Case contribution: Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 43 years old
- Complaint of right nipple retraction, no nipple discharge
- No breast lump palpable
- Initially thought change is due to breastfeeding a one year old child
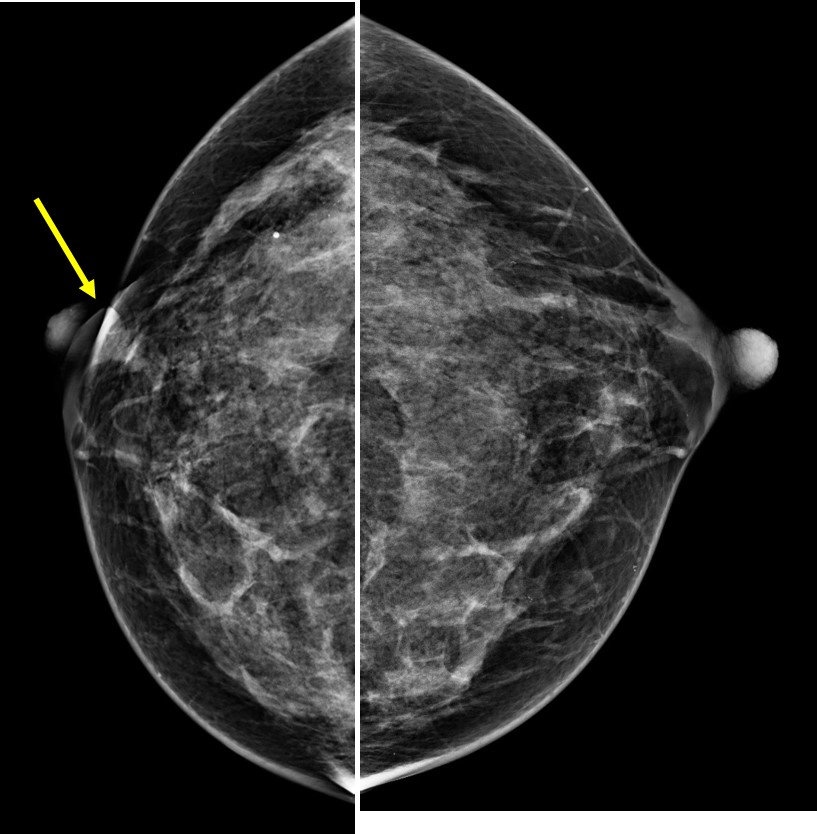
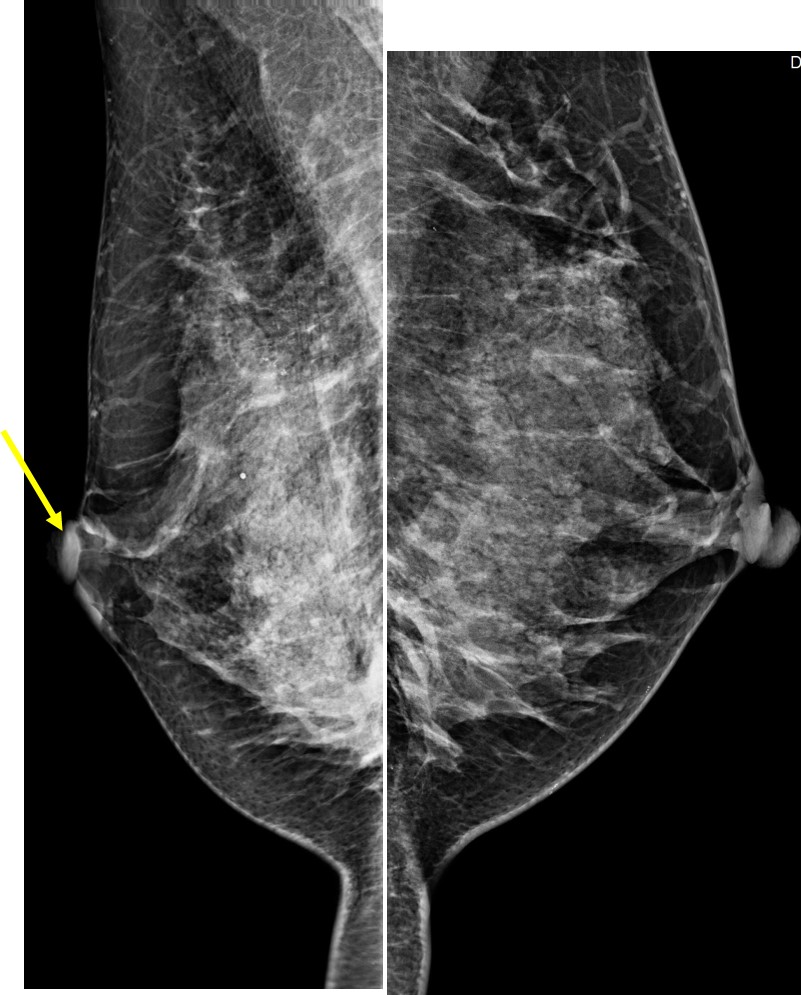
Mammogram findings:
- Bilateral dense breasts BIRADS C with slight asymmetry in density
- There is right nipple retraction (arrows)
- No obvious mass on digital mammogram images
- However tomosythesis shows a focal stromal distortion in right upper quadrant
- A clustered microcalcifications is also seen at right upper outer quadrant near axillary tail
- No skin thickening. No abnormal axillary node.
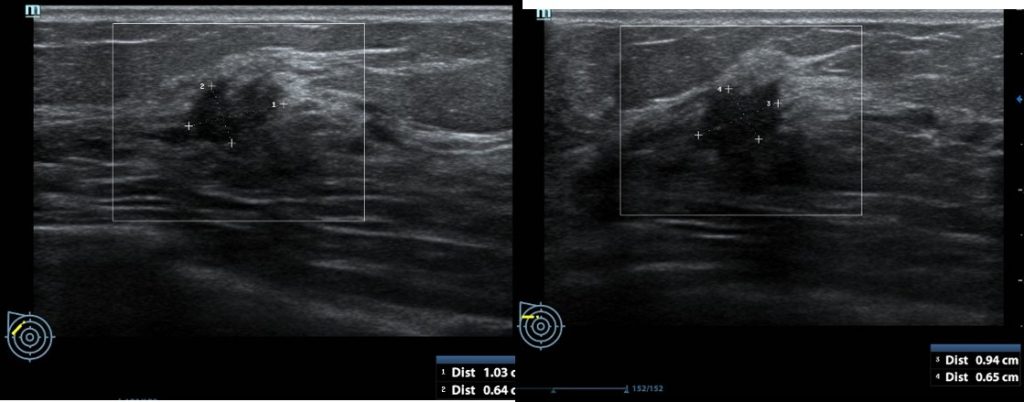
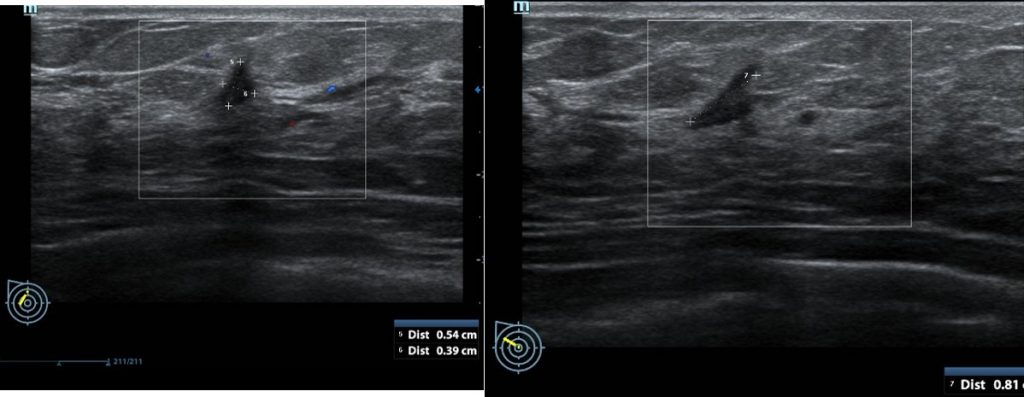
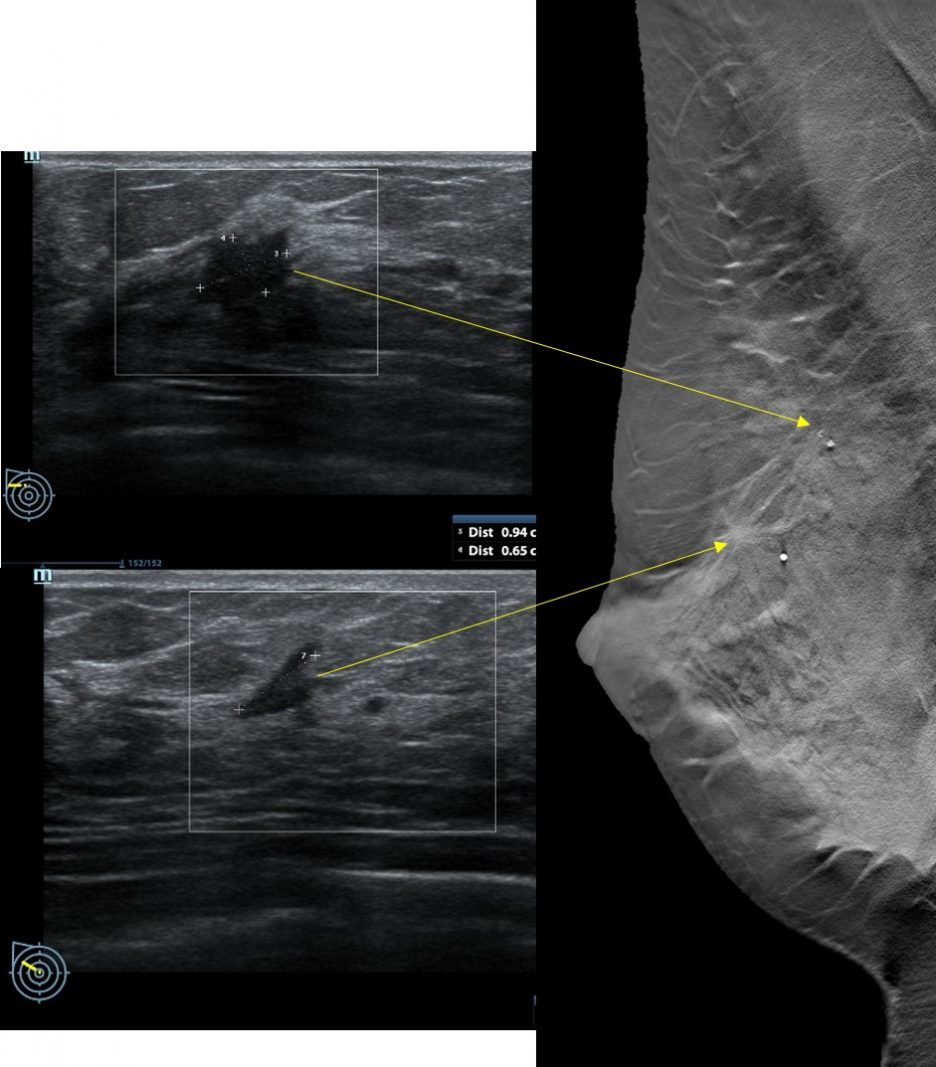
Ultrasound findings:
- Two suspicious lesions are seen in the right breast.
- A lesion adjacent to right areolar region measures 8 mm in its largest dimension
- It shows irregular outline with some posterior shadowing
- Another lesion as same quadrant but further away near axillary region measuring 10×9 mm.
- It shows irregular outline with papillary projection
- It also shows posterior shadowing
- No continuation of these two lesions are seen.
Progress of patient:
- Biopsy shows invasive carcinoma
- Surgical team inquired whether this is a unifocal or multifocal lesions as patient requested breast-sparing surgery
- Based on imaging it was concluded as multifocal lesion.
- Patient subsequently had right mastectomy and axillary clearance. HPE shows invasive carcinoma NST, Bloom and Richardson Grade 3, florid lymphovascular invasion, extensive DCIS component (50%), the closest DCIS margin is 1 mm from lateral margin and deep margin is 2 mm from the invasive component. Positive nodal metastasis in 6 out of 7 lymph nodes, ER/PR –ve, Cerb B2: +ve.
- Conclusion: only one tumour identified based on gross and microscopic analysis of the specimen measuring 40x30x16 mm.
Discussion:
- Presence of two or more foci of cancer within the same breast quadrant is defined as multifocal (MF)
- Presence of two or more foci of cancer in different quadrants of the same breast is defined as multicentric (MC)
- Some defined that the separation between two lesions should be more than 4 cm to be classified as MF/MC tumours
- MF/MC have been reported in 40-70% in serial studies of mastectomy specimens
- Usually a contraindication for breast-conserving surgery
- MRI has been shown to have higher accuracy than mammogram/ultrasound assessment
- TNM classification use only the diameter of the largest focus and may underestimates higher tumour burden of MF/MC breast cancers.
- MF/MC cancers are biologically more aggressive than unicentric tumours with higher incidence of metastasis and related with worse outcome.