Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 72 years old lady, no known medical illness
- Presented with left breast lump for 2 months
- Associated with mild pain. No fever, no nipple discharge
- Clinically a superficial lump felt at upper outer quadrant of left chest wall near to the axilla. No breast lump. No enlarged axillary nodes.
- She was given a trial of antibiotics for 2 weeks, pain subsided but the lump persist
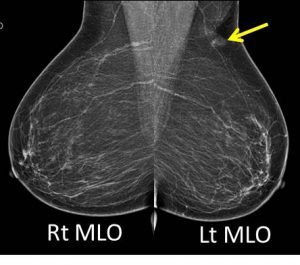
Mammogram findings:
- Bilateral fatty breasts (BIRADS A) with symmetrical parenchymal pattern.
- No dominant intraparenchymal lesion or stromal distortion seen.
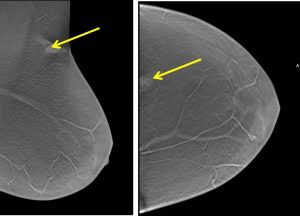
- A superficially located likely skin lesion with minimal surrounding tissue distortion is seen at upper outer quadrant of the left breast (best seen on tomosynthesis images-yellow arrows).
- No other skin changes elsewhere. No nipple retraction bilaterally.
- No suspicious clustered microcalcifications.
- Vascular calcifications are seen in both breasts.
- No abnormal axillary node enlargement
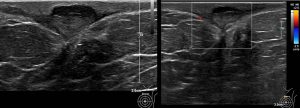
Ultrasound findings:
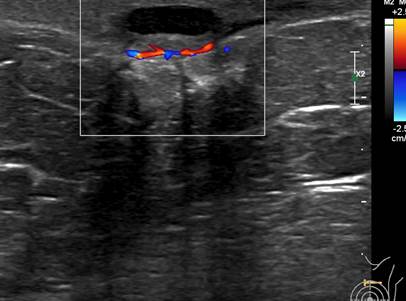
- There is a heterogenous hypoechoic lesion seen at left 12H approximately 5 cm from nipple.
- The lesion measures approximately 0.7 x 1.9 x 1.6 cm (AP x W x CC).
- This lesion is superficial and located mainly in the skin and subcutaneous layer.
- No internal calcifications seen within. Peripheral vascularity is demonstrated on Doppler study.
- There is also presence of skin thickening immediate to the lesion.
Intra-operative findings:
- Excision biopsy under local analgesia done
- A ruptured sebaceous cyst measuring 1×1 cm seen.
- Cyst wall was removed
- Minimal bleeding noted
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: specimen labelled as left breast sebaceous cyst, consists of multiple pieces of tan whitish tissue measuring 9 mm in diameter
- Microscopy: section shows multiple fragments of skin tissue lined by mildly acanthotic epidermis with focal basal vacuolar changes. No dyskeratotic cells noted. There is a collapsed cyst lined by keratinizing stratified squamous epithelial cells with granular cell layer. Lamellated keratin squames are present. Occasional lymphocytes are seen within the dermis. No evidence of dysplasia or malignancy.
- Left breast: consistent with epidermal cyst
Diagnosis: Breast epidermal cyst
Discussion:
- Breast epidermal cyst is also known as epidermal inclusion cyst or epidermoid cyst or breast sebaceous cyst
- It is a benign breast lesion classified as BIRADS II.
- This lesion is typically located in the skin or subcutaneous tissue.
- There is a predilection towards the inframammary fold
- On mammogram it is seen as a well-circumscribed rounded soft tissue density lesion close to the skin surface
- Ultrasound shows the lesion as small hypoechoic lesion close to the skin surface with no detectable vascular flow. If flow is seen on doppler ultrasound, there is possibility of infection.
- Complications include infection, inflammation, cyst rupture, granulomaotus reaction or abscess formation and malignant transformation to low-grade squamous cell carcinoma (rare)