Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 46 years old man
- Initially presented with jaundice, ERCP and stenting done in another hospital
- Presented with abdominal pain 2 days after being discharged following the above-said procedure
Radiographic findings:
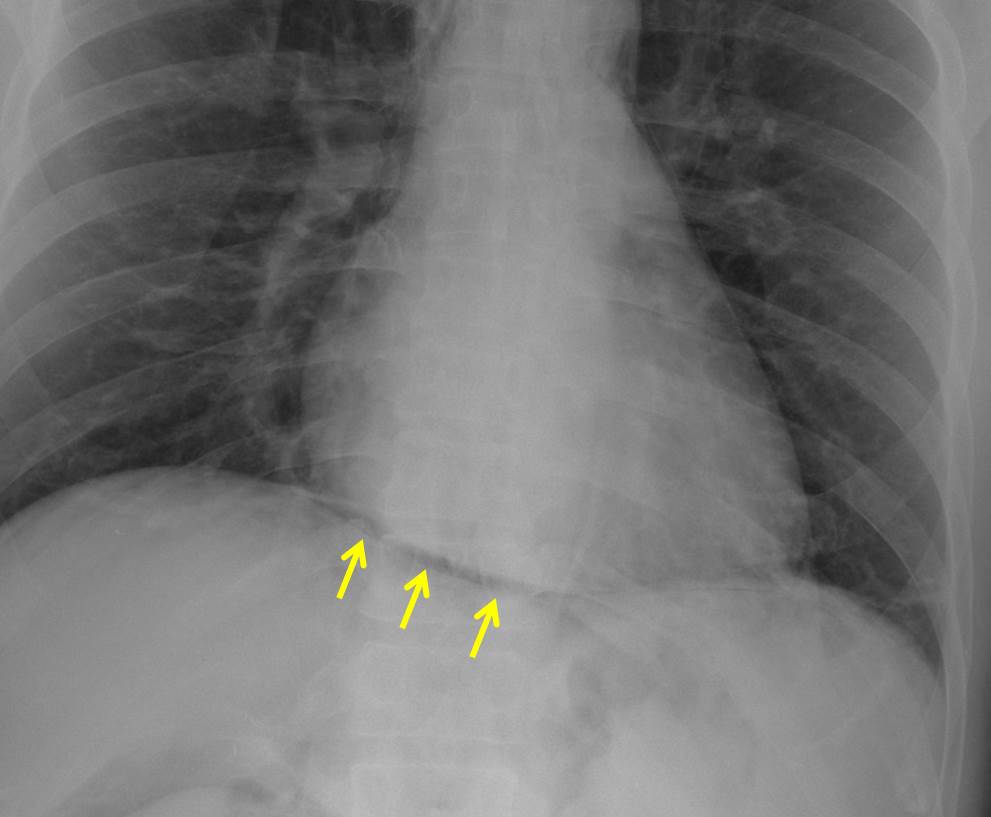
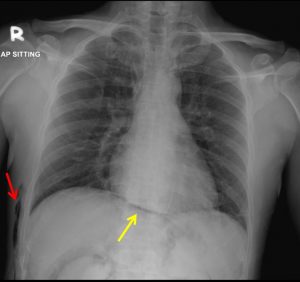
- There is a lucent curvilinear line (yellow arrow) outlining right and left hemidiaphragm in continuity without its normal obliteration at midline region
- No obvious free air at subdiaphragmatic region
- No lucent line outlining the heart or mediastinum
- No active lung lesion. No pneumothorax or pleural effusion.
- Air pockets seen at right lateral chest wall (red arrow)
Radiographic diagnosis: Continuous diaphragm sign
Discussion:
- Continuous diaphragm sign is a radiographic sign seen on chest radiograph
- It is described as continuous visualization of the diaphragm across the midline which is normally not seen due to presence of free ga
- If the lucency is above the diaphragm then the free gas is within the mediastinum (pneumomediastinum) or pericardium (pneumopericardium).
- If the lucency is seen below the diaphragm, the free gas is within the peritoneum (pneumoperitoneum) as seen in this case.
Progress of patient:
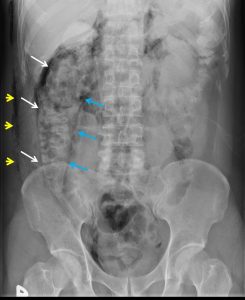
- Abdominal radiograph shows pneumoretroperitoneum (image shown below).
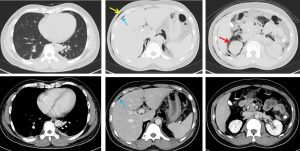
- CT scan abdomen performed confirmed presence of pneumoperitoneum, pneumoretroperitoneum and subcutaneous emphysema (selected images below).
- No pneumothorax or pneumomediastinum seen.
- Extensive subcutaneous emphysema with pneumoretroperitoneum and pneumoperitoneum are known complications post ERCP especially if sphincterotomy is performed.
- Patient was managed conservatively and recovered well.
- A repeat ERCP done shows oedematous sphincterotomy scar which is well healed
- Stent was removed.
- Planned for laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
References/further reading:
1) https://radiopaedia.org/articles/continuous-diaphragm-sign
2) Pneumomediastinum revisited;Zylac CM, RadioGraphics 2000; 20:1043–1057.