Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 57 years old lady
- Married with 6 children
- All children delivered via SVD with no complication
- Under follow up for chronic back and gluteal pain
- Clinical examination is unremarkable
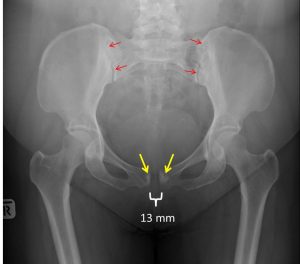
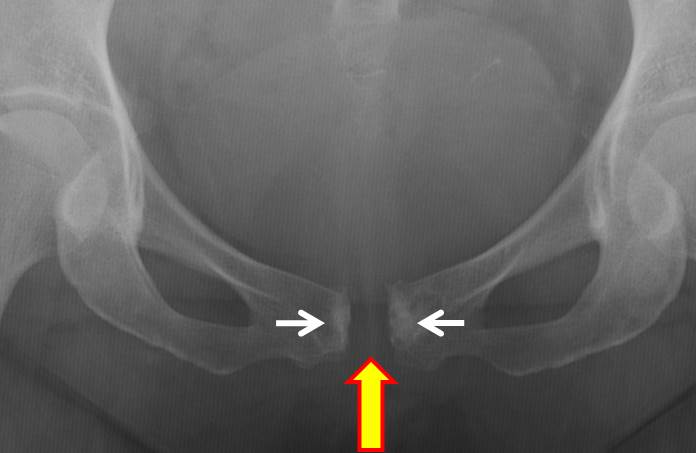
Plain radiograph of the pelvis:
- Separation of the symphysis pubis measuring about 13 mm
- There is sclerotic change at parasymphyseal region bilaterally (yellow arrow)
- The sacroiliac joints are normal (red arrow)
- No fracture of visualized bones
- No soft tissue swelling
Diagnosis: Symphysis pubis diastasis
Discussion:
- The pubic symphysis is a non-synovial joint that connects the right and left superior pubic rami
- The joint is reinforced by four ligaments: the superior, inferior, anterior, and posterior pubic ligaments
- A normal radiographic separation width of symphysis pubis is 4 to 5 mm.
- The gap can increase by 2-3 mm and remain after delivery, called physiological pubic symphysis diastasis.
- A pathological pubic symphysis diastasis is defined as joint widening of > 10 mm without concomitant fractures
- Pubic symphysis diastasis can be symptomatic or asymptomatic. It is most commonly associated with pregnancy childbirth. In general, one in four women are affected, to a varying degree. The reported prevalence of non-traumatic diastasis varies from 1 in 300 pregnancies to 1 in 30,000 pregnancies.
- The leading symptom of symphyseal separation is pubic joint pain and inflammation. Pain can radiate to the abdominal or inguinal area, to lower extremities or to the back. The symptoms tend to worsen while moving, bearing a load, or raising a leg. Sometimes it may contribute to lower back discomfort or be followed by complicated locomotion leading to instability and incapacity while walking or standing
- There are various non-operative and operative treatment options, but no gold standard treatment has been defined. In general practice, uncomplicated and mild cases are dealt with by conservative treatment. If conservative treatment fails or severe and/or complicated cases develop, surgery is performed.
Progress of patient:
- Patient is managed conservatively with analgesics and physiotherapy.