Clinical:
- A 13 years old boy foreigner
- Complains of back pain for 2/12.
- Associated chronic cough with greenish sputum, LOA, LOW.
- He also had left elbow pain.
- Clinically there is reduced sensation T8 downward.
- ESR 109 mm/hr. CSF normal
Radiographic findings:
- Multi level lytic lesions with reduction in vertebral body heights
- Mainly involved the thoracic spine
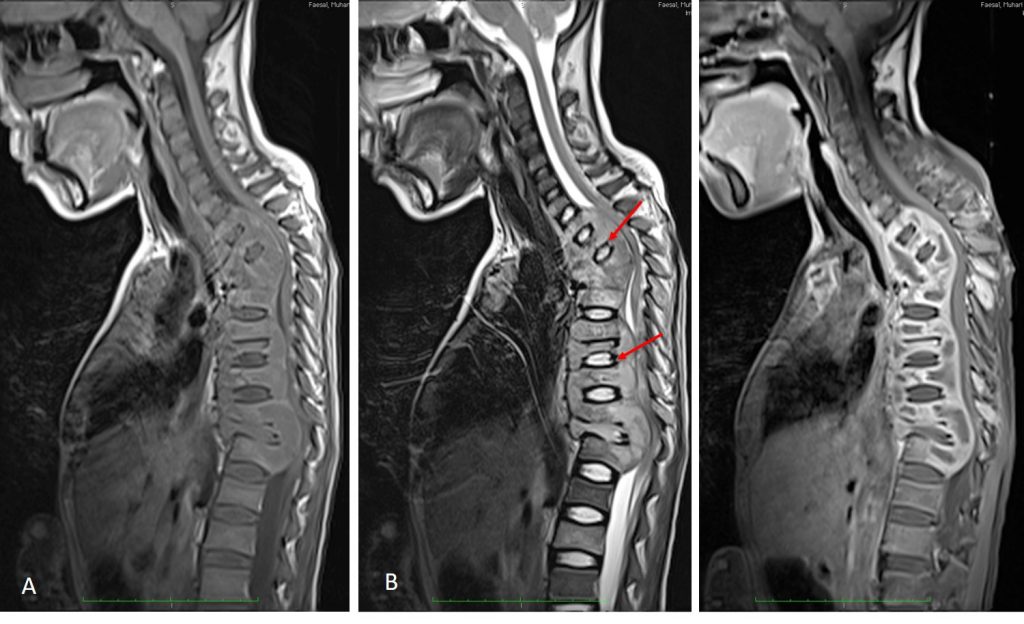
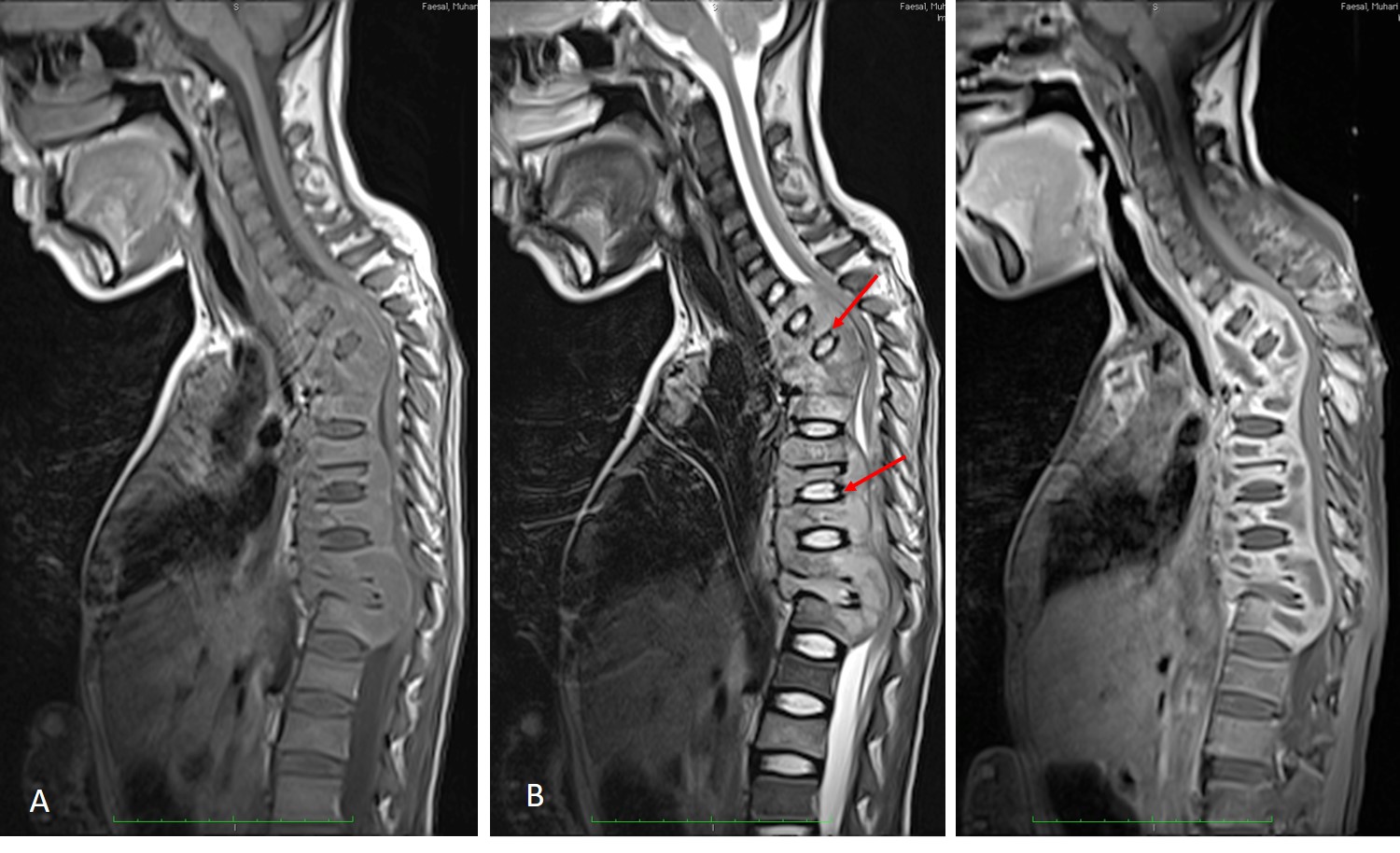
MRI findings:
- There is gibbus formation of the upper thoracic spine with the apex at T2/T3 level.
- There is extensive multilevel abnormal marrow signal in the vertebral body involving C7 till T12, L2, L3 and L5 till S5 level. It exhibit hypointense on T1, hyperintense on T2 and STIR, and heterogenously enhancing post gadolinium administration.
- Associated paravertebral soft tissue involvement.
- It was associated with extensive lower cervical thoracic and sacral paraspinal subligamentous collection/inflammatory process.
- The paravertebral colection is hypointense on T1 and shows rim enhancement post contrast in keeping with abscess collection.
- Presence of the soft tissue component causes significant spinal stenosis and cord compression in the upper and lower thoracic region. Most of the neural foramina is occupied by the hyperintense inflammatory tissue, likely compromizing the exiting nerves. The posterior elements are also shows abnormal signal intensity and enhancement suggestive of involvement.
- Few level of intervertebral discs shows abnormal signal intensity, mainly seen at upper thoracic, T8/T9 and T11/T12 level. The rest of the intervertebral disc relatively spared.
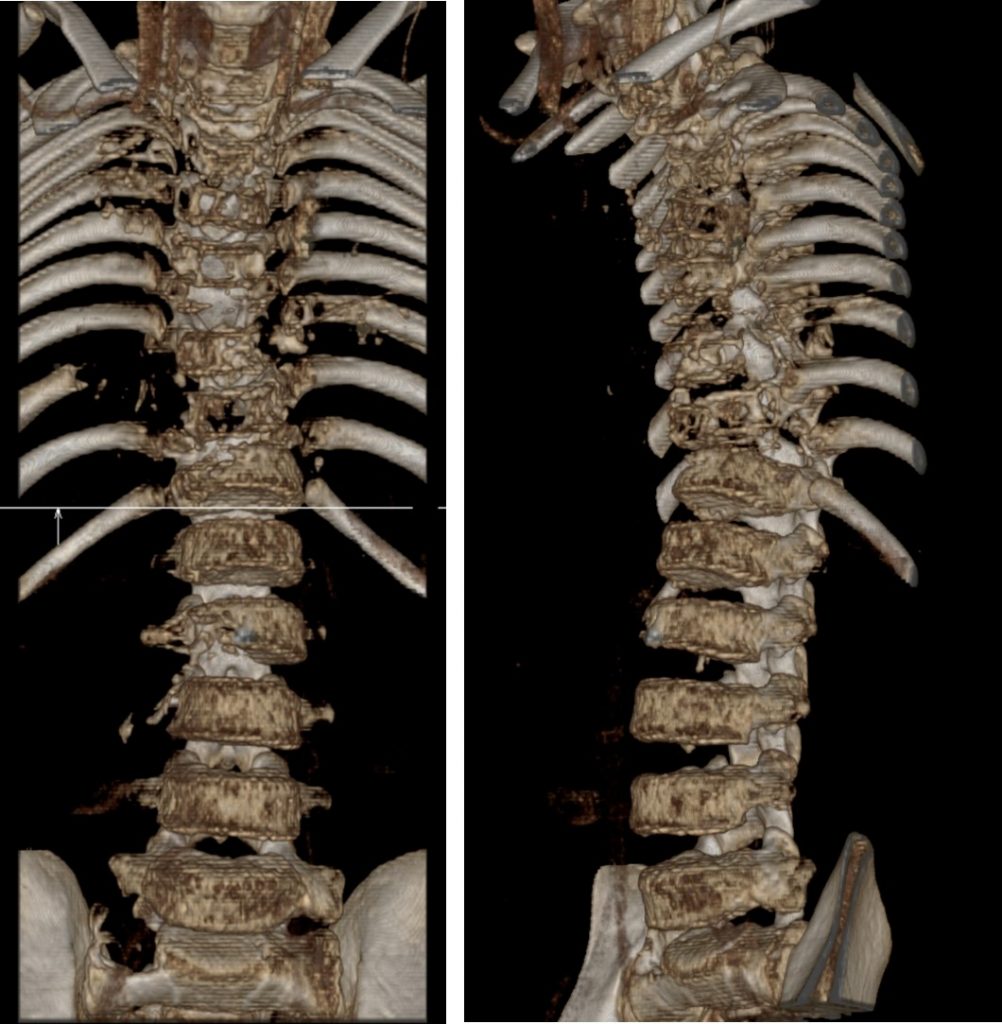
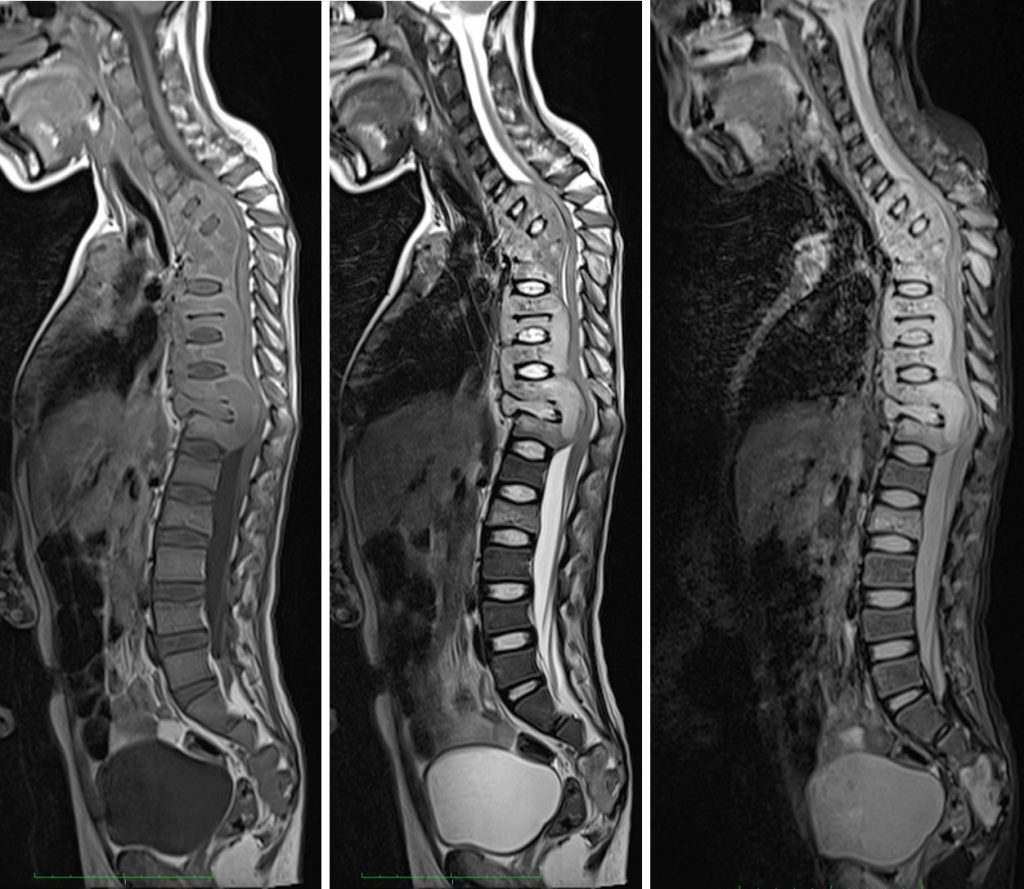
CT scan findings:
- There is gibbus deformity of the upper thoracic spine with the apex at T2/T3 level.
- Multilevel reduced vertebral body height with expensile lytic and some of this lesion also demonstrate bone destruction. The lesions involving the vertebral bodies of thoracic vertebra till L3 vertebra. Skip lesion is also seen in the right sacrum. The posterior elements also show similar changes.There is also lytic lesions in the right L3 pedicle.
- Associated paravertebral, prevertebra and postvertebra soft tissue involvement/collection.
- Some of the ribs are also involve with periosteal reaction.
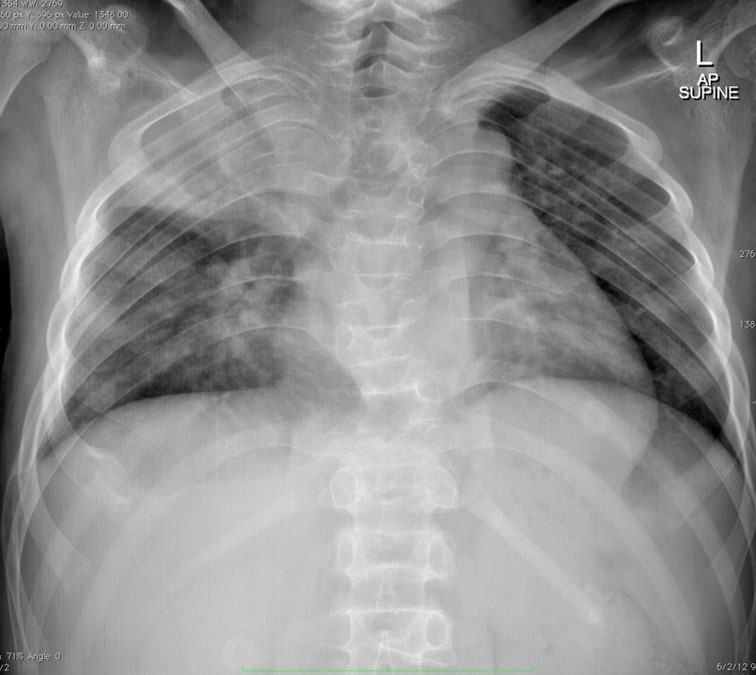
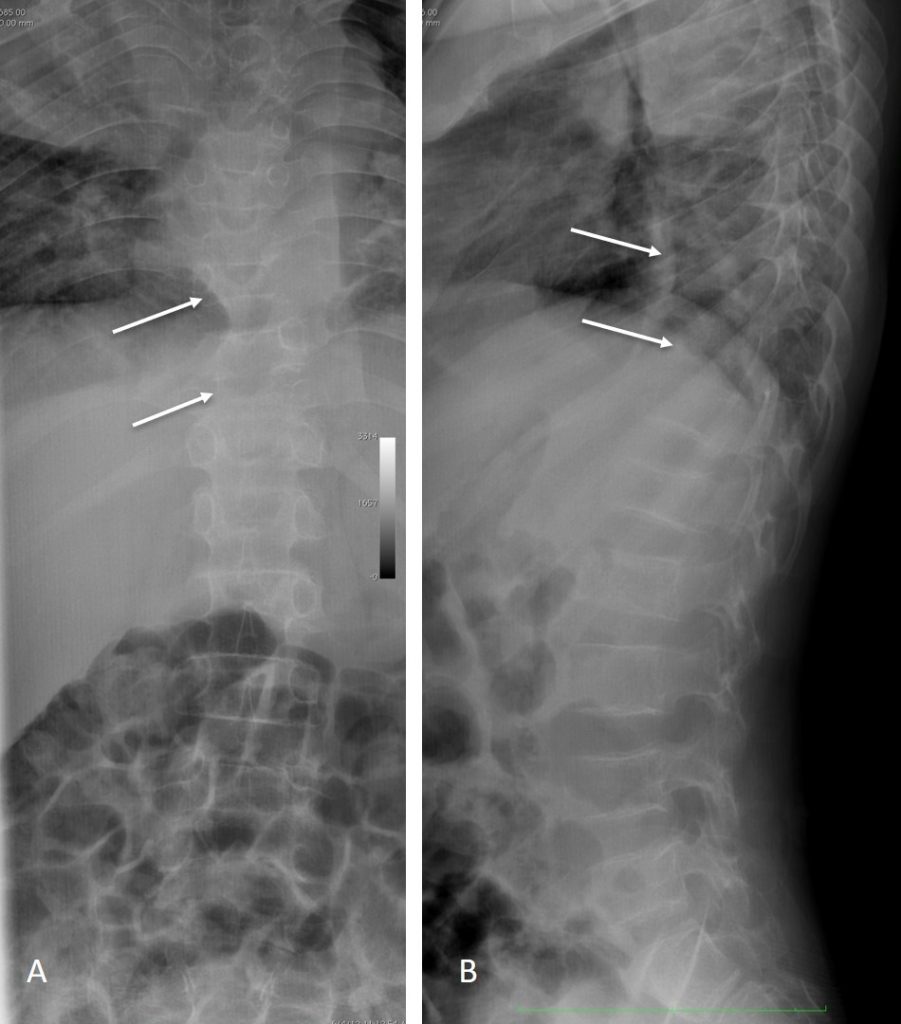
Chest radiograph:
- Collapsed consolidation seen at right upper lobe
- Prominent right hilar region
- No pleural effusion or pneumothorax
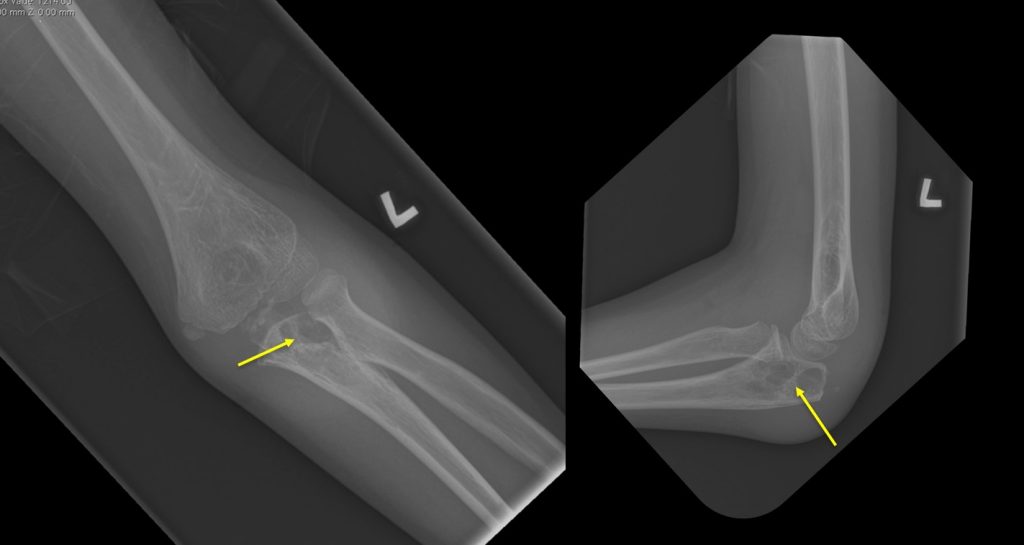
Left elbow radiograph:
- Lytic lesions at the proximal ulna
- No periosteal reaction
- No obvious soft tissue lesion
HPE findings:
- Presence of multiple loose agregates of epithelioid histiocytic granulomatous with occasional multinucleated giant cells.
- Small amount of necrosis.
- No langerhans giant cell types are seen.
- Interpretation: Chronic granulomatous inflammation
Final diagnosis: Disseminated Tuberculosis (spine, pulmonary and bone involvement)
Discussion:
- Disseminated tuberculosis (TB) is defined as the presence of two or more noncontiguous sites resulting from hematogenous dissemination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- It occurs as a result of progressive primary infection or reactivation of a latent focus with subsequent spread.
- Disseminated TB is considered an important cause of morbidity and mortality in developing countries, especially in children under the age of 15 years.
- Disseminated TB may involve many organs such as the lung, liver, spleen, bone marrow, kidney, adrenals, eyes, and thyroid.