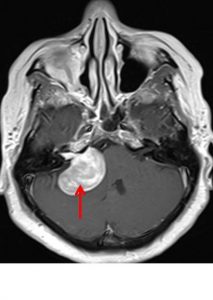
- MRI shows mass at right cerebellopontine angle (red arrow) which is hypointense on T1, hyperintense on T2 and marked enhancement post contrast.
- Blooming artifact noted on GRE sequence (yellow arrow).
- The lesion extend and expand the right internal auditory meatues (blue arrow).
- Cystic areas with layering also noted in the mass lesion (green arrow).
- There is compression effect causing distortion of right pons.
Histopathology result:
- Macroscopy: Brain tumour consists of multiple pieces of yellowish and blackish tissue measuring 31 mm in aggregate diameter.
- Microscopy: section shows fragments of lesional tissue displaying hypercellular and hypocellular areas. The hypercellular area is composed of proliferation of spindle cells. In areas, spindle cells exhibit some nuclear atypia. However there is no mitosis seen. The hypocellular area is composed of sheets of foamy macrophages. Hyalinization of the blood vessel is seen. Immunohistochemical stain reveals the spindle cells are diffusely positive for S100 antibody.
- Interpretation: Brain schwannoma.
Final Diagnosis: Vestibular schwannoma
Discussion:
- Vestibular schwannoma is also known as acoustic neuroma.
- most common neoplasm of internal auditory canal
- Usual presentation include long history or slowly progressive unilateral sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus, unsteadiness, vertigo, ataxia and dizziness
- arises from within IAM (80%) and CPA (5%)
- seen as mass centered on long axis of IAM forming acute angles with dural surfaces of petrous bone
- IAM enlargement/extension/erosion (70-90%).
- shift or asymmetry of 4th ventricle with hydrocephalus
- cystic changes with hemorrhages are common
- intense enhancement post contrast.
Progress of patient:
- Suboccipital craniotomy and tumour excision done
- Complicated by CSF otorrhoea
- Surgical exploration and dura repair done