Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 29 years old lady
- Migraine since 15 years old under neuromedical follow up
- Depression under psychiatry follow up
- Presented with blurring of vision and headache x 1 year
- Clinical examination: normal
- Opthalmology assessment: low myopia, no other abnormality
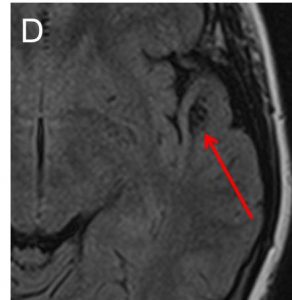
MRI findings:
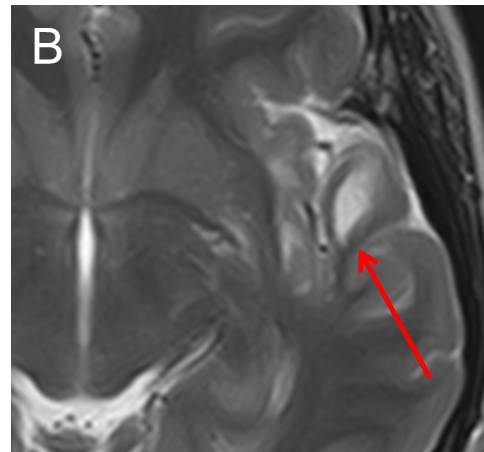
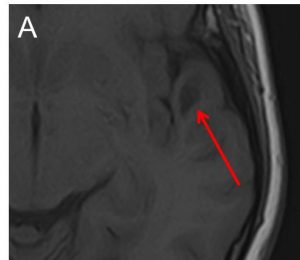
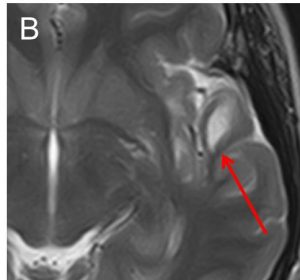
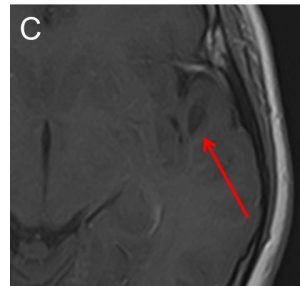
- A well-defined lesion in the white matter of left temporal lobe (red arrow).
- The lesion is hypointense on T1-weighted image (A), hyperintense on T2-weighted image (B), not enhanced post contrast (C) and fully suppressed on FLAIR (D).
- No expansion of the cortex is seen. No mass effect. No volume loss.
- No extension to ventricles. No surrounding sclerotic rim.
- No other lesion in the brain.
Differential diagnosis:
- Neuroglial cysts
- Porencephalic cyst: communicates with lateral ventricle, usually shows surrounding gliosis
- Enlarged perivascular space: typically multiple, clusters in basal ganglia
- Neurocysticercosis: partially enhance, presence of central hyperintensity
- Cerebral hydatid cyst: usually large, may be indistinguishable
- Ependymal cyst: periventricular
- Epidermoid cyst: do not follow CSF in all sequence, restricted diffusion, usually at CPA/sellar
Diagnosis: Neuroglial cyst (no HPE)
Discussion:
- Neuroglial cyst is also known as glioependymal cyst.
- Benign, glial-lined, fluid containing cavity within the cerebral white matter
- may occur anywhere throughout the brain, frontal lobe is most common
- size varies from a few mm up to several cm
- no calcification
- signal intensity similar to CSF, does not restrict on DWI
- no enhancement
- minimal or no surrounding signal abnormality
Patient progress:
- Patient is under conservative management.
- No surgical intervention done.