Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 56 years old lady
- No known medical illness
- Had a fall, wearing high heels
- Complaint of ankle pain and swelling after the fall
Radiograph findings:
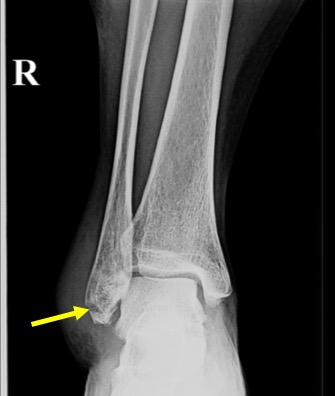
- A transverse fracture is seen of distal fibula (yellow arrow)
- The fracture line is seen below the syndesmosis
- Minimal inferior displacement of fracture fragment
- Soft tissue swelling seen surrounding the fracture region.
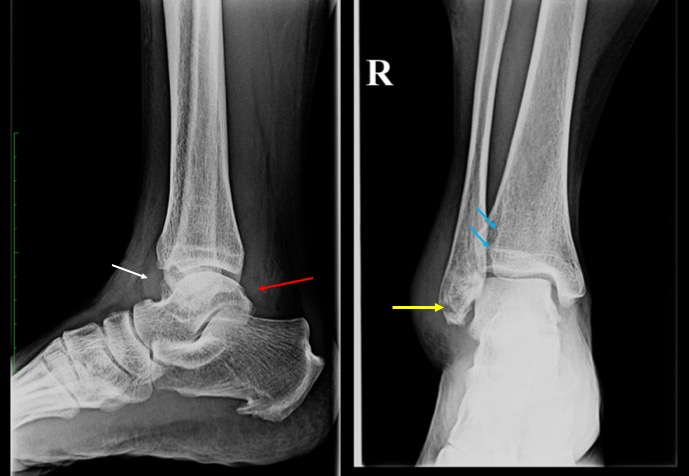
- Presence of ankle effusion evidenced by anterior convex soft tissue density at tibiotalar joint on lateral view (white arrow).
- Fat plane at pre-Achilles tendon also appear streaky (red arrow) suggestive of soft tissue inflammation.
- Articulation of fibula with tibial fibular notch (blue arrows) is preserved.
- Ankle mortise is normal (regular space over the entire talus measuring about 3-4 mm)
- No other fracture of visualized bone is seen
Diagnosis: Weber A fibula fracture
Discussion:
- Distal fibula fractures are the most common ankle injury
- Classification of distal fibula fractures commonly used is Weber classification that use position of fracture relative to the syndesmosis
- Weber A: below the syndesmosis and stable
- Weber B: at the syndesmosis and may be unstable
- Weber C: above the syndesmosis and unstable