Clinical:
- A 46 years old lady
- Underlying hyperparathyroidism
- Complaint of left loin pain
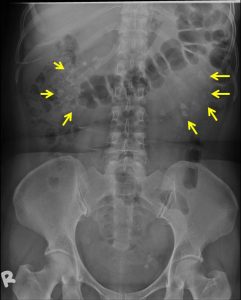
Radiographic findings:
- clustered opacities/calcification overlying both renal region
- bilateral with slight asymmetry
- some are fine, mottled while others are coarse
- correspond to location and shape of renal pyramids
- a small rounded opacity also seen at left hemipelvis region
-
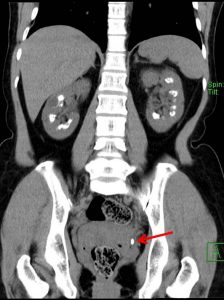
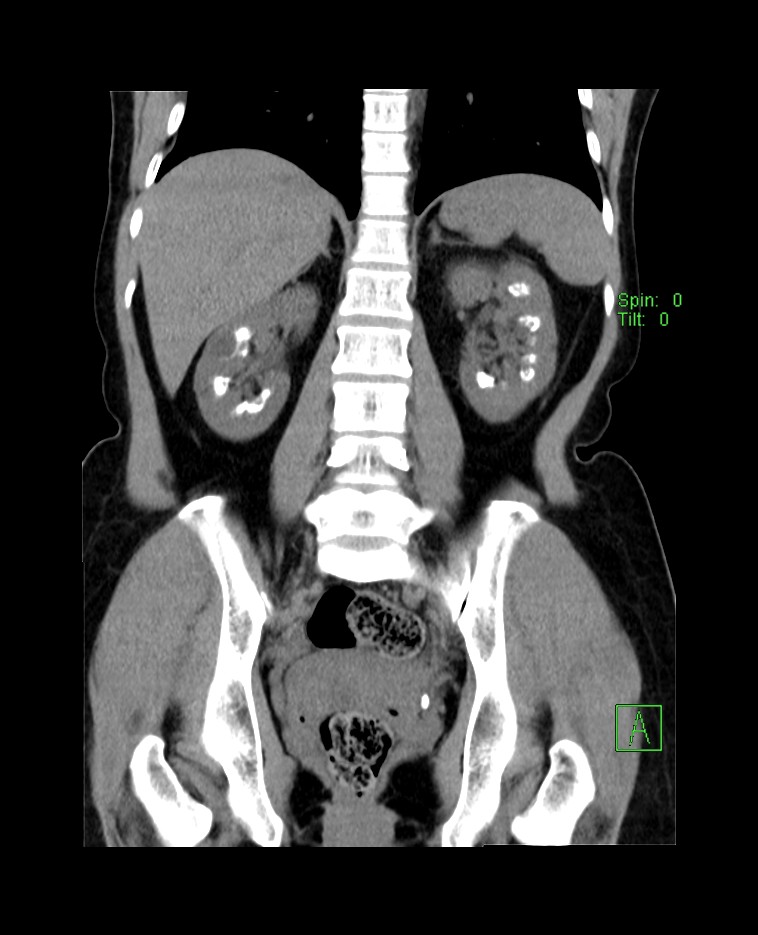
Coronal reformatted CT KUB non-contrast soft tissue window 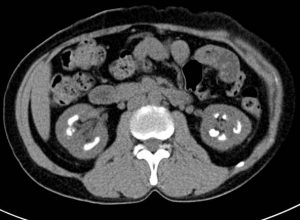
Axial CT scan non-contrast soft tissue windowCT findings: CT findings:
- There are multiple clustered calcifications seen within renal medulla bilaterally.
- An elongated hyperdense focus is seen at the left vesicoureteric junction (VUJ) measuring 0.9 cm suggestive of calculus (red arrow).
Diagnosis: Bilateral medulllary nephrocalcinosis with left ureteric calculus
Discussion:
- Medullary nephrocalcinosis refers to the deposition of calcium salts in the medulla of the kidney.
- It is caused by multiple different conditions including hyperparathyroidism as seen in this patient