Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 47 years old man with underlying lung carcinoma
- Non-operable non-small cell ca Stage III on immunotherapy
- Presented with headache since past one month
- No fever, no history of trauma
- No vomiting, no blurred vision
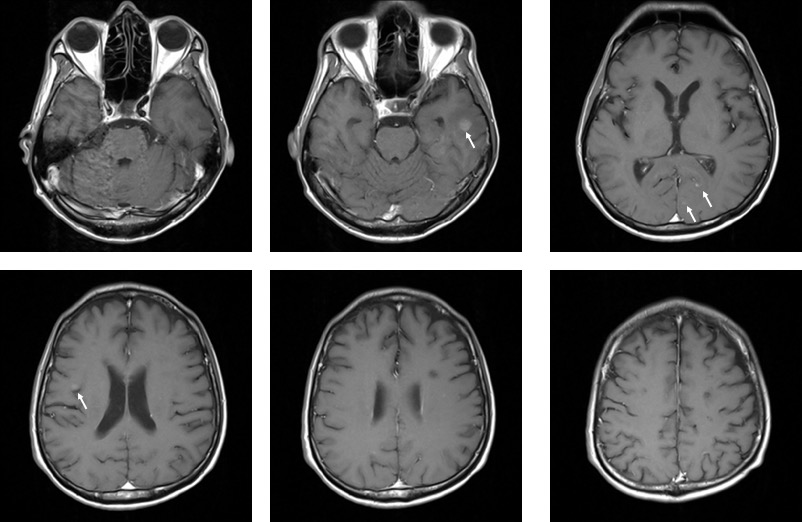
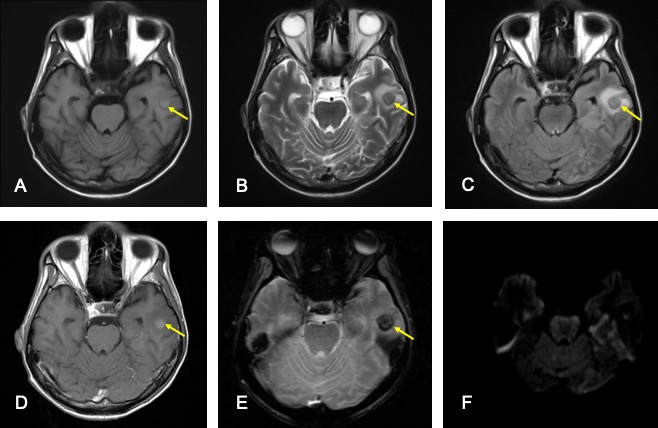
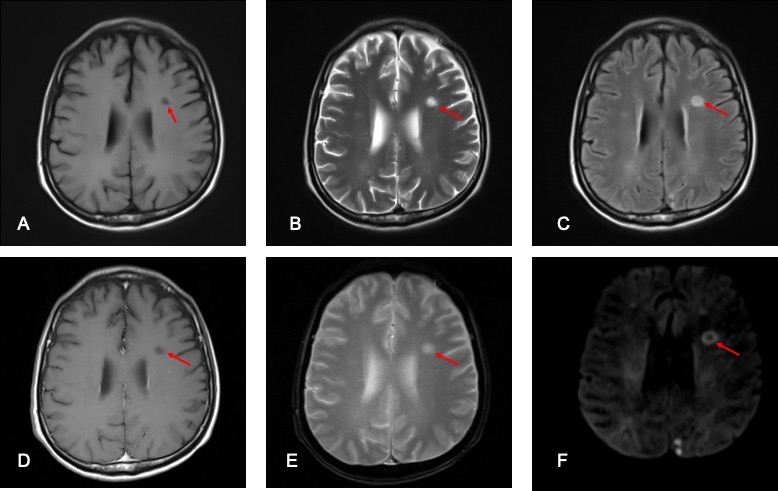
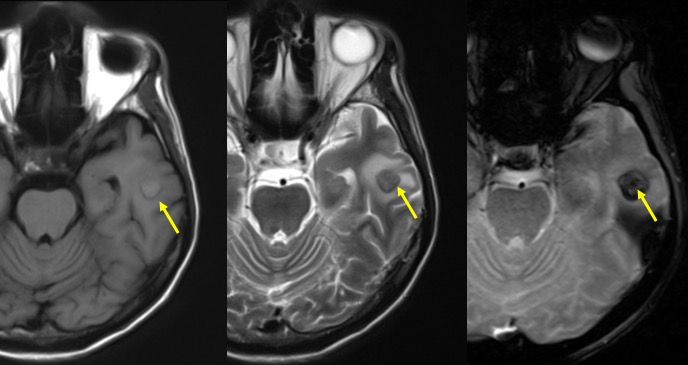
MRI findings:
- There are multiple lesions within the brain parenchyma
- Some the lesions are hypo on T1, hyper on T1 with homogenous enhancement post contrast (white arrows)
- Some of the lesions are hypo on T1, hyper on T2 and not enhanced post contrast.
- A lesion at left temporal region (yellow arrow) shows blooming artifact on hemo sequence suggestive of hemorrhagic component
- Another lesion at left frontal lobe shows restricted diffusion of its wall (red arrow) and no obvious enhancement on post contrast image.
Diagnosis: Cerebral metastasis from lung cancer (presumed diagnosis, no biopsy done)
Discussion:
- Brain is one of the common sites of distant metastasis as well as initial recurrence in patients with lung cancer with an incidence of 20% at diagnosis and up to more than 50% at autopsy.
- Non-small cell lung cancer does not have a set of clinical pattern of metastasis and it may exist in neurologically asymptomatic patients.
- No single feature is pathognomonic. Due to great variation in imaging appearance, diagnosis may be a diagnostic challenge.
- 80% of metastasis localize to cerebral hemisphere, 15% localized to cerebellum and 3% localized to the basal ganglia.
- Although multiplicity favours metastasis, about 50% of metastasis are solitary at diagnosis. Grey white matter junction and watershed areas are common location of cerebral metastasis.
- In this case the lesions show mixed feature, some are solid enhancing nodules, a hemorrhagic lesion and another lesion shows restricted diffusion at wall of lesion.
- Metastasis that haemorrhage include melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, choriocarcinoma, thyroid cancer, lung and breast cancers.