Clinical:
- A 66 years old man
- Presented with chronic cough and worsening shortness of breath
- Associated with constitutional symptoms
Radiographic findings:
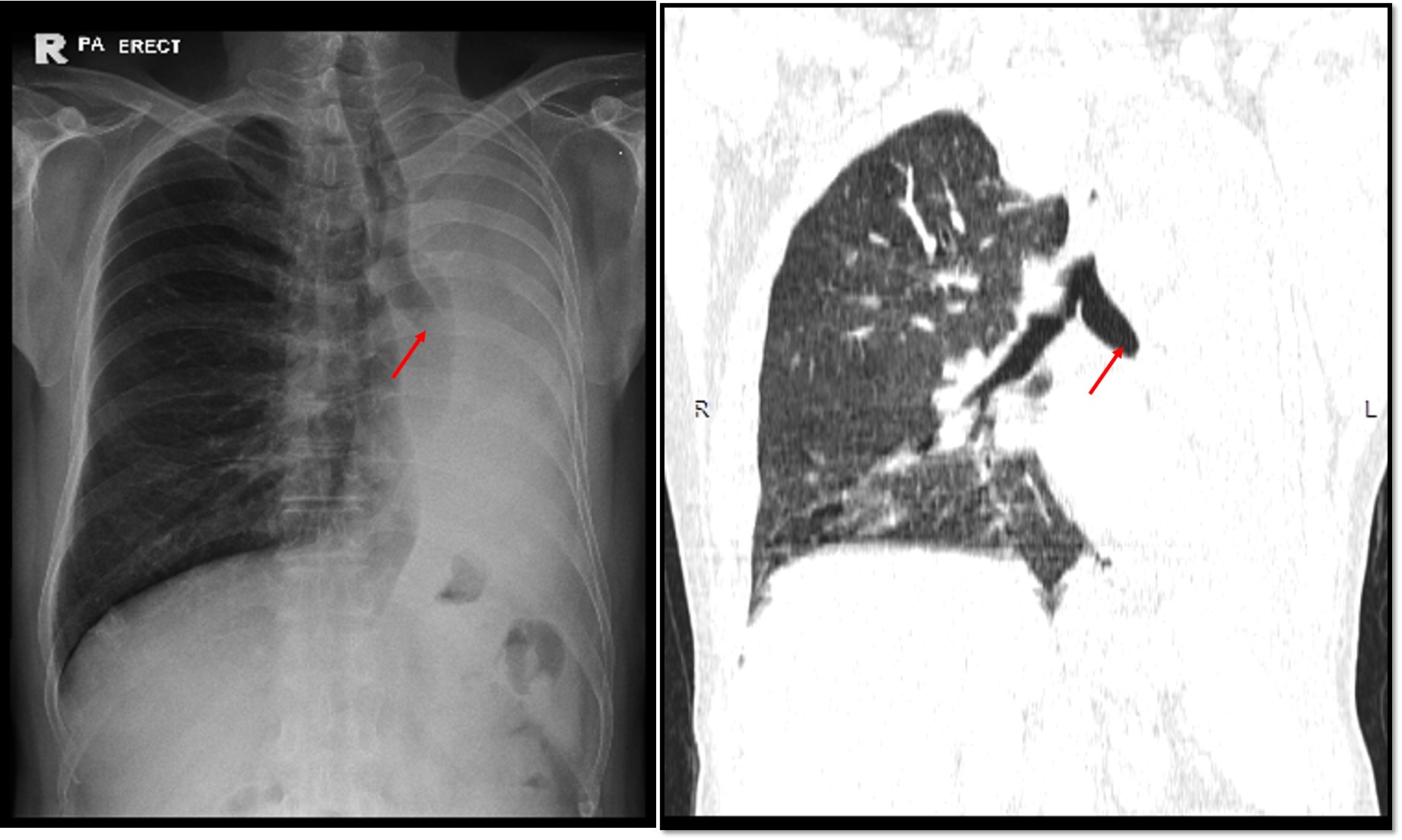
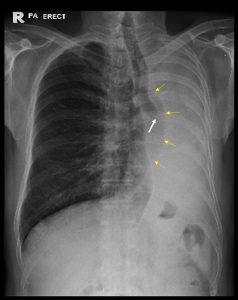
- There is opacity of the whole left hemithorax.
- Obliteration of cardiac outline and left hemidiaphragm.
- There is tracheal and mediastinal shift to the same side.
- Abrupt termination of the left bronchus shadow with soft tissue opacity within it (white arrow).
- Compensatory hyperinflation of the right lung (yellow arrows).
- Right lung is well aerated. No lung nodule or mass in the right lung.
- No pleural effusion or pneumothorax on the right side.
- Bones are unremarkable.
Radiologic diagnosis: Opaque left hemithorax with ipsilateral mediastinal shift
Discussion:
- Complete opacification of a hemithorax on chest X-ray is termed opaque hemithorax
- The differential diagnosis of an opaque hemithorax is primarily based on the volume of the affected hemithorax, as determined by the position of the mediastinum
- increased hemithoracic volume-mediastinal shift to the unaffected side
- reduced hemithoracic volume-mediastinal shift to the affected side
- normal hemithoracic volume-no mediastinal shift
- The differential diagnosis of an opaque hemithorax with reduced ipsilateral volume and ipsilateral mediastinal shift includes pulmonary agenesis, pneumonectomy, and atelectasis. Bronchial obstruction by a foreign body (in children) or an endobronchial tumor (in adults) is the most common cause of atelectasis/lung collapsed.
Progress of patient:
- CT scan performed
- Biopsy showed Non-small cell lung carcinoma
CT scan findings:
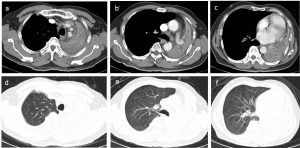
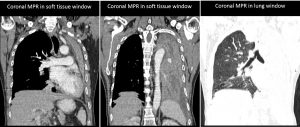
- There is soft tissuel lesion seen extending into and causing total obliteration of distal left main bronchus.
- There is total collapsed of the left lung.
- Multiple ill-defined relatively hypodense lesions within the collapsed left lung could represent lung nodules.
- There is ipsilateral shift of the trachea, mediastinum and heart.
- Minimal left pleural effusion is seen. No pleural thickening or abnormal enhancement.
- Right lung field is well aerated with no focal lesion seen within it.
- There is no pericardial effusion. Heart is not enlarged.
- There are a few mediastinal nodes seen.