Clinical:
- A 45 years old lady
- presented with back pain and microscopic hematuria of one year duration
-
No hypertension or cardiac problem
- UFEME- RBC 5+, others normal. All blood investigations are normal
- Screening for connective tissue disease are negative
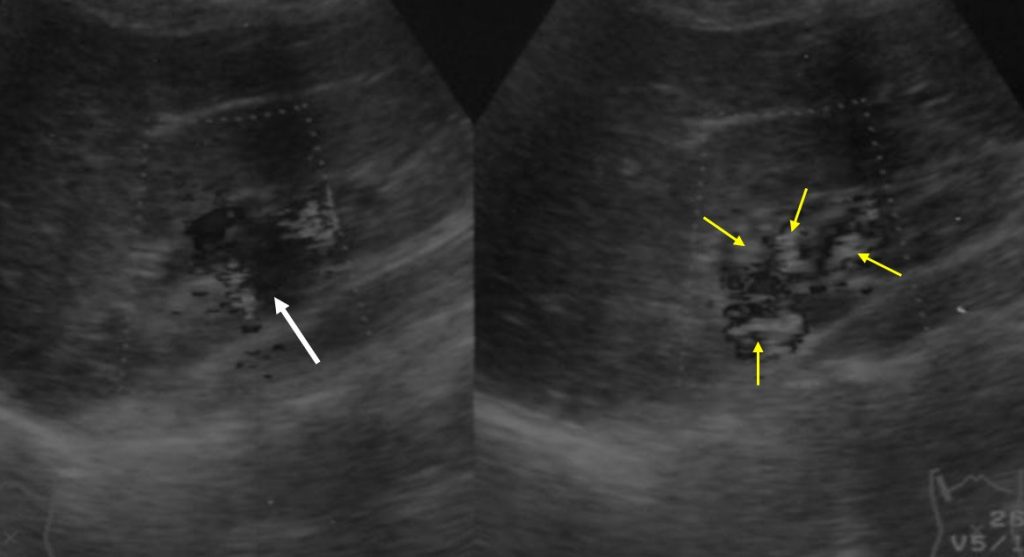
Ultrasound findings:
- There is mild separation of pelvicaliceal systems of right kidney.
- However on colour doppler study, the centrally located cystic lesions thought to be part of prominent pelvicalyceal systems are actually prominent vessels
- No lesion within the renal parenhcyma.
- Left kidney reported as normal.
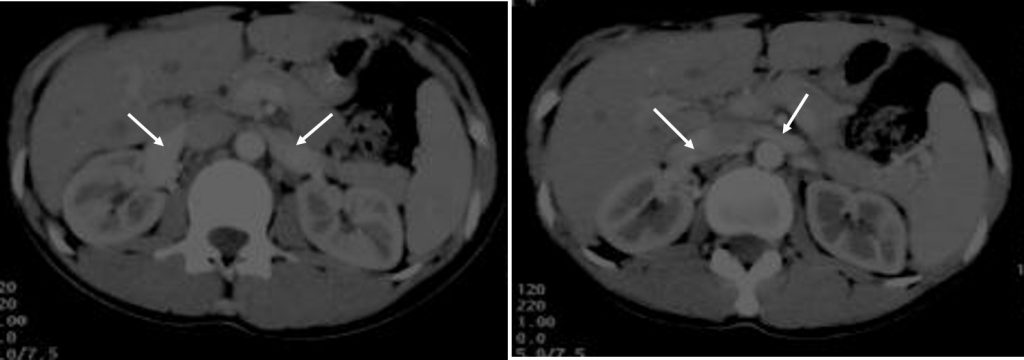
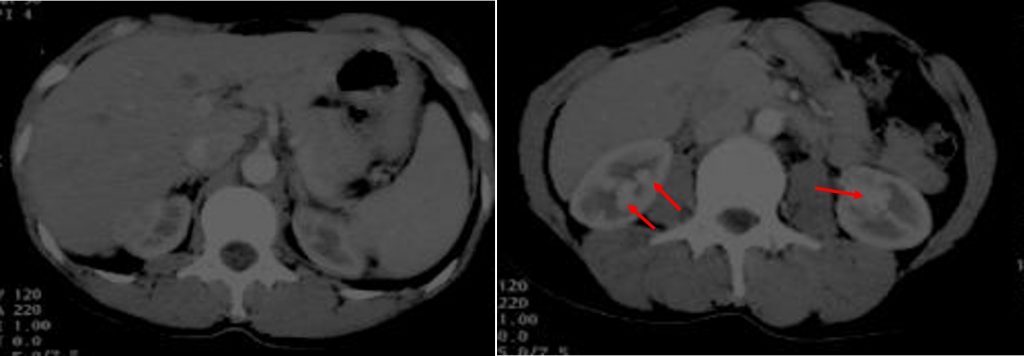
CT scan findings:
- Early enhancement of both renal veins is seen during arterial phase (white arrows).
- Multiple rounded enhancing structures in both kidneys with enhancement pattern similar to vessels.
- No hydronephrosis or cortical lesions bilaterally.
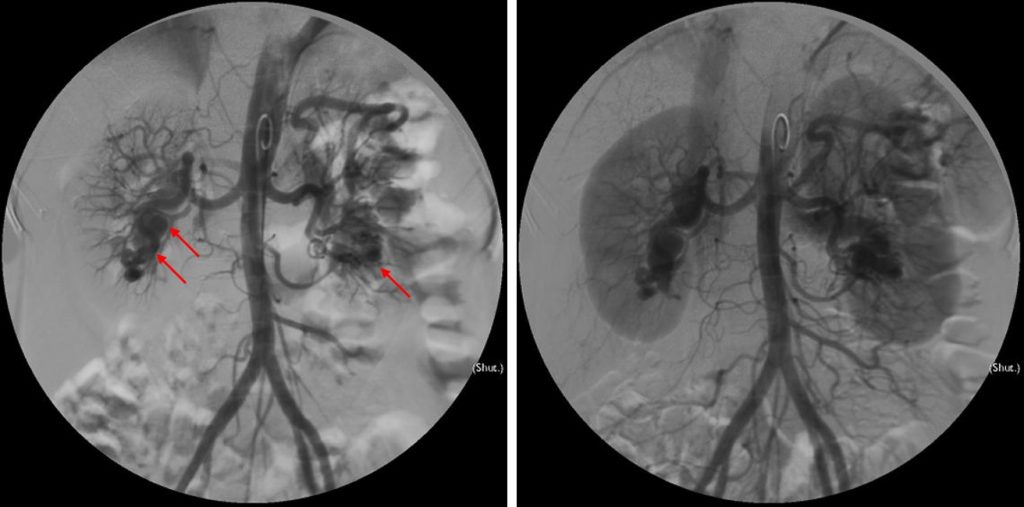
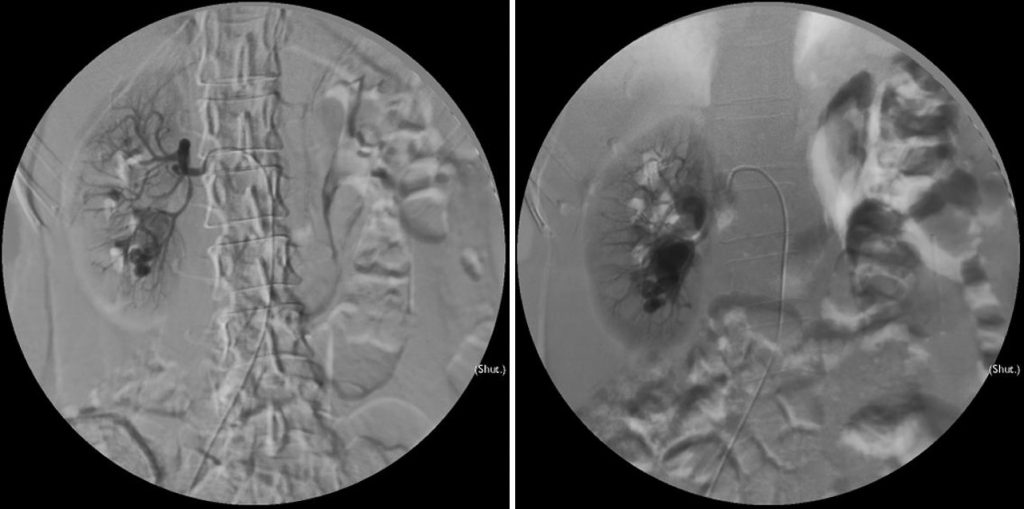
Renal angiogram findings:
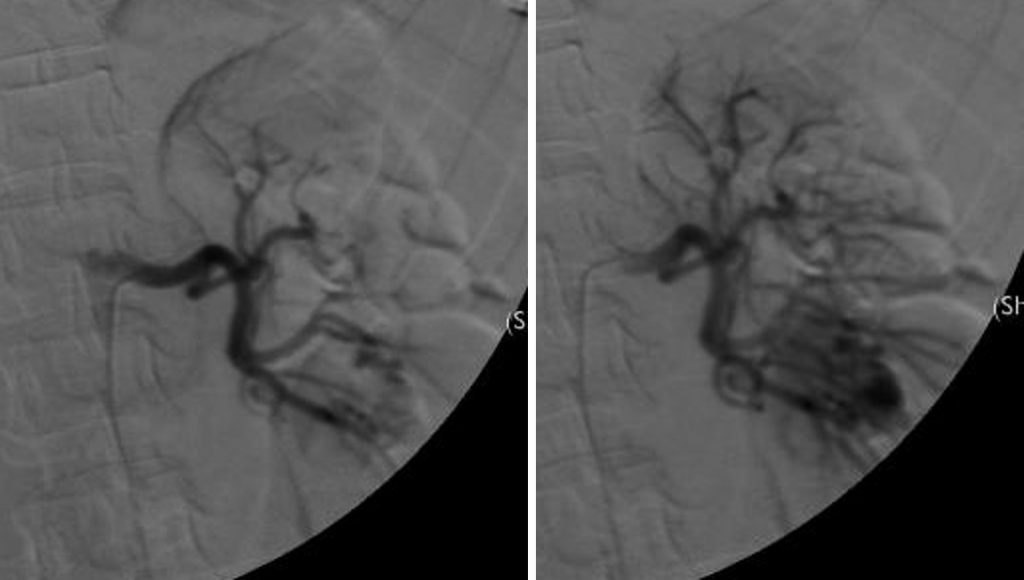
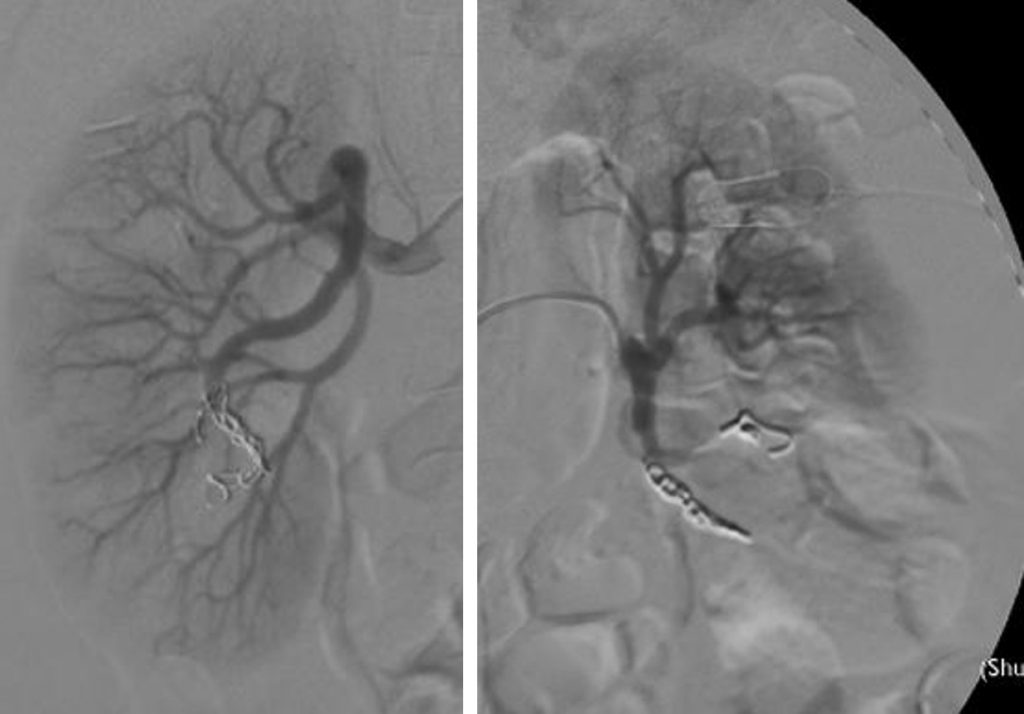
- Flush aortogram shows presence of tortuous vessels at the lower pole of both kidneys. Early draining veins into the inferior vena cava and left renal veins are also seen.
- Selective right renal arteriogram shows multiple tortuous vascular channels in the lower pole of right renal. Feeding vessels are from right inferior interlobar arteries.
- Selective left renal artery arteriogram shows tortuous cirsoid vessels in the lower pole. Feeding arteries are inferior interlobar arteries.
Diagnosis: Bilateral renal arteriovenous malformation.
Discussion:
- Renal AVM is formed by a connection between the arterial and venous structures, without flowing through a capillary bed.
- It is a rare condition.
- Ultrasound shows irregular, hypoechoic region in the renal parenchyma. Unable to differentiate with cyst unless color Doppler is used
- Colour dopple ultrasound shows high-flow lesion with possible pulsatility.
-
CT scan shows well-marginated renal lesion that enhances similar to the blood pool with early enhancement of the draining renal vein.
-
Currently, the most common treatment of renal AVM is transcatheter embolization.
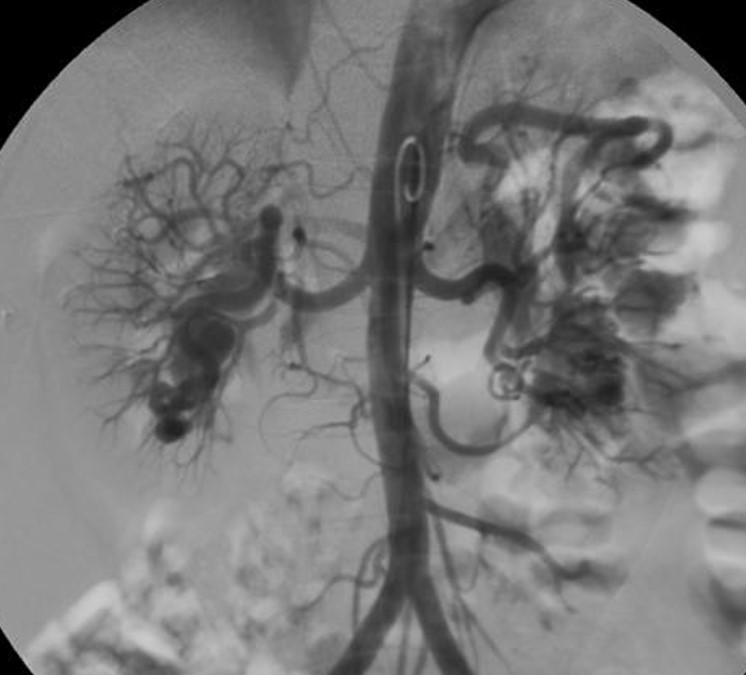
Progress of patient:
- Embolization done for both renal AVMs.
- Relieves of symptoms (backpain) after the treatment.
Recent Comments