Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 33 years old man, no known medical illness
- Presented with sudden onset of slurred speech and left sided body weakness
- Clinical examinations: GCS=15/15, slurred speech, left hemiparesis 4/5, other examination normal
- Other investigations: ECG normal, echo normal, Blood electrolytes and thyroid function tests are normal
- After 2 days admission patient developed fitting episodes, also noted to have alternating alertness.
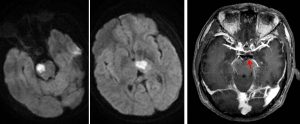
MRI findings:
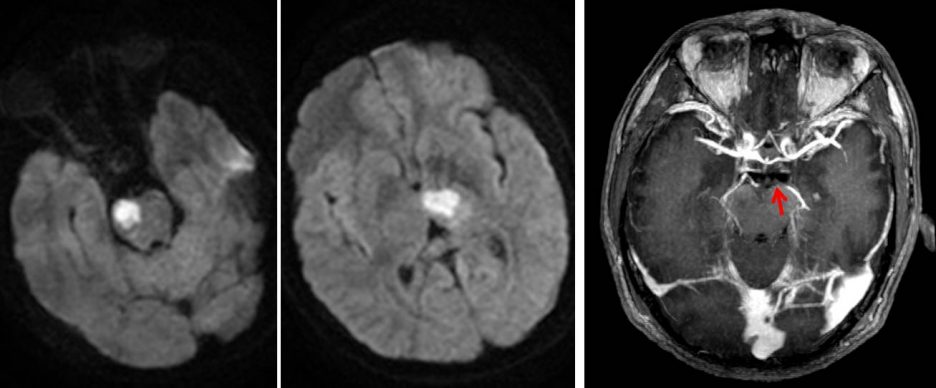
- Initial MRI on presentation shows T2/FLAIR hyperintense signal in the right side of pons.
- No other abnormality seen.
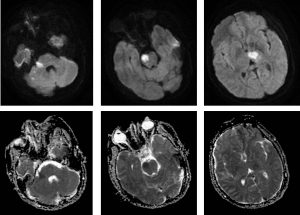
- A repeat MRI 3 days later shows new involvement at left thalamus and midbrain
- These lesions show restricted diffusion on DWI/ADC sequences
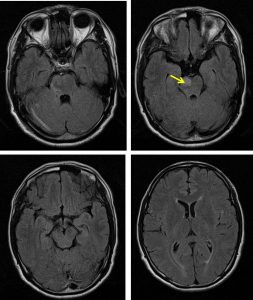
- No enhancement seen on post gadolinium images
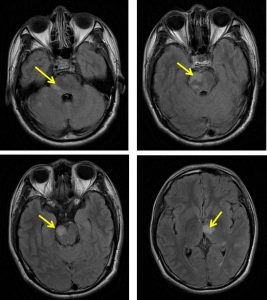
- However post contrast shows a faint enhancement of distal basilar artery with no enhancement of P1 posterior cerebral artery (red arrow). The P2 segment of left PCA is well opacified and normal in calibre. MRV was normal.
Diagnosis: Posterior circulation infarction
Discussion:
- Posterior circulation strokes count for about 20% of stroke cases
- Some of posterior circulation stroke is associated with some interesting syndrom
- Areas of brain affected by occlusion in the vertebrobasilar arterial system include; brainstem (basilar, superior cerebellar and anterior inferior cerebellar arteries), cerebellum (superior, anterior inferior and posterior inferior cerebellar arteries), thalamus (posterior cerebral artery) and other cortical regions including medial temporal and parietal lobes