Clinical:
- A 30 years old man
- Involved in motor vehicle accident
- Presented with headache and persistent vomiting
- GCS on arrival in Emergency Department is 14/15
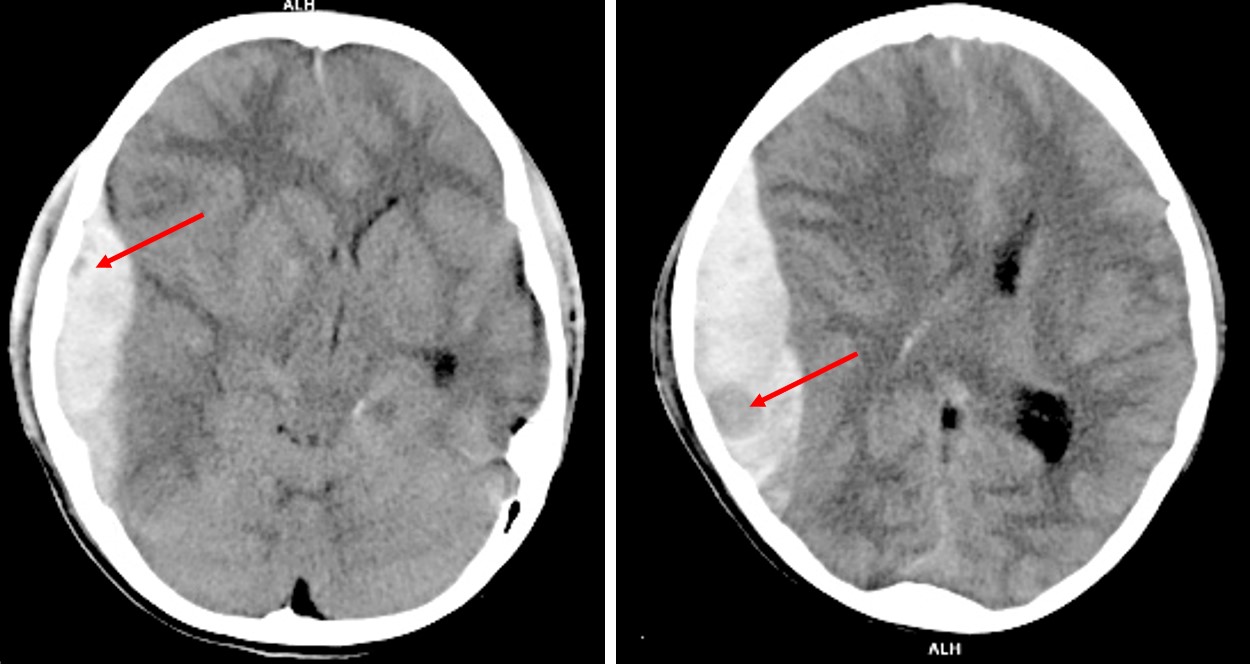
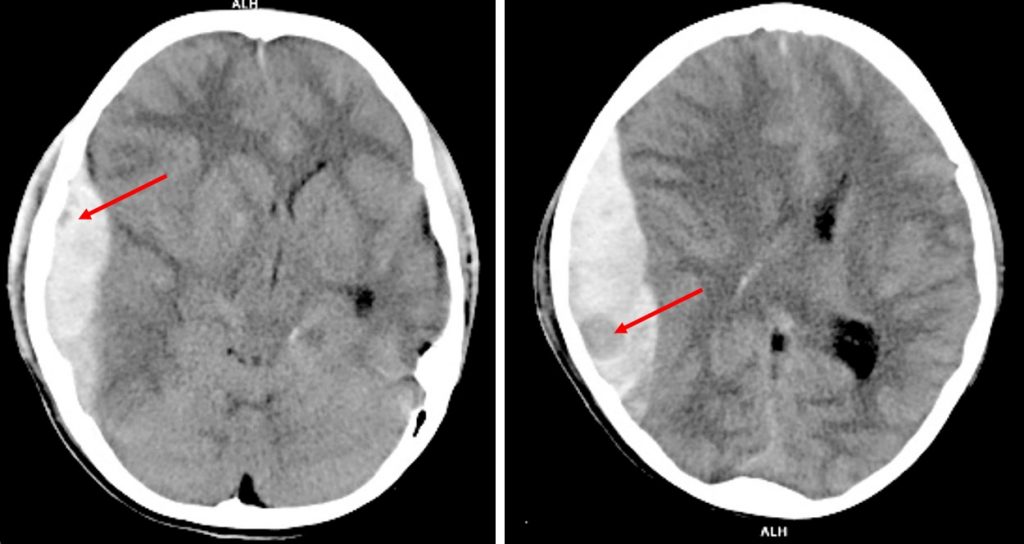 Non-contrast CT brain axial plane in soft tissue window
Non-contrast CT brain axial plane in soft tissue windowCT scan findings:
- There is subdural hemorrhage at right fronto-temporo-parietal region
- Areas of hypodensity seen (red arrows) within the hemorrhage representing swirl sign
- There is midline shift to the left side
- Compression of ipsilateral lateral ventricle
Radiological diagnosis: Swirl sign in acute subdural hemorrhage
Discussion:
- Swirl sign is seen in non-contrast CT brain in acute extradural or subdural hemorrhage.
- It represents unclotted blood which is hypodense compared to surrounding clotted blood which is hyperdense (50-70HU).
- It has been verified as active bleeding site at the time of surgery
- Identification of patients with a potential risk for hematoma expansion in acute intracranial hemorrhage is crucial for planning of the treatment and prediction of the functional outcome.
- Swirl sign is an indicator of possible hematoma expansion and associated with higher mortality compared to patient without this sign.