Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 57 years old lady
- Previously diagnosed Wagener granulomatosis (biopsy-proven) with lung involvement
- Also had renal tubular acidosis and corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis
- Latest presentation of progressive body weakness with reduced oral intake
- The weakness is more on the right side
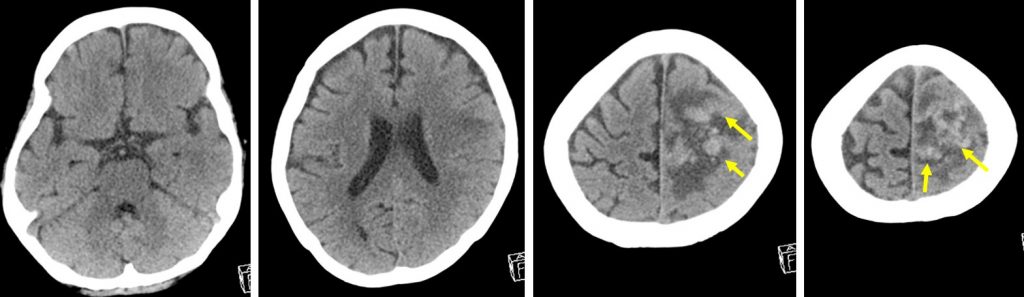
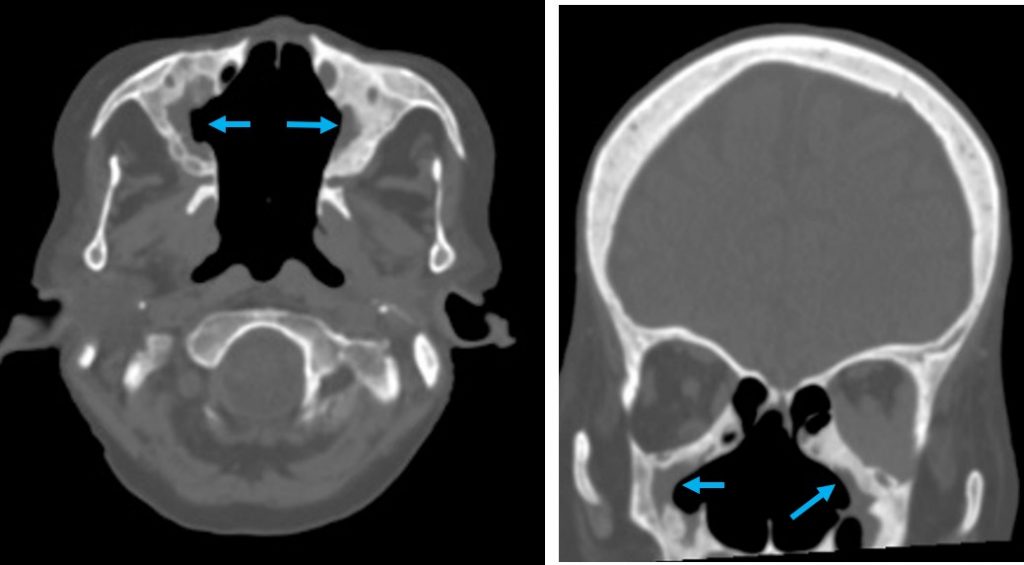
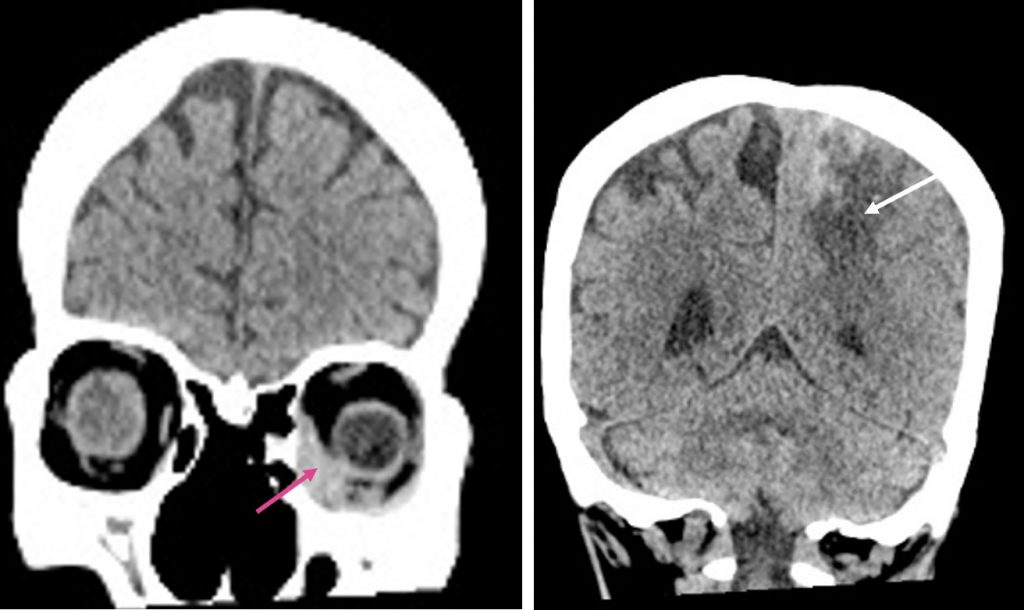
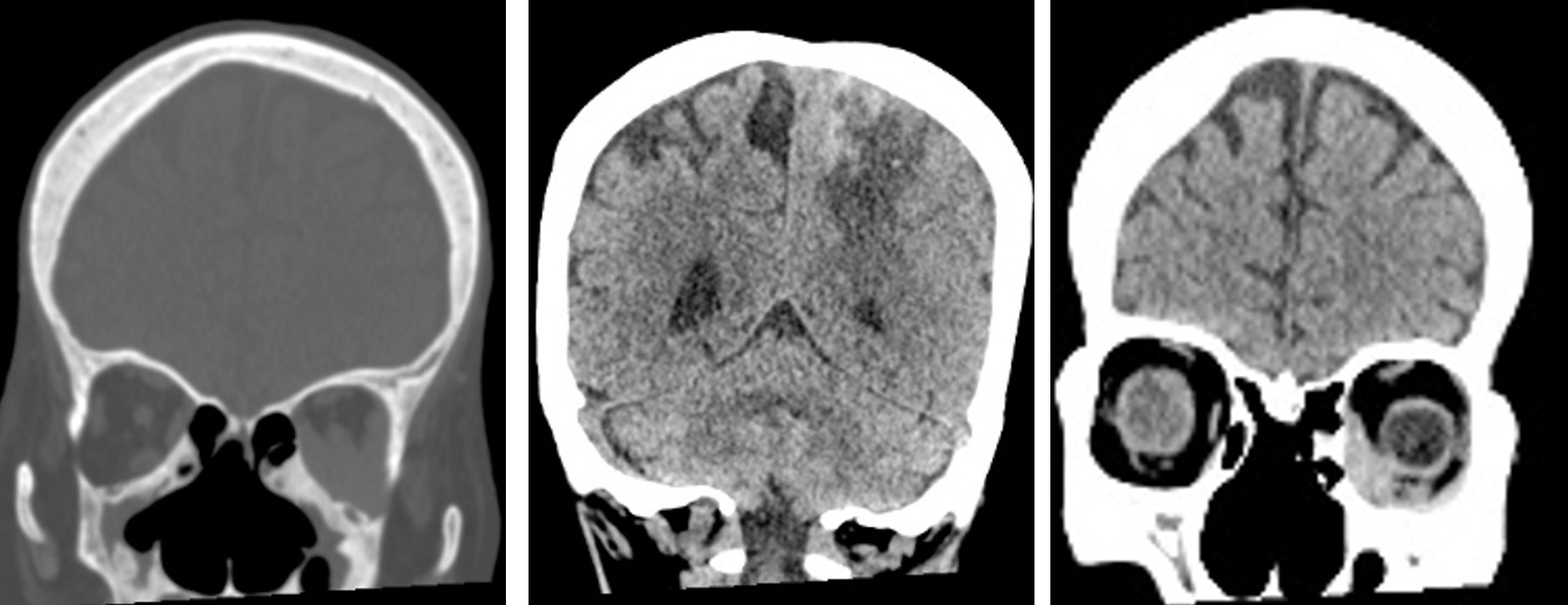
CT scan findings:
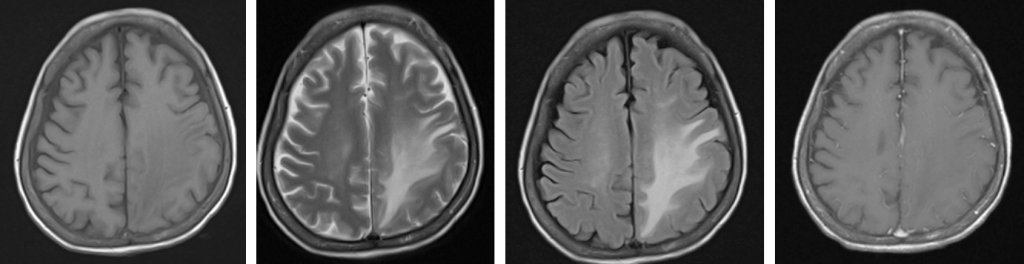
- An area of hypodensity at left frontoparietal region
- There are hyperintense foci within this hypodensity (yellow arrows)
- Minimal mass effect and effacement of ipsilateral cerebral sulci
- No midline shift
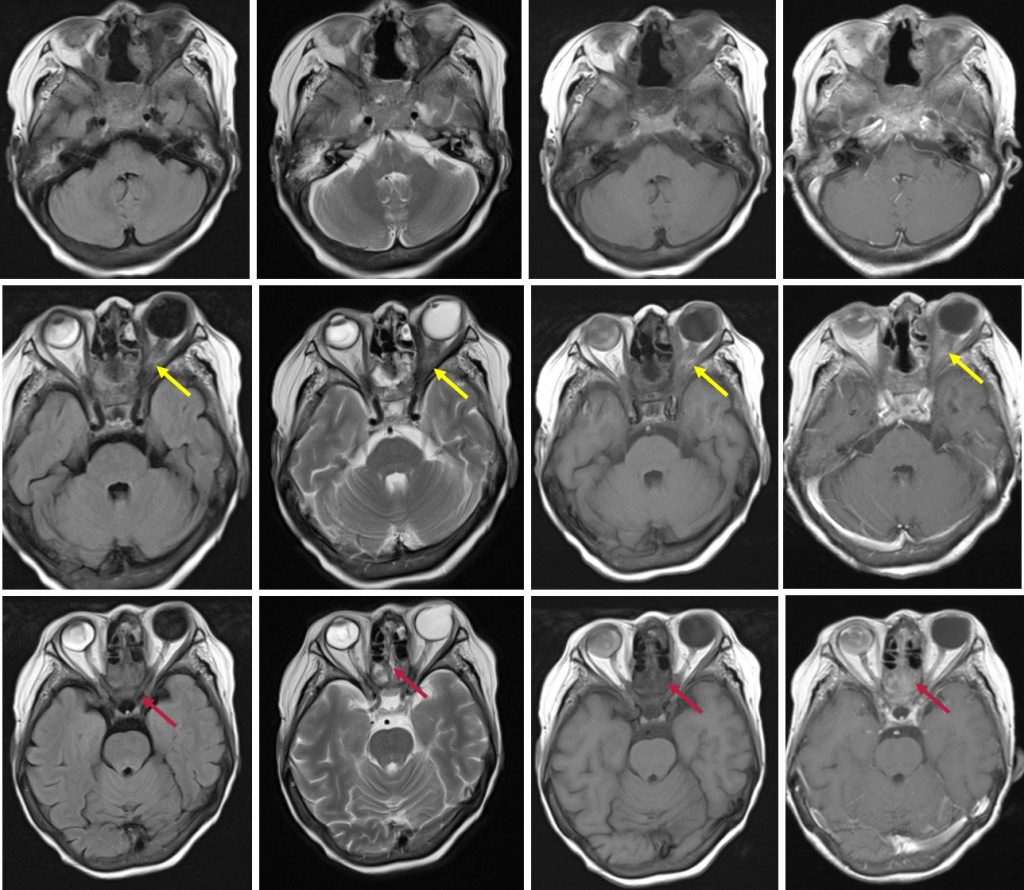
- Presence of extraconal soft tissue density mass in the left orbital cavity (red arrow)
- Abnormality also noted at paranasal sinuses with mucosal thickening and wall thickening (blue arrows)
MRI findings:
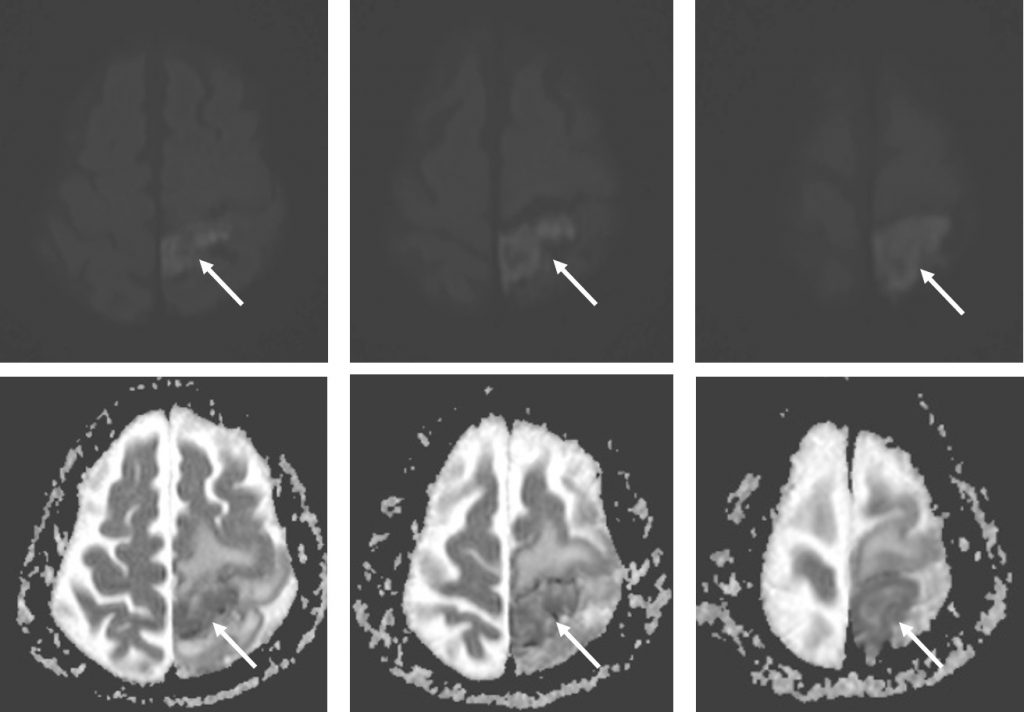
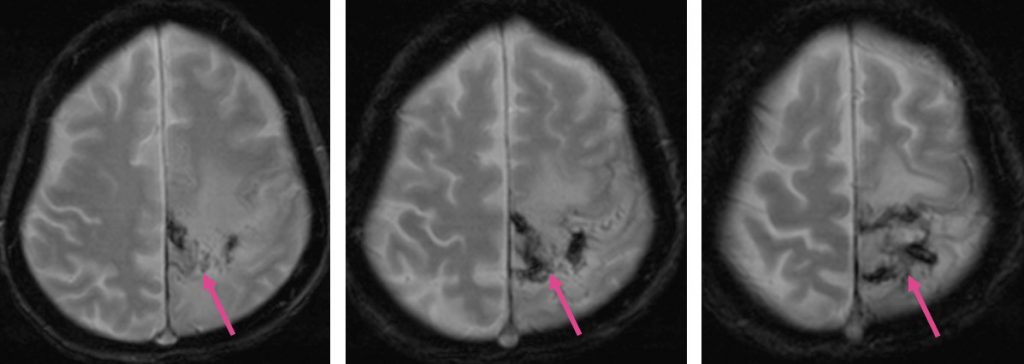
- There is restricted diffusion at left frontoparietal region.
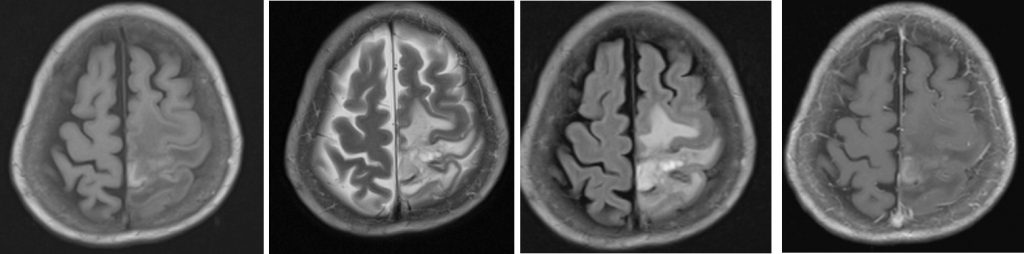
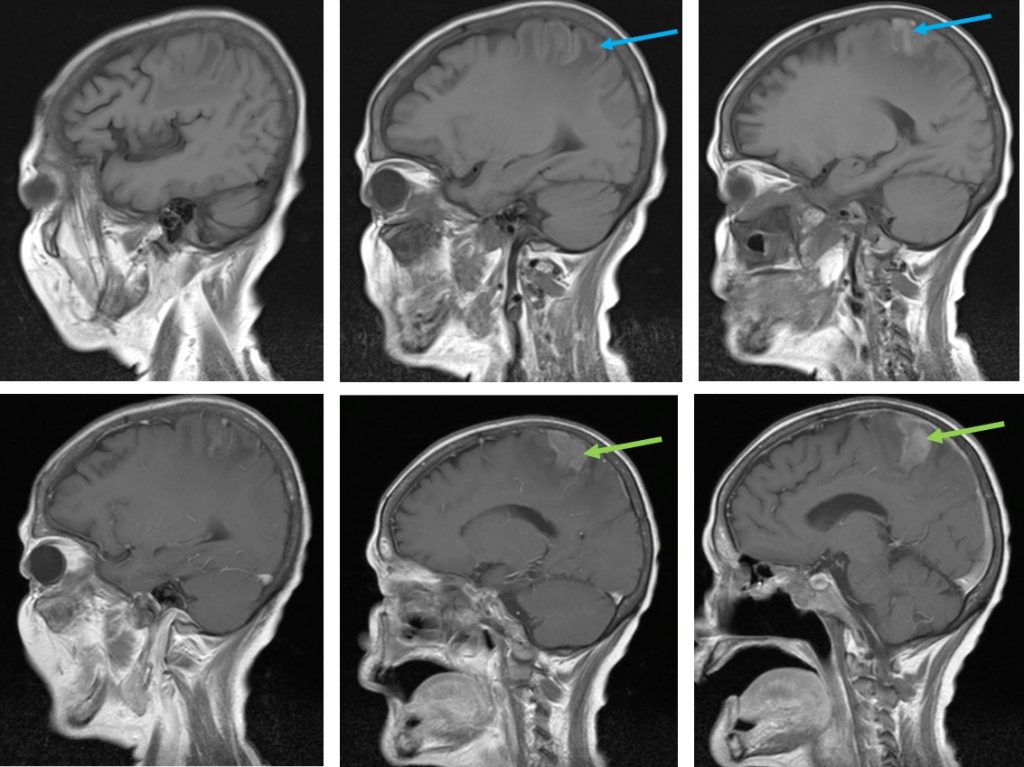
- Areas of T1-hyperintensity seen also at the same region (blue arrows)
- There is abnormal vasogenic oedema of surrounding brain
- Gyriform enhancement is seen at this region (green arrows)
- Blooming artifacts are seen on hemo sequences (pink arrows)
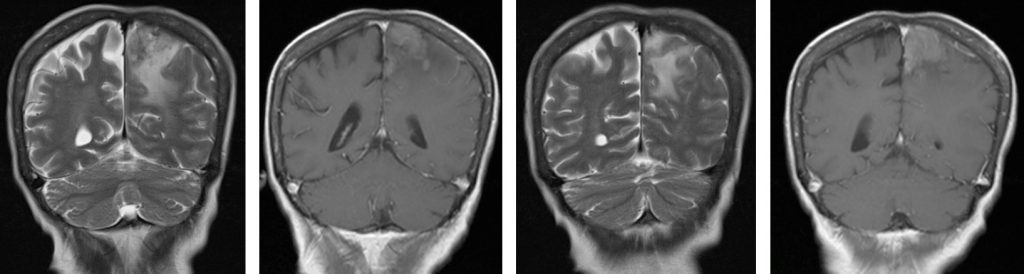
- All the paranasal sinuses shows mucosal thickening and fluid filled with heterogenous enhancement post contrast (red arrows)
- Both globes are distorted. Enhancing lesion is seen in the right globe. Retro-orbital lesion is seen in the left side causing left proptosis (yellow arrows)
- No significant finding on MRA and MRV (images not shown)
Diagnosis: Granulomatosis with polyangiitis: CNS, PNS and orbital manifestation
Discussion:
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis was previously known as Wagener granulomatosis.
- It is a multisystem necrotizing non-caseating granulomatous vasculitis affecting small to medium-sized arteries, capillaries and veins with a predilection to respiratory system and kidneys.
- There is slight male predilection and onset is typically at approximately 50 years of age.
- Pulmonary manifestation: interstitial fibrosis at bases, multiple pulmonary nodules, cavitating nodule, pleural effusion and mediastinal nodes enlargement
- Renal manifestation: either focal or diffuse lesion, focal glomerulonephritis
- Upper respiratory tract and paranasal sinuses: mucosal ulceration and granulomatous masses within the nasal cavities with adjacent bony and cartilagenous destruction
- Eyes and ears: proptosis and otitis media
- Heart and pericardium : myocardial infarction
- Skin : inflammatory skin lesion
- Joints: migratory polyarthopathy
- Spleen: may cause splenic infarction
- CNS manifestation is rare and occurs in only about 5% of cases. Cerebral or meningeal granulomatous lesion include; hypertrophic pachymeningitis, small vessel CNS vasculitis causing infarcts and arterial occlusion, intracanial hemorhrage or continuous invasion of extracranial granuloma