Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 70 years old man
- Underlying DM, HPT and Gout
- CKD for last 3 years, not on dialysis
- Presented with lumbar pain and hematuria
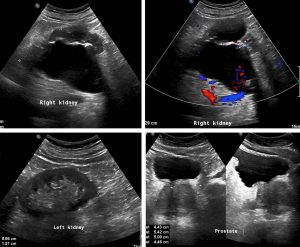
Ultrasound findings:
- Right kidney is larger than the left side. Bipolar length: Right: 11.4cm, Left: 8.7cm.
- Gross hydronephrosis of right kidney. No calculus seen.
- Unable to trace the right ureter distally due to obscuration by bowel gas.
- Solitary cyst seen at midpole of right kidney measures 4.5cm x 6.1cm x 5.3cm (APxWxCC).
- Urinary bladder bladder is partially distended filled with clear urine. No focal lesion or calculus seen.
- Prostate is heterogenous and enlarged measures 4.4cm x 5.4cm x 5.0cm (APxWxCC). Foci of calcification noted.
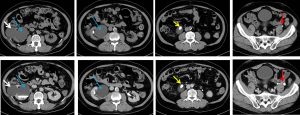
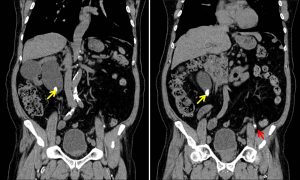
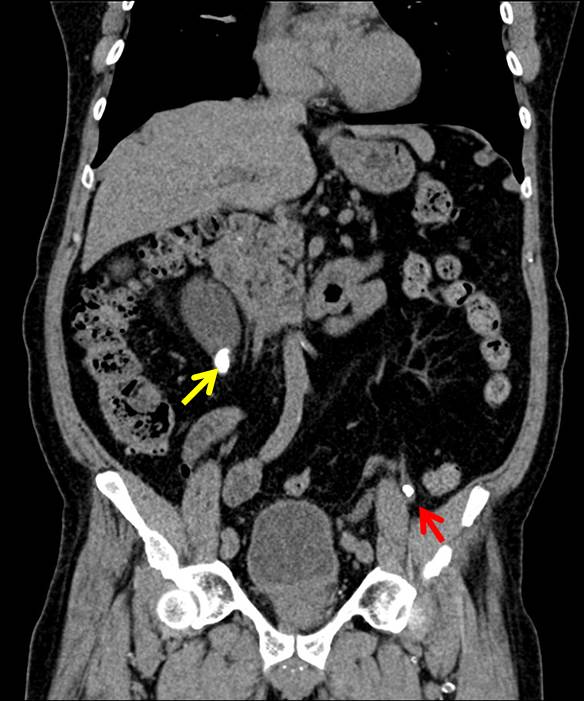
CT scan findings:
- A calculus at proximal right ureter (yellow arrows) causing moderate right hydronephrosis (blue arrows) and proximal hydroureter
- Another smaller ureteric calculus at left distal ureter (red arrows) not causing any obstruction to left collecting system
- A renal cyst at right midpole (white arrows) as seen on ultrasound
Diagnosis: Bilateral ureteric calculi with obstructive uropathy on the right side.
Discussion:
- Ureteric calculi are stones lying within the ureter at any point from the ureteropelvic junction (PUJ) to the vesicoureteric junction (VUJ)
- The prevalence is high, about 12% of men and 7% of women
- Most patients present between ages 30-60 years
- The risk increased with past history of ureteric calculus and with positive family history.
- Other risk factors include low fluid intake, frequent UTI and medications that may crystallize within the urine
- Plain radiograph can identify large radiopaque calculi.
- Small calculi and radiolucent stones may go undetected.
- Non-contrast CT scan (CT KUB) is the gold standard for ureteric stone. On CT scan, 99% seen as hyperdense focus. Stones >1mm are visualized, specificity as high as 100%.
- Ultrasound is helpful as initial screening. It may avoid unnecessary CT scan in certain cases.
- Ultrasound features include echogenic foci, acoustic shadowing, assessment of hydronephrosis or pyonephrosis.
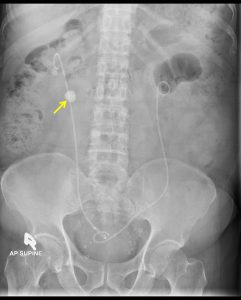
Progress of patient:
- Bilateral retrograde ureteric stenting done
- DTPA scan shows severe reduced right kidney function with mild reduced left kidney function