Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 16 years old girl, no known medical illness
- Presented with neck swelling for 3 months
- Associated with cough and weight loss about 6 kg
- Noted a palpable lesion at the sternum area
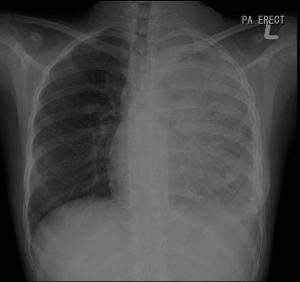
Findings of chest radiograph:
- A veil-like opacity of the left hemithorax
- The pulmonary markings are not obscured
- Left mediastinum and cardiac margin are not visualized
- Left hemidiaphragm outline is also obscured
- No tracheal or mediastinum shift. No air bronchogram sign
- Right hilum is normal. Left hilum is not seen.
- No rib lesion is seen
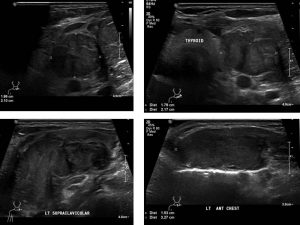
Ultrasound findings:
- There are multiple enlarged nodes at upper part of left cervical and supraclavicular region. The largest lesion is measuring 1.9 x 2.1 cm (AP x W).
- Another heterogeneous lesion is detected at the left anterior chest wall measuring 1.4 x 2.8 cm (AP x W).
- No calcification seen within these lesions.
- No cystic lesion seen within to suggest area of necrosis.
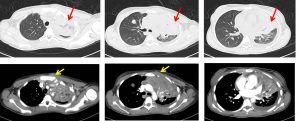
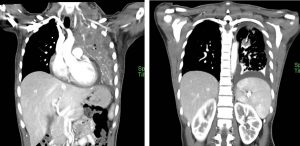
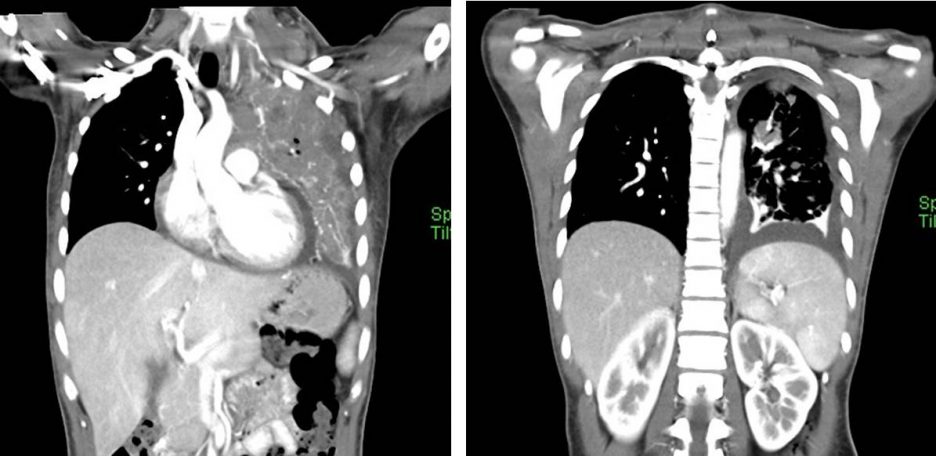
CT scan findings:
- Collapsed consolidation of left upper lobe (red arrows). Multiple hypodense lesions are seen within the collapsed left lung.
- Multiple lung nodules are seen scattered throughout both lungs.
- Associated left pleural effusion is also seen.
- There is enlarged lobulated enhancing lesion is seen at left supraclavicular region measuring 4.1 x 5.9 x 5.7 cm (AP x W x CC). Central hypodensity is observed in keeping with central necrosis. The lesion is seen displaced the left thyroid lobe medially. No clear margin observed with the surrounding neck muscles.
- Multiple enlarged cervical nodes also seen
Progress of patient:
- Biopsy done under ultrasound guidance shows Hodgkin lumphoma
- CT scan shows Stage IVb Hodgkin lymphoma
- On chemotherapy
Discussion:
- Left upper lobe collapse can present with a ‘veil-like’ opacity of the left lung field.
- This is because the left upper lobe collapses anteriorly becoming a sheet of tissue apposed to the anterior chest wall and appears as a hazy or veiling opacity extending out from the left hilum and fading out inferiorly.
- Part of the cardiac and mediastinal outline can be obscured if lingular segments are involved. Part of the aortic arch are also often obscured.
- Other signs of left upper lobe collapsed include:
- elevation of the hemidiaphragm
- ‘peaked’ or ‘tented’ hemidiaphragm
- crowding of the left ribs
- shift of the mediastinum to the left
- posterior and left lateral rotation of the heart
-
CT