Clinical:
- A 49 years old lady
- Incidental finding of cystic lesion in the pelvis during ultrasound done for routine medical check up.
- No abdominal pain. Menses are normal
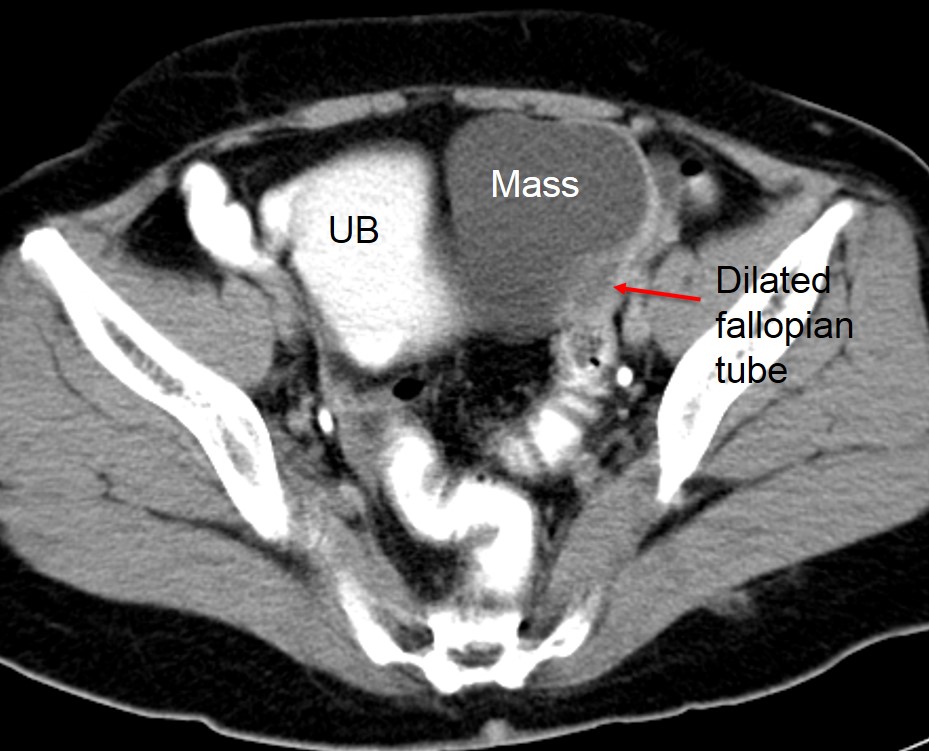
CT scan findings:
- A cystic lesion on the left side of pelvis, measuring about 7x7x6 cm (yellow arrows)
- The lesion has thin wall, no septa, no calcification within it, no fat component and no enhancement seen post contrast
- Fluid level is seen within the mass
- A tubular cystic structure seen adjacent to it may represent dilated fallopian tube (red arrows)
- No local infiltration, no distant metastasis, no ascites
Intraoperative findings:
- Left ovarian tumour mainly cystic, 8x10x6 cm. Adhered to lateral pelvic side wall, bladder peritoneum anteriorly and medially to descending colon
- Left fallopian tube dilated, Right fallopian tube normal
- No ascites
- Omentum, bowel, liver and spleen undersurface normal
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: specimen labelled as left ovarian cyst consists of a cystic mass weighing 150 gms. The mass measures 95x70x65 mm. Cut section shows a uniloculated cyst filled with fluid. The cyst wall ranging from 1 mm to 6 mm in thickness. There are 2 solid areas noted measuring 22x15x15 mm and 40x25x9 mm.
- Microscopy: Left ovarian cyst show a benign cyst lined by a single layer or ciliated cuboidal to flattened epithelium. No nuclear atypia. The solid areas show ruptured corpus luteum and area of hemorrhage surrounded by hemosiderin-laden macrophages. No lining epithelium seen. No evidence of malignancy.
- Interpretation: left ovary: serous cystadenoma
Diagnosis: Ovarian serous cystadenoma
Discussion:
- Ovarian serous cystadenomas are benign ovarian epithelial tumours.
- It is the commonest type of ovarian epithelial neoplasm and accounts for 60% of ovarian serous tumours.
- The peak incidence is at the 4th to 5th decades of life.
- Usually asymptomatic, if symptoms are present, they are usually related to mass effect with displacement of adjacent structures.
- It can be bilateral in 15% of cases.
- On imaging, it is often seen as a unilocular cystic mass with homogeneous CT attenuation, with a thin regular wall or septum, and usually no endocystic or exocystic vegetation