Clinical:
- A 71 years old lady
- Known case of ESRF on CAPD, T2DM, HPT
- Sudden onset of reduce consciousness during PD, right body weakness and slurring of speech.
- Able to recognise daughter. No fits, no neck stiffness.
- GCS: 11/15. Muscle power left upper and lower limb 3/5
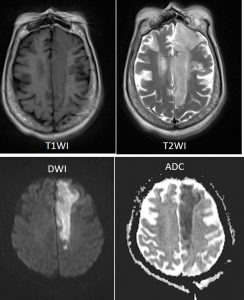
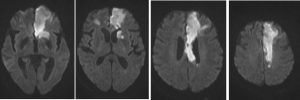
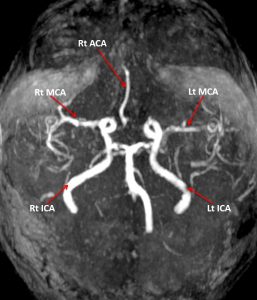
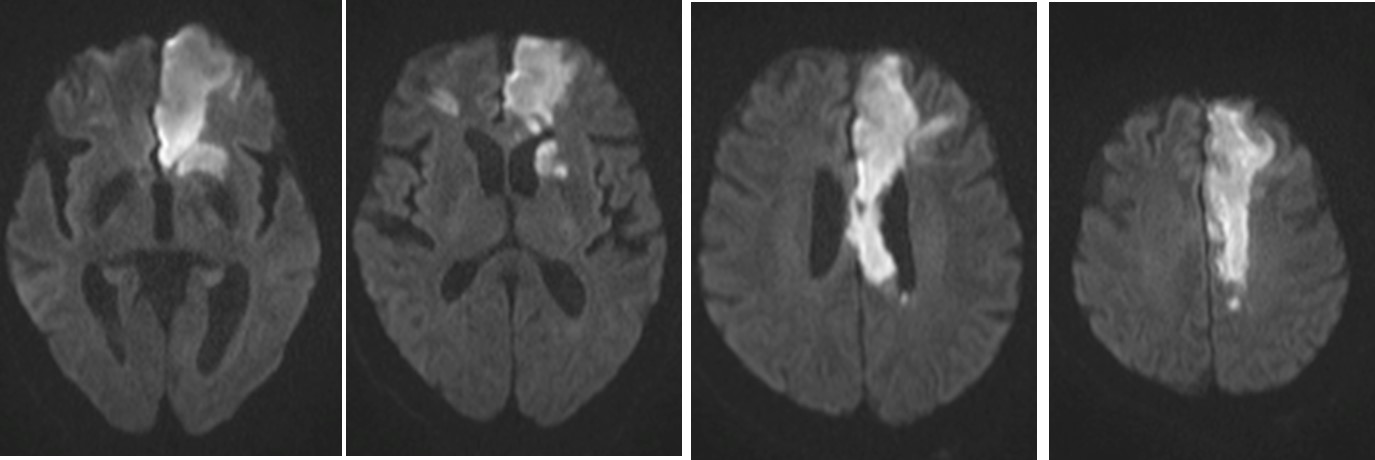
MRI findings:
- There is abnormal signal intensity in the left parasagittal, anterior limb of left internal capsule and head of left caudate nucleus regions. It is hypointense in T1, hyperintense on T2 and FLAIR, restrictive diffusion in DWI and low signal intensity on ADC maps which represent acute infarct of left ACA territory.
- MRA shows no visualisation of the whole left ACA. There are short segment and mild stenosis at the M1 of bilateral MCA.
Diagnosis: Acute infarction at left ACA territory
Discussion (Anterior cerebral artery infarction):
- ACA infarction is uncommon affecting about 2% of all ischaemic stroke
- The ACA supplies the medial part of the frontal and the parietal lobe and the anterior portion of the corpus callosum, inferior part of caudate head, basal ganglia and anterior limb of internal capsule.
- Signs and symptoms of ACA infarction include: contralateral hemiparesis or hemiplegia, contralateral sensory deficit, apraxia (due to supplementary branches supplying the motor area and corpus callosum), disconnection syndrome (due to callosal branches), anosmia (due to branches to olfactory bulb and tract) and urinary incontinence