Clinical:
- A 73 years old man
- Underlying DM and HPT
- CT scan done for lung carcinoma
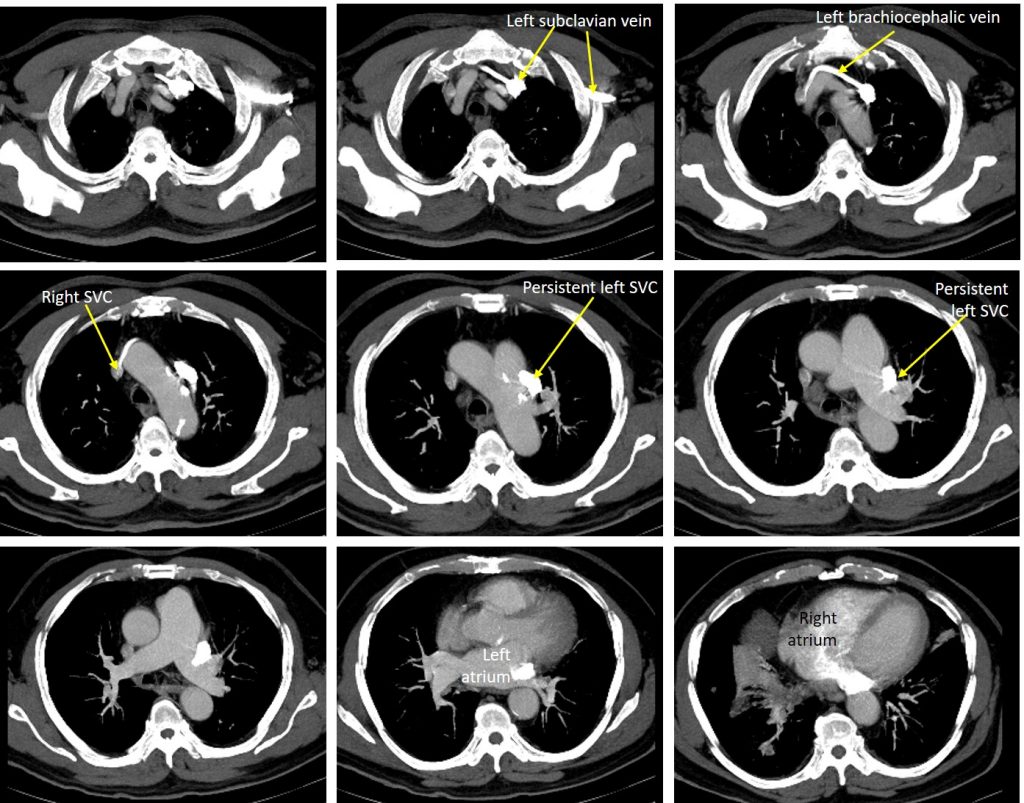
CT scan findings:
- Apart from lung mass with mediastinal nodes (images not shown), incidental findings of vascular variant noted.
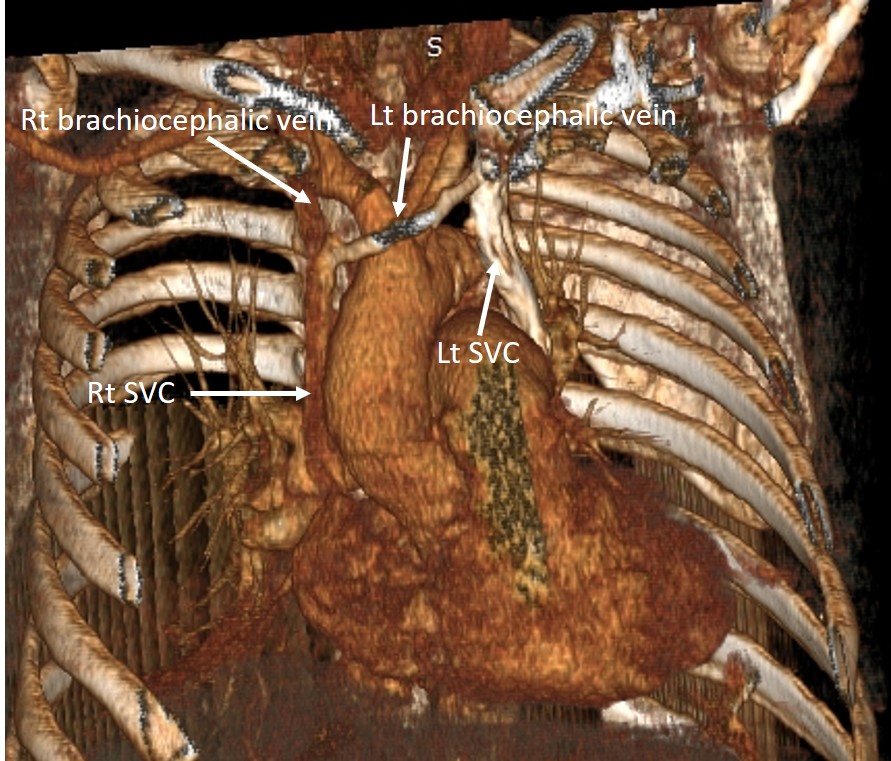
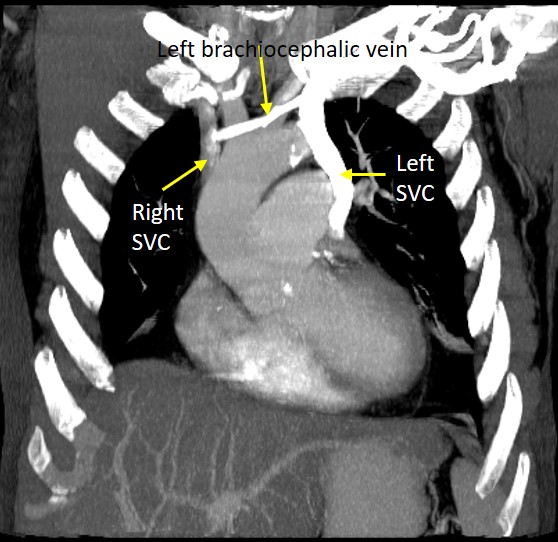
- Contrast is seen filling the left subclavian vein into left brachiocephalic vein and subsequently to right SVC to drain into right atrium.
- Another branch is seen from the left subclavian vein passes inferiorly lateral to the aortic arch towards the left hilum. This vessel drain into the right atrium via the coronary sinus.
Diagnosis: Persistent left subclavian vein (PLSVC).
Discussion:
- Persistent left SVC is the most common congenital thoracic venous anomaly with a prevalence of 0.3–0.5% in general population
- The most common subtype of PLSVC results in the presence of both left and right SVCs.
- A bridging innominate vein (brachiocephalic vein) is seen in 25-35% of cases.
- In 80–90% of individuals, the persistent LSVC drains into the right atrium via the coronary sinus and is of no hemodynamic consequence.
- Thus, vast majority of cases are asymptomatic and the presence of the vessel is only identified incidentally during CT scanning of the chest, or as a result of line placement.
- In the remaining 10% of cases, it may drain in left atrium resulting in a right to left sided shunt. However, the shunt is usually not large enough to cause cyanosis since it only drains the left upper limb and left side of the head and neck.
Recent Comments