Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 50 years old lady
- No known medical illness
- Presented with left breast lump for 2 weeks duration.
- No family history of breast cancer
- Associated with pain, no fever
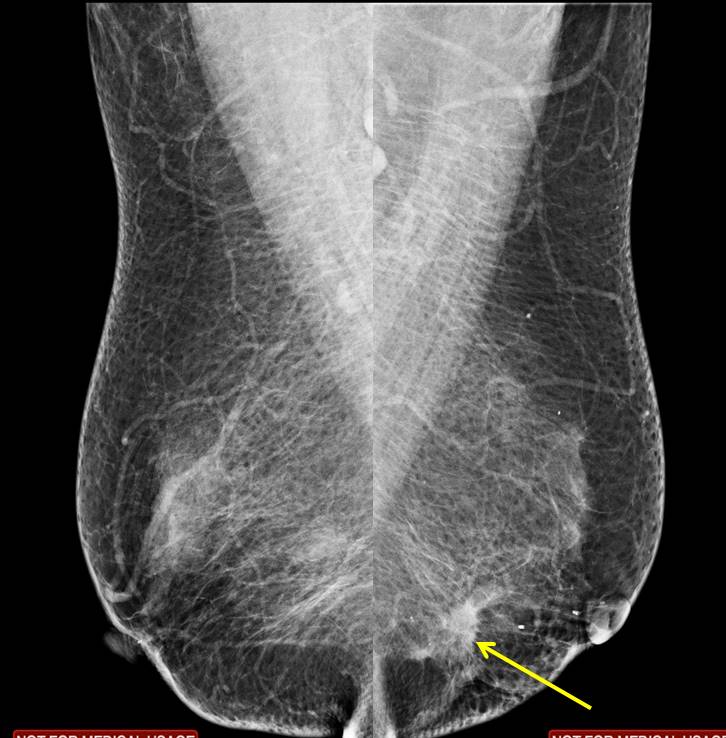
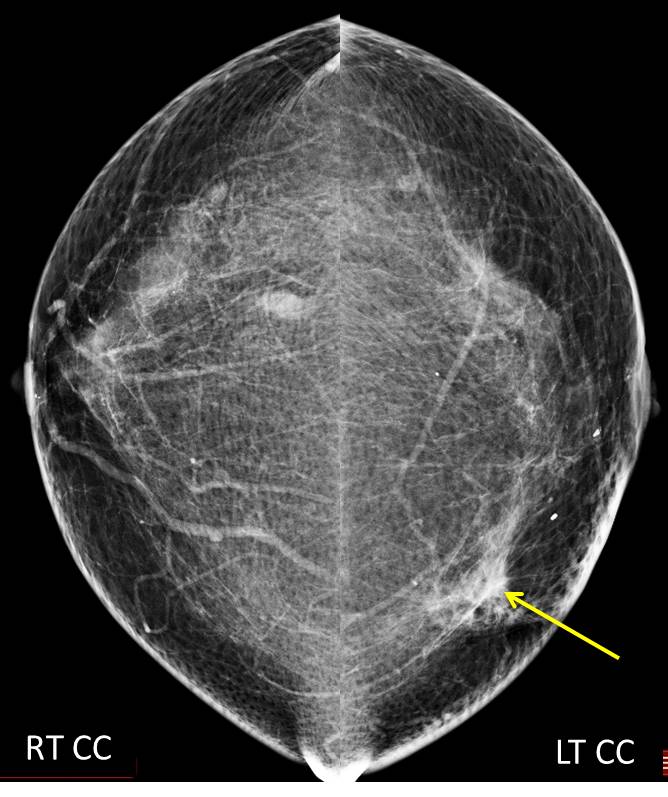
Mammogram findings:
- A focal stromal distortion is seen at left lower inner quadrant (yellow arrows)
- No suspicious clustered microcalcification
- Minimal skin thickening seen
- No nipple retraction, no abnormal axillary nodes
- Well-defined small lesions seen in the right breast
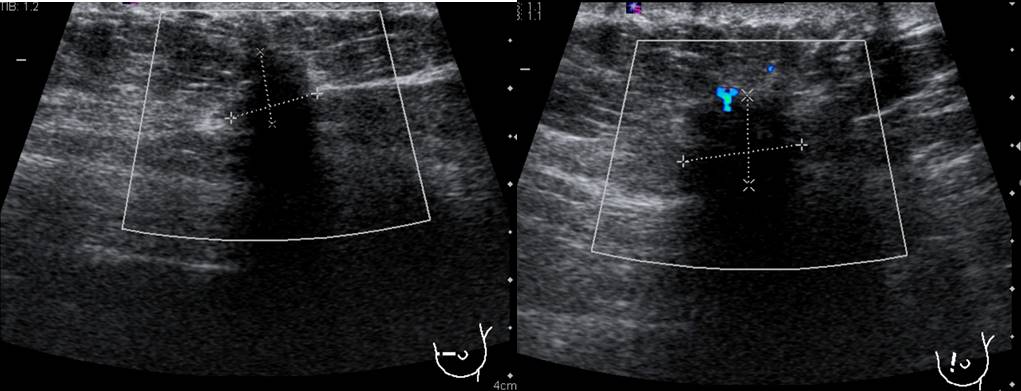
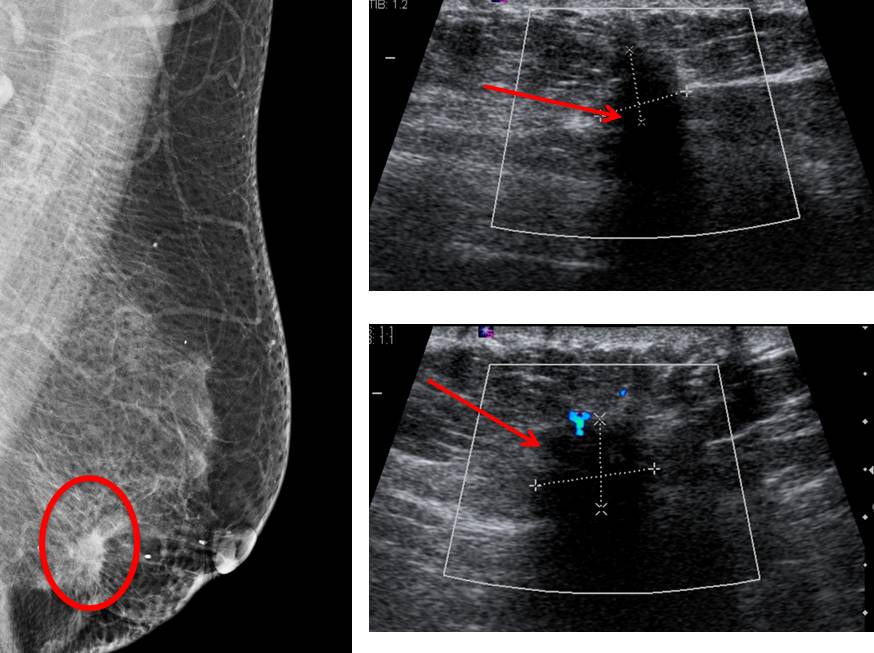
Ultrasound findings:
- A spiculated mass at Lt9H measuring 13×9 mm
- The lesion is taller than its width
- Presence of posterior shadowing
- Penetrating vessels seen
- Breast cysts at right breast (images not shown)
- No abnormal lymph nodes
Progress of patient:
- Biopsy done shows minimal tissue obtained. Suspicious area of malignancy seen
- Wide local excision done shows DCIS infiltrative gland. Axillary sampling shows all nodes removed were clear
- ER, PR +ve. HER2-negative
- Impression: intraductal DCIS low to intermediate, mitosis grade 2, histopathological grade 1.
Diagnosis: Ductal carcinoma in situ
Discussion:
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a breast carcinoma limited to the ducts with no extension beyond the basement membrane
- It accounts for 25-40% of mammographically detected breast cancers
- DCIS have varied appearance on mammogram.
- Casting-type calcifications is the most common (present in 50-75% of cases)
- It can be also be seen as an uncalcified, round, oval, irregular or microlobulated, mass with partially circumscribed or spiculated margins, distortion, parenchymal asymmetry or diffuse change.
- On ultrasound, the most common feature is a microlobulated mild hypoechoic mass with ductal extension.
- On MRI, DCIS most commonly appears as non-mass enhancement, most commonly with a segmental or linear distribution and clumped or heterogeneous internal enhancement pattern.
Reference:
- El-Feky and Radswiki et al, Ductal carcinoma in situ. At https://radiopaedia.org/articles/ductal-carcinoma-in-situ